Bob
enjoys playing computer games, especially strategic games, but
sometimes he cannot find the solution fast enough and then he is very
sad. Now he has the following problem. He must defend a medieval city,
the roads of which form a tree. He has to put the minimum number of
soldiers on the nodes so that they can observe all the edges. Can you
help him?
Your program should find the minimum number of soldiers that Bob has to put for a given tree.
The input file contains several data sets in text format. Each data set represents a tree with the following description:
the number of nodes
the description of each node in the following format
node_identifier:(number_of_roads) node_identifier1 node_identifier2 ... node_identifier
or
node_identifier:(0)
The
node identifiers are integer numbers between 0 and n-1, for n nodes (0
< n <= 1500). Every edge appears only once in the input data.
For example for the tree:
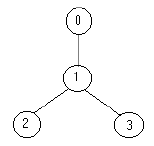
the solution is one soldier ( at the node 1).
The
output should be printed on the standard output. For each given input
data set, print one integer number in a single line that gives the
result (the minimum number of soldiers). An example is given in the
following table:
4
0:(1) 1
1:(2) 2 3
2:(0)
3:(0)
5
3:(3) 1 4 2
1:(1) 0
2:(0)
0:(0)
4:(0)
1
2
题解:这个题意思是保卫城市,给一棵树,让求放几个士兵,可以看到所有的树的节点,二分匹配vec建图,最大匹配的值除以2就是答案;
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define mem(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int MAXN=1510;
vector<int>vec[MAXN];
int vis[MAXN],usd[MAXN];
bool dfs(int u){
for(int i=0;i<vec[u].size();i++){
int v=vec[u][i];
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=1;
if(usd[v]==-1||dfs(usd[v])){
usd[v]=u;return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int N;
while(~scanf("%d",&N)){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)vec[i].clear();
int a,t,b;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
scanf("%d:(%d)",&a,&t);
while(t--){
scanf("%d",&b);vec[a].push_back(b);
vec[b].push_back(a);
}
}
mem(vis,0);mem(usd,-1);
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
mem(vis,0);
if(dfs(i))ans++;
}
printf("%d\n",ans/2);
}
return 0;
}
