R的极客理想系列文章,涵盖了R的思想,使用,工具,创新等的一系列要点,以我个人的学习和体验去诠释R的强大。
R语言作为统计学一门语言,一直在小众领域闪耀着光芒。直到大数据的爆发,R语言变成了一门炙手可热的数据分析的利器。随着越来越多的工程背景的人的加入,R语言的社区在迅速扩大成长。现在已不仅仅是统计领域,教育,银行,电商,互联网….都在使用R语言。
要成为有理想的极客,我们不能停留在语法上,要掌握牢固的数学,概率,统计知识,同时还要有创新精神,把R语言发挥到各个领域。让我们一起动起来吧,开始R的极客理想。
关于作者:
- 张丹(Conan), 程序员R,Nodejs,Java
- weibo:@Conan_Z
- blog: http://blog.fens.me
- email: bsspirit@gmail.com
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-cpp-rcpp
前言
使用R语言已经很多年了,对很多的R包都已经了解,唯独没有碰和C++相关的部分,这可能很大的原因和我长期使用Java的背景有关。但随着多语言的发展,跨语言应用的流行,打通各语言界限的方法也已经是成熟。让R和C++实现通信,已经变得很简单。
跟上跨语言的步伐,打开R和C++的通道,让C++来解决R性能的诟病吧。
目录
- Rcpp的简单介绍
- 5分钟上手
- 数据类型转换
1. Rcpp的简单介绍
Rcpp包是一个打通R语言和C++语言的通信组件包,提供了R语言和C++函数的相互调用。R语言和C++语言的数据类型通过Rcpp包进行完整的映射。
Rcpp的官方网站:https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Rcpp/index.html
本文做为入门教程,只是简单介绍,如何能打通R语言和C++的通信通道,并不做深入地探讨。R语言和其他语言也有类似的通信实现,R语言和JAVA的调用,请参考文章解惑rJava R与Java的高速通道;R语言和Nodejs的调用,请参考文章Nodejs与R跨平台通信。
2. 5分钟上手
做为5分钟上手的教程,我们只讲例子不讲API。
本文的系统环境
- Win10 64bit
- R version 3.2.3 (2015-12-10)
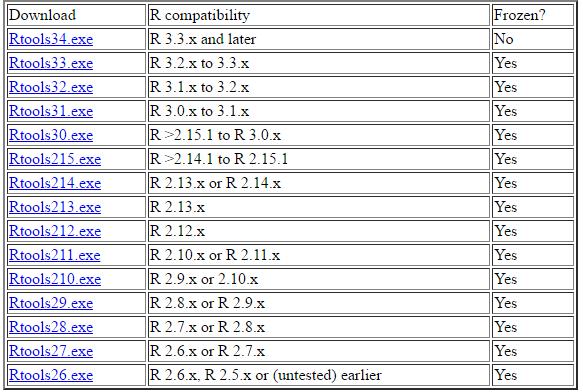
由于Windows系统的环境下需要Rtools支持,所以要手动下载对应版本的Rtoosl包,下载地址。我的R语言版本是3.2.3,所以我需要安装Rtools33.exe。安装EXE程序就不多说了,双击完成即可。
下载Rcpp的程序包,进行安装,一行代码搞定。
> install.packages("Rcpp")
trying URL ‘https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/CRAN/bin/windows/contrib/3.2/Rcpp_0.12.6.zip‘
Content type ‘application/zip‘ length 3221864 bytes (3.1 MB)
downloaded 3.1 MB
package ‘Rcpp’ successfully unpacked and MD5 sums checked
Warning in install.packages :
cannot remove prior installation of package ‘Rcpp’
The downloaded binary packages are in
C:\Users\tinkpad\AppData\Local\Temp\RtmpKkg8zo\downloaded_packages
2.1 从hello world开始
从一个简单程序hello world开始吧,让R语言程序调用C++中的hello()函数。我用需要新建2个文件,放在同一个目录中。
- demo.cpp,C++程序的源文件
- demo.r,R程序源文件
首先,编辑demo.cpp,定义hello()函数。
~ notepad demo.cpp
#include <Rcpp.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
using namespace Rcpp;
//[[Rcpp::export]]
string hello(string name) {
cout << "hello " << name << endl;
return name;
}
/*** R
hello(‘world‘)
hello(‘Conan‘)
*/
上面Rcpp的代码,我们可以从3部分来看。
- #include和using部分: 为包引用和命名空间的声明。<Rcpp.h>和namespace Rcpp是必要要加载的,另外由于使用了string的类型作为参数和返回值,所以需要<string>和namespace std。
- 功能函数部分: 们定义了一个 hello(string name) 函数,有一个参数是string类型,返回值也为string类型。需要强调的是,对R开放的函数必须增加 //[[Rcpp::export]] 的注释声明。
- 代码执行: 用/*** R 和 */ 包含的部分,为R语言的代码,会默认被执行。
编辑demo.r,用来调用demo.cpp的hello()函数。
~ notepad demo.r
library(Rcpp)
sourceCpp(file=‘demo.cpp‘)
hello(‘R‘)
执行R语言的代码
# 加载Rcpp包
> library(Rcpp)
# 编译和加载demo.cpp文件
> sourceCpp(file=‘demo.cpp‘)
# 执行封装在demo.cpp中的R代码
> hello(‘world‘)
hello world
[1] "world"
> hello(‘Conan‘)
hello Conan
[1] "Conan"
# 执行hello函数
> hello(‘R‘)
hello [1]R
"R"
一个非常简单的helloworld程序,就这样子完成了。
2.2 R和Rcpp的混写代码
上面2行代码,就完成了R对C++程序的调用,sourceCpp()函数真是强大。其实,sourceCpp()函数还提供了一种代码混写的方法,就是在R的代码中,直接嵌入C++代码。
sourceCpp(code=‘
#include >Rcpp.h<
#include >string<
using namespace std;
using namespace Rcpp;
//[[Rcpp::export]]
string hello(string name) {
cout << "hello " << name << endl;
return name;
}
‘)
hello(‘R2‘)
运行代码
> sourceCpp(code=‘
+ #include >Rcpp.h<
+ #include >string<
+
+ using namespace std;
+ using namespace Rcpp;
+
+ //[[Rcpp::export]]
+ string hello(string name) {
+ cout << "hello " << name << endl;
+ return name;
+ }
+ ‘)
> hello(‘R2‘)
hello R2
[1] "R2"
这种多语言混写的语法虽然不太推荐,但对于这只有几行代码来说,还是很方便的。
2.2 用RStudioIDE生成cpp文件
如果你使用的RStudio IDE,开发起来将会非常方便,可以直接新建C++程序,生成一段标准的代码模板。
生成的代码模板如下
#include <Rcpp.h>
using namespace Rcpp;
// This is a simple example of exporting a C++ function to R. You can
// source this function into an R session using the Rcpp::sourceCpp
// function (or via the Source button on the editor toolbar). Learn
// more about Rcpp at:
//
// http://www.rcpp.org/
// http://adv-r.had.co.nz/Rcpp.html
// http://gallery.rcpp.org/
//
// [[Rcpp::export]]
NumericVector timesTwo(NumericVector x) {
return x * 2;
}
// You can include R code blocks in C++ files processed with sourceCpp
// (useful for testing and development). The R code will be automatically
// run after the compilation.
//
/*** R
timesTwo(42)
*/
通过RStudio可以快速生成一段标准的代码模板,改改马上就能用了。
3. 数据类型转换
上面的例子中,我们测试了字符串类型的调用。R语言有多种的数据类型,我接下来都测试一下!
3.1 基本类型
基本类型,C++对应R语言的默认映射关系。C++的代码部分,如下所示:
// [[Rcpp::export]]
char char_type(char x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
int int_type(int x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
double double_type(double x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
bool bool_type(bool x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
void void_return_type(){
Rprintf( "return void" );
}
执行R语言调用
# char类型
> a1<-char_type(‘a‘)
> a1;class(a1) # 默认对应R的character类型
[1] "a"
[1] "character"
> char_type(‘bbii‘) # 只处理字符串的第一个字节
[1] "b"
# int类型
> a2<-int_type(111)
> a2;class(a2) # 默认对应R的integer类型
[1] 111
[1] "integer"
> int_type(111.1) # 直接去掉小数位
[1] 111
# double类型
> a3<-double_type(111.1)
> a3;class(a3) # 默认对应R的numeric类型
[1] 111.1
[1] "numeric"
> double_type(111)
[1] 111
# boolean类型
> a4<-bool_type(TRUE)
> a4;class(a4) # 默认对应R的logical类型
[1] TRUE
[1] "logical"
> bool_type(0) # 0为FALSE
[1] FALSE
> bool_type(1) # 非0为TRUE
[1] TRUE
# 无参数无返回值 的函数
> a5<-void_return_type()
return void
> a5;class(a5) # 返回值为NULL
NULL
[1] "NULL"
3.2 向量类型
向量类型,C++对应R语言的默认映射关系。C++的代码部分,如下所示:
// [[Rcpp::export]]
CharacterVector CharacterVector_type(CharacterVector x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
StringVector StringVector_type(StringVector x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
NumericVector NumericVector_type(NumericVector x) {
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
IntegerVector IntegerVector_type(IntegerVector x) {
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
DoubleVector DoubleVector_type(DoubleVector x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
LogicalVector LogicalVector_type(LogicalVector x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
DateVector DateVector_type(DateVector x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
DatetimeVector DatetimeVector_type(DatetimeVector x){
return x;
}
执行R语言调用
# Character向量
> a6<-CharacterVector_type(c(‘abc‘,‘12345‘))
> a6;class(a6) # 默认对应R的character类型
[1] "abc" "12345"
[1] "character"
> CharacterVector_type(c(‘abc‘,123.5, NA, TRUE)) # NA不处理
[1] "abc" "123.5" NA "TRUE"
# String向量,完全同Character向量
> a7<-StringVector_type(c(‘abc‘,‘12345‘))
> a7;class(a7) # 默认对应R的character类型
[1] "abc" "12345"
[1] "character"
> StringVector_type(c(‘abc‘,123.5, NA, TRUE))
[1] "abc" "123.5" NA "TRUE"
# Numeric向量
> a8<-NumericVector_type(rnorm(5))
> a8;class(a8) # 默认对应R的numeric类型
[1] -0.2813472 -0.2235722 -0.6958443 -1.5322172 0.5004307
[1] "numeric"
> NumericVector_type(c(rnorm(5),NA,TRUE)) # NA不处理,TRUE为1
[1] 0.1700925 0.5169612 -0.3622637 1.0763204 -0.5729958
[6] NA 1.0000000
# Integer向量
> a9<-IntegerVector_type(c(11,9.9,1.2)) # 直接去掉小数位
> a9;class(a9) # 默认对应R的integer类型
[1] 11 9 1
[1] "integer"
> IntegerVector_type(c(11,9.9,1.2,NA,TRUE)) # NA不处理,TRUE为1
[1] 11 9 1 NA 1
# Double向量,同Numeric向量
> a10<-DoubleVector_type(rnorm(5))
> a10;class(a10) # 默认对应R的numeric类型
[1] 0.9400947 -0.8976913 0.2744319 -1.5278219 1.2010569
[1] "numeric"
> DoubleVector_type(c(rnorm(5),NA,TRUE)) # NA不处理,TRUE为1
[1] 2.0657148 0.2810003 2.1080900 -1.2783693 0.2198551
[6] NA 1.0000000
# Logical向量
> a11<-LogicalVector_type(c(TRUE,FALSE))
> a11;class(a11) # 默认对应R的logical类型
[1] TRUE FALSE
[1] "logical"
> LogicalVector_type(c(TRUE,FALSE,TRUE,0,-1,NA)) # NA不处理,0为FALSE, 非0为TRUE
[1] TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE TRUE NA
# Date向量
> a12<-DateVector_type(c(Sys.Date(),as.Date(‘2016-10-10‘)))
> a12;class(a12) # 默认对应R的Date类型
[1] "2016-08-01" "2016-10-10"
[1] "Date"
> DateVector_type(c(Sys.Date(),as.Date(‘2016-10-10‘),NA,TRUE,FALSE)) # NA不处理,TRUE为1970-01-02, FALSE为1970-01-01
[1] "2016-08-01" "2016-10-10" NA "1970-01-02"
[5] "1970-01-01"
# Datetime向量
> a13<-DatetimeVector_type(c(Sys.time(),as.POSIXct(‘2016-10-10‘)))
> a13;class(a13) # 默认对应R的POSIXct类型
[1] "2016-08-01 20:05:25 CST" "2016-10-10 00:00:00 CST"
[1] "POSIXct" "POSIXt"
> DatetimeVector_type(c(Sys.time(),as.POSIXct(‘2016-10-10‘),NA,TRUE,FALSE)) # NA不处理
[1] "2016-08-01 20:05:25 CST" "2016-10-10 00:00:00 CST"
[3] NA "1970-01-01 08:00:01 CST"
[5] "1970-01-01 08:00:00 CST"
3.3 矩阵类型
矩阵类型,C++对应R语言的默认映射关系。C++的代码部分,如下所示:
// [[Rcpp::export]]
CharacterMatrix CharacterMatrix_type(CharacterMatrix x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
StringMatrix StringMatrix_type(StringMatrix x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
NumericMatrix NumericMatrix_type(NumericMatrix x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
IntegerMatrix IntegerMatrix_type(IntegerMatrix x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
LogicalMatrix LogicalMatrix_type(LogicalMatrix x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
ListMatrix ListMatrix_type(ListMatrix x){
return x;
}
执行R语言调用
# Character矩阵
> a14<-CharacterMatrix_type(matrix(LETTERS[1:20],ncol=4))
> a14;class(a14)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] "A" "F" "K" "P"
[2,] "B" "G" "L" "Q"
[3,] "C" "H" "M" "R"
[4,] "D" "I" "N" "S"
[5,] "E" "J" "O" "T"
[1] "matrix"
# String矩阵,同Character矩阵
> a15<-StringMatrix_type(matrix(LETTERS[1:20],ncol=4))
> a15;class(a15)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] "A" "F" "K" "P"
[2,] "B" "G" "L" "Q"
[3,] "C" "H" "M" "R"
[4,] "D" "I" "N" "S"
[5,] "E" "J" "O" "T"
[1] "matrix"
# Numeric矩阵
> a16<-NumericMatrix_type(matrix(rnorm(20),ncol=4))
> a16;class(a16)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 1.2315498 2.3234269 0.5974143 0.9072356
[2,] 0.3484811 0.3814024 -0.2018324 0.8717205
[3,] -0.2025285 2.1076947 -0.3433948 1.1523710
[4,] -1.4948252 -0.7724951 -0.7681800 -0.5406494
[5,] 0.4815904 1.4930873 -1.1444258 0.2537099
[1] "matrix"
# Integer矩阵
> a17<-IntegerMatrix_type(matrix(seq(1,10,length.out = 20),ncol=4))
> a17;class(a17)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] 1 3 5 8
[2,] 1 3 6 8
[3,] 1 4 6 9
[4,] 2 4 7 9
[5,] 2 5 7 10
[1] "matrix"
# Logical矩阵
> a18<-LogicalMatrix_type(matrix(c(rep(TRUE,5),rep(FALSE,5),rnorm(10)),ncol=4))
> a18;class(a18)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4]
[1,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
[2,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
[3,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
[4,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
[5,] TRUE FALSE TRUE TRUE
[1] "matrix"
# List矩阵,支持多类型的矩阵
> a19<-ListMatrix_type(matrix(rep(list(a=1,b=‘2‘,c=NA,d=TRUE),10),ncol=5))
> a19;class(a19)
[,1] [,2] [,3] [,4] [,5]
[1,] 1 1 1 1 1
[2,] "2" "2" "2" "2" "2"
[3,] NA NA NA NA NA
[4,] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[5,] 1 1 1 1 1
[6,] "2" "2" "2" "2" "2"
[7,] NA NA NA NA NA
[8,] TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
[1] "matrix"
3.4 其他数据类型
其他数据类型包括了,R语言特有的数据类型数据框(data.frame),环境空间(Environment),S3,S4,RC等的对象类型。
// [[Rcpp::export]]
Date Date_type(Date x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
Datetime Datetime_type(Datetime x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
S4 S4_type(S4 x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
RObject RObject_type(RObject x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
SEXP SEXP_type(SEXP x){
return x;
}
// [[Rcpp::export]]
Environment Environment_type(Environment x){
return x;
}
执行R语言调用
# data.frame类型
> a19<-DataFrame_type(data.frame(a=rnorm(3),b=1:3))
> a19;class(a19)
a b
1 -1.8844994 1
2 0.6053935 2
3 -0.7693985 3
[1] "data.frame"
# list类型
> a20<-List_type(list(a=1,b=‘2‘,c=NA,d=TRUE))
> a20;class(a20)
$a
[1] 1
$b
[1] "2"
$c
[1] NA
$d
[1] TRUE
[1] "list"
# Date类型
> a21<-Date_type(Sys.Date())
> a21;class(a21)
[1] "2016-08-01"
[1] "Date"
> Date_type(Sys.time()) # 不能正确处理POSIXct类型的数据
[1] "4026842-05-26"
# POSIXct类型
> a22<-Datetime_type(Sys.time())
> a22;class(a22)
[1] "2016-08-01 20:27:37 CST"
[1] "POSIXct" "POSIXt"
> Datetime_type(Sys.Date()) # 不能正确处理Date类型的数据
[1] "1970-01-01 12:43:34 CST"
# S3面向对象类型,对应S4的类型定义
> setClass("Person",slots=list(name="character",age="numeric"))
> s4<-new("Person",name="F",age=44)
> a23<-S4_type(s4)
> a23;class(a23)
An object of class "Person"
Slot "name":
[1] "F"
Slot "age":
[1] 44
[1] "Person"
attr(,"package")
[1] ".GlobalEnv"
# S3面向对象类型 ,没有对应的类型,通过RObject来传值
> s3<-structure(2, class = "foo")
> a24<-RObject_type(s3)
> a24;class(a24)
[1] 2
attr(,"class")
[1] "foo"
[1] "foo"
# RObject也可以处理S4对象
> a25<-RObject_type(s4)
> a25;class(a25)
An object of class "Person"
Slot "name":
[1] "F"
Slot "age":
[1] 44
[1] "Person"
attr(,"package")
[1] ".GlobalEnv"
# RObject也可以处理RC对象
> User<-setRefClass("User",fields=list(name="character"))
> rc<-User$new(name="u1")
> a26<-RObject_type(rc)
> a26;class(a26)
Reference class object of class "User"
Field "name":
[1] "u1"
[1] "User"
attr(,"package")
[1] ".GlobalEnv"
# RObject也可以处理function类型
> a27<-RObject_type(function(x) x+2)
> a27;class(a27)
function(x) x+2
[1] "function"
# environment类型
> a28<-Environment_type(new.env())
> a28;class(a28)
<environment: 0x0000000015350a80>
[1] "environment"
# SEXP为任意类型,通过具体调用时再进行类型判断
> SEXP_type(‘fdafdaa‘)
[1] "fdafdaa"
> SEXP_type(rc)
Reference class object of class "User"
Field "name":
[1] "u1"
> SEXP_type(data.frame(a=rnorm(3),b=1:3))
a b
1 -0.5396140 1
2 0.1694799 2
3 -1.8818596 3
> SEXP_type(function(x) x+2)
function(x) x+2
最后总结一下,R和Rcpp中类型对应的关系。
| C++类型 | R类型 |
|---|---|
| char | character |
| int | integer |
| double | numeric |
| bool | logical |
| Rcpp::Date | Date |
| Rcpp::Datetime | POSIXct |
| Rcpp::CharacterVector | character |
| Rcpp::StringVector | character |
| Rcpp::NumericVector | numeric |
| Rcpp::IntegerVector | integer |
| Rcpp::DoubleVector | numeric |
| Rcpp::LogicalVector | logical |
| Rcpp::DateVector | Date |
| Rcpp::DatetimeVector | POSIXct |
| Rcpp::CharacterMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::StringMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::NumericMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::IntegerMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::LogicalMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::ListMatrix | matrix |
| Rcpp::DataFrame | data.frame |
| Rcpp::List | list |
| Rcpp::S4 | S4 |
| Rcpp::Environment | environment |
| Rcpp::RObject | 任意类型 |
| Rcpp::SEXP | 任意类型 |
本文简单地介绍了通过R语言Rcpp包调用C++程序的一种方法,调用的关键点就在于数据类型的匹配,而从保证R语言和C++之间的数据传输。从上面测试来看,R语言中的所有数据类型,都可以通过Rcpp包进行映射到C++的程序中。接下来,我们就可以根据自己的需求,把一些更关注的性能的程序放到C++中来实现,从而提高计算效率。
转载请注明出处:
http://blog.fens.me/r-cpp-rcpp