一.Nginx特性
* *模块化,目前只能将模块编译进Nginx,暂时不支持动态装卸模块.(httpd优势)
* *可靠性,一个主进程(master)控制多个工作进程(worker),工作进程响应用户多个请求(httpd劣势)
* *低内存消耗,(httpd劣势)
* *支持热部署,(httpd相同)
* *支持事件驱动I/O,AI/O,支持mmap(httpd2.4才算支持event,劣势)
二.Nginx基本架构
Nginx由一个master进程生成多个worker进程,每个worker进程接收用户请求,支持sendfile,AIO,mmap.

三.Nginx基本功能
* *静态资源WEB服务器,能缓存打开的文件描述符
* *http,反向代理服务器,缓存服务器,负载均衡服务器
* *支持fastcgi(php),uwsgi(python)与动态程序结合
* *支持ssl传输
* *支持虚拟主机
* *支持keepalive
* *支持平滑升级
* *支持定制日志,日志缓存
* *支持url重写
* *支持路径别名
* *支持限速,并发控制
四.Nginx安装(编译安装)
编译安装过程如下:
# yum -y groupinstall "Development Tools" "Server Platform Libraries"
# yum -y install pcre-devel openssl-devel
# groupadd -r nginx
# useradd -r -g nginx -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx
# cd /usr/src/
# tar xf nginx-1.11.3.tar.gz
# cd nginx-1.11.3
# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx > --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf > --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log > --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log > --pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid > --lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock > --user=nginx > --group=nginx > --with-http_ssl_module > --with-http_stub_status_module > --with-http_gzip_static_module > --with-http_flv_module > --with-http_mp4_module > --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/client/ > --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/proxy/ > --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/fcgi/ > --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/uwsgi/ > --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/tmp/nginx/scgi/ > --with-pcre
# make && make install
# mkdir -pv /var/tmp/nginx/{client,proxy,fcgi,uwsgi,scgi}
# ll /usr/local/nginx/html --才两个目录,我们的配置文件和log文件存放在其他目录
total 8 --可见nginx多轻量级
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 1 11:23 html
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Sep 1 11:23 sbin
--配置nginx程序执行环境变量
# echo "export PATH=/usr/local/nginx/sbin:$PATH" > /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
# . /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh
--配置nginx语法着色
# mkdir .vim
# cp -ra /usr/src/nginx-1.11.3/contrib/vim/* .vim/为nginx提供SysV init脚本:
新建文件/etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx,内容如下:
# vim /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/sh
#
# nginx - this script starts and stops the nginx daemon
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: Nginx is an HTTP(S) server, HTTP(S) reverse # proxy and IMAP/POP3 proxy server
# processname: nginx
# config: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# config: /etc/sysconfig/nginx
# pidfile: /var/run/nginx/nginx.pid
# Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
nginx="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
prog=$(basename $nginx)
NGINX_CONF_FILE="/etc/nginx/nginx.conf"
[ -f /etc/sysconfig/nginx ] && . /etc/sysconfig/nginx
lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/nginx
make_dirs() {
# make required directories
user=`nginx -V 2>&1 | grep "configure arguments:" | sed ‘s/[^*]*--user=\([^ ]*\).*/\1/g‘ -`
options=`$nginx -V 2>&1 | grep ‘configure arguments:‘`
for opt in $options; do
if [ `echo $opt | grep ‘.*-temp-path‘` ]; then
value=`echo $opt | cut -d "=" -f 2`
if [ ! -d "$value" ]; then
# echo "creating" $value
mkdir -p $value && chown -R $user $value
fi
fi
done
}
start() {
[ -x $nginx ] || exit 5
[ -f $NGINX_CONF_FILE ] || exit 6
make_dirs
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $nginx -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile
return $retval
}
stop() {
echo -n $"Stopping $prog: "
killproc $prog -QUIT
retval=$?
echo
[ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile
return $retval
}
restart() {
configtest || return $?
stop
sleep 1
start
}
reload() {
configtest || return $?
echo -n $"Reloading $prog: "
killproc $nginx -HUP
RETVAL=$?
echo
}
force_reload() {
restart
}
configtest() {
$nginx -t -c $NGINX_CONF_FILE
}
rh_status() {
status $prog
}
rh_status_q() {
rh_status >/dev/null 2>&1
}
case "$1" in
start)
rh_status_q && exit 0
$1
;;
stop)
rh_status_q || exit 0
$1
;;
restart|configtest)
$1
;;
reload)
rh_status_q || exit 7
$1
;;
force-reload)
force_reload
;;
status)
rh_status
;;
condrestart|try-restart)
rh_status_q || exit 0
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload|configtest}"
exit 2
esac而后为此脚本赋予执行权限:
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/nginx
添加至服务管理列表,并让其开机自动启动:
# chkconfig --add nginx # chkconfig nginx on
而后就可以启动服务并测试了:
# service nginx start
五.Nginx配置文件
# ll /etc/nginx/
total 60
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1077 Sep 1 11:23 fastcgi.conf #FPM配置文件段
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1077 Sep 1 11:23 fastcgi.conf.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1007 Sep 1 11:23 fastcgi_params
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1007 Sep 1 11:23 fastcgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2837 Sep 1 11:23 koi-utf
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2223 Sep 1 11:23 koi-win
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3957 Sep 1 11:23 mime.types #mime类型配置文件
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3957 Sep 1 11:23 mime.types.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Sep 1 11:23 nginx.conf #nginx主配置文件
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2656 Sep 1 11:23 nginx.conf.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 636 Sep 1 11:23 scgi_params
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 636 Sep 1 11:23 scgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 664 Sep 1 11:23 uwsgi_params #uwsgi配置文件段
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 664 Sep 1 11:23 uwsgi_params.default
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3610 Sep 1 11:23 win-utf
nginx的配置文件主要分为两段:main http
main主要是控制nginx程序的运行
http主要是操作web服务器,且http配置段下还可以继续分为server段(虚拟主机)
配置文件分段即可把分段的配置文件从主文件剥离出来,形成单独的配置文件,并且只要在主配置文件中include此配置文件即可,比如说server虚拟主机配置文件段
================================
主配置段:
user nginx nginx; #worker进程运行的属主与属组
worker_processes 3; #worker进程数,建议与CPU核心数少1
pid /var/run/nginx/nginx.pid; #指定pid文件位置
worker_rlimit_nofile 50000; #显示所有worker进程所能打开的文件数目
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100; #绑定CPU,八核cpu就8个0,
events {
worker_connections 10240; #每个worker进程所能并发处理的连接数
}
http配置段:
include mime.types; #包含mime配置文件所有配置内容
sendfile on; #开启sendfile功能
keepalive_timeout 65; #开启长连接
server配置段:
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name localhost; #服务器名字
location{} #针对匹配到不同的url可以下发不同的配置段
gzip on; #开启gzip压缩六.Nginx http服务功能测试
(1).root path:定义网页文件存放的路径
(2).location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { … }:符号表示匹配后面的url的优先级
(3).alias path:路径别名
(4).error_page:根据http响应状态码来指明特定的错误页面
(5).auth_basic:安全访问web页面
(6).ssl:使用https套接字安全连接配置
(7).stu_status内置状态页面
(8).url重写
(9).if语法
(10).log_format:日志格式定制
(11).valid_referers:定义防盗链
示例(1):root path指定网页文件存储路径应用
root是指定网页文件存放的路径,可以在server配置段,也可以在location配置段,
存在location配置段时:
绝对路径:优先级最高
root /htdocs/web/;
location / {
root /htdocs/web1; #访问的是/htdocs/web1/index.html
index index.html index.htm;
}
相对路径:是相对于nginx安装路径目录下html
root /htdocs/web/;
location / {
root html; #相对路径,访问的是/usr/local/nginx/html/index.html,
index index.html index.htm;
}
存在server配置段时:location建议不要配置.
root /htdocs/web/; #此时才是访问/htdocs/web/index.html
location / {
index index.html index.htm;
}示例(2):location [ = | ~ | ~* | ^~ ] uri { … }:符号表示匹配后面的url的优先级:
准备好测试文件如下所示:
符号表示匹配后面uri的优先级,[=] > [^~] > [~|~*] >不带任何修饰符,其中[~]表示区分大小写,[~*]表示不区分大小写 测试图片,图片本身就标注了存放位置:
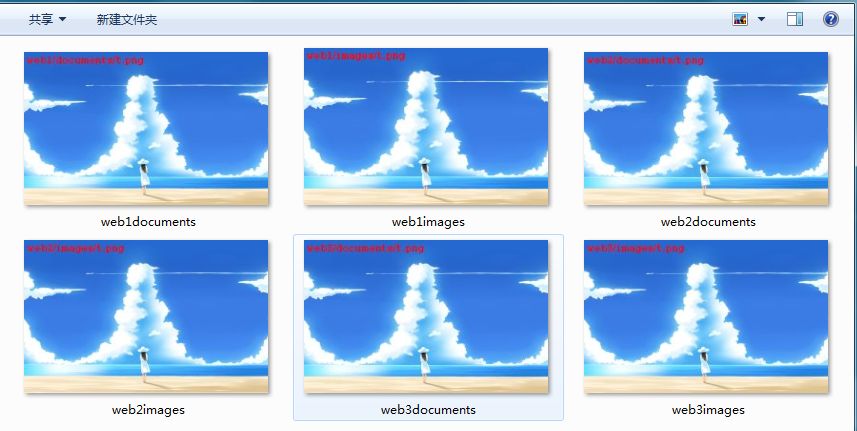
--创建测试目录:
# mkdir -pv /htdocs/{web1,web2,web3}/{documents,images}
# tree
.
|-- web1
| |-- documents
| | `-- t.png
| `-- images
| `-- t.png
|-- web2
| |-- documents
| | `-- t.png
| `-- images
| `-- t.png
`-- web3
|-- documents
| `-- t.png
`-- images
`-- t.png
9 directories, 6 files
测试配置如下:
location /documents/ {
root /htdocs/web1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ^~ /images/ {
root /htdocs/web2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~* \.(png|jpg|jpeg)$ {
root /htdocs/web3;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location = /a.png {
root /htdocs;
index index.html index.htm;
}测试结果(1)如下:
当我们访问:172.16.100.99/images/t.png 说明:根据我们的URL[/images/t.png],服务器匹配location事先定义好的url, 可以匹配到第二个与第三个location,因为[^~] > [~*],所在才有看到的是/htdocs/web2/images/t.png
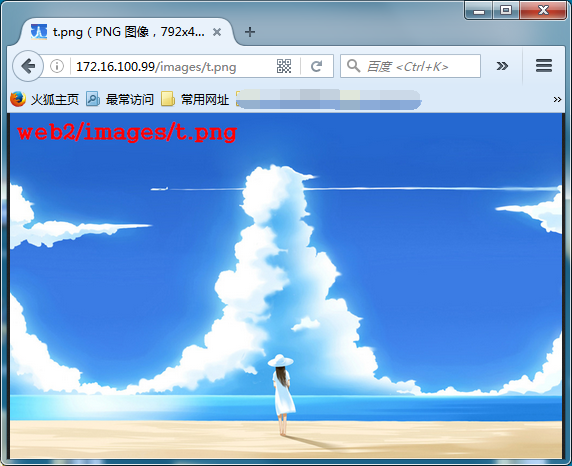
测试结果(2)如下:
当我们访问:172.16.100.99/documents/a.png 说明:根据我们的URL[/documents/t.png],服务器匹配location事先定义好的url, 可以匹配到第一个与第三个location,因为[~|~*] >不带任何修饰符,所以才看到的是/htdocs/web3/documents/t.png
[=]的匹配也可以参考如上说明, 结论:匹配方式是根据用户输入的URL部分去匹配我们定义的location, 当URL可以匹配到多个location的时候,就有了优先级的定义,
优先级:[=] > [^~] > [~|~] >不带任何修饰符*
示例(3):alias path路径别名应用
访问资源是的URL与实际资源存储位置不一样,就需要别名定义实际存储位置,
location /documents/ {
alias /htdocs/web1/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
当我们访问172.16.100.99/documents/时,显示的却是:示例(4):error_page 错误页面定义
根据http响应状态码来指明特定的错误页面
location / {
root /htdocs/web1/;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html; #当访问不存在的资源时,就会回应404错误代码,
根据404错误代码会显示特定的404.html,这个页面是存在与/htdocs/web1/目录下测试如下:
示例(5):auth_basic:安全访问web页面
配置如下:
location /documents/ {
alias /htdocs/web1/;
index index.html index.htm;
auth_basic "Restricted Area.......";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.user;
}生成访问用户密码文件:
# htpasswd -c -m /etc/nginx/.user tom # htpasswd -m /etc/nginx/.user jerry
测试如下:
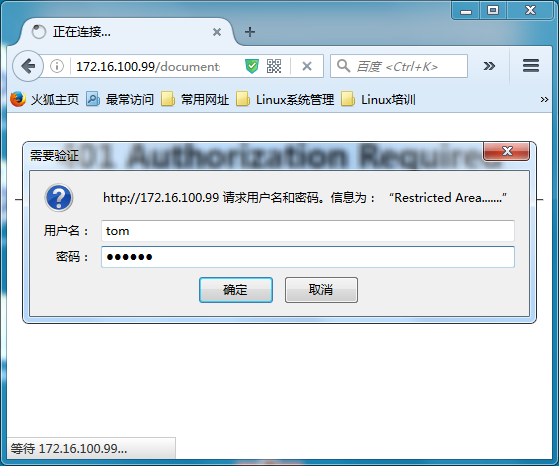
示例(5):ssl:使用https套接字安全连接配置
(1)配置证书密钥
编译时需要选择此模块 --with-http_ssl_module(httpd程序是需要安装mod_ssl模块,并且配置是在ssl配置文件中配置)
CA服务器生成私钥,自己对自己签名:
# cd /etc/pki/CA/
# touch index.txt
# echo 01 > serial
# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem -days 3560
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:Guangdong
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Guangzhou
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Samlee.LTD
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Tech
Common Name (eg, your name or your server‘s hostname) []:ca.samlee.com
Email Address []:caadmin@samlee.com
===========================================================================
客户端服务器生成私钥,并且生成证书申请请求
# mkdir /usr/local/nginx/ssl
# openssl genrsa -out /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.key 1024
# openssl req -new -key /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.key -out /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.csr
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN
State or Province Name (full name) []:Guangdong
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Guangzhou
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:Samlee.LTD
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Tech
Common Name (eg, your name or your server‘s hostname) []:web1.samlee.com
# scp /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.csr root@caserver:/tmp/nginx.csr
============================================================================
CA服务器对客户端传送过来的证书请求签发
# openssl ca -in /tmp/nginx.csr -out /tmp/nginx.web1.samlee.com.crt -days 365
# scp /tmp/nginx.web1.samlee.com.crt root@web1:/usr/local/nginx/ssl/
============================================================================
Nginx服务器配置支持ssl,我们在编译此nginx服务器时就包括了:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name localhost;
ssl_certificate /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.web1.samlee.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /usr/local/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}测试效果如下:
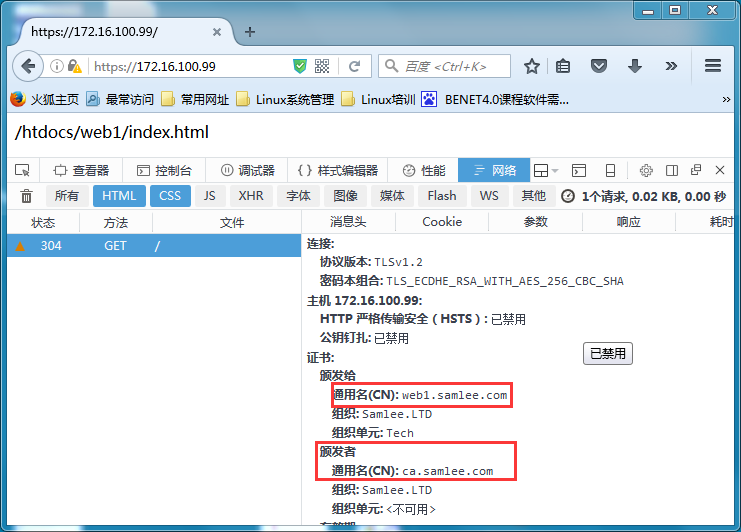
示例(6):stu_status内置状态页面
在location中定义:
location /nginx-status {
allow 172.16.100.7; #基于IP地址访问控制
deny all;
stub_status on; #开启状态页面
access_log off; #关闭状态页面的访问日志
}
测试访问:
# curl http://web1.samlee.com/nginx-status
Active connections: 1
server accepts handled requests
1 1 1
Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0
=====解释如下=====
Active connections:当前所有处于打开状态的连接数
accepts:已经接收进来的连接
handled:已经处理过的连接
requests:已经处理过的请求数
Reading:正处于接收请求状态的连接数
Writing:请求已经接收完成,正处于处理请求或发送响应过程的连接数
Waiting:保持连接且处理于活动状态的连接数示例(8):url重写
将用户请求特定资源的URL路径修改重定向到其他路径,(break,last,redirect,permanent是可选参数)
location / {
root /htdocs/web1;
rewrite /documents/(.*\.png)$ /images/$1 break; #将访问/htdocs/web1/documents/路径下以.png结尾的资源,全部重定向到/htdocs/web1/images/
index index.html index.htm;
}测试如下:
break:一旦对此rewrute规则重写后,由user agent对新的url重新发起新的请求,且不会在被location内的rewrite规则检查,
last:一旦对此rewrute规则重写后,由user agent对新的url重新发起新的请求,如果还有被location内的rewrite匹配中那么就继续重写URL,这是多么痛的领悟,
location / {
root /htdocs/web1;
rewrite /documents/(.*\.png)$ /images/$1 last; #采用last,重写后的URL会匹配到下面一条location规则,并且还会被在重写,
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ^~ /images/ { #利用^~强行将URL的images抓到此location下进行URL重写
root /htdocs/web2/;
rewrite /images/(.*\.png)$ /documents/$1 break; #用户输入web1.samlee.com/documents/t.png最后其实访问的是/vhosts/web2/documents/t.png
index index.html index.htm;
}redirect:以302状态响应码(临时重定向),返回新的URL,
location / {
root /htdocs/web2;
rewrite /documents/(.*\.png)$ /images/$1 redirect;
index index.html index.htm;
}permanent:以301 #状态响应码(永久重定向),返回新的URL,
location / {
root /htdocs/web1;
rewrite /documents/(.*\.png)$ /images/$1 permanent;
index index.html index.htm;
}示例(9):if语法使用
if语句的语法:if(condition) {},应用位置:server,location配置段
condition:
1. 变量赋值:禁止变量赋值为空或者以"0"开头,其他都OK
2. 以变量为操作数构成的比较表达式,可使用=,!=类似操作符比较
3. 正则表达式的模式匹配操作
~:区分大小写
~*:不区分大小写
!~和!~*对上面两种测试取反
4. 测试路径为文件的可能性:-f | !-f
5. 测试指定路径为目录的可能性:-d | !-d
6. 测试文件存在性:-e | !-e
7. 检查文件是否有执行权限:-x | !-x
location / {
root /htdocs/web1;
if ($http_user_agent ~* Chrome) { #如果是谷歌浏览器就把URL重写到/htdocs/web1/images/index.html
rewrite ^(.*)$ /images/$1 break;
}
index index.html index.htm;
}示例(10):log_format:日志格式定制及启用
log_format main ‘$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ‘ ‘$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ‘ ‘"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"‘; access_log logs/access.log main; #上面定义的日志在此处调用,定义日志信息的变量都是内置变量 以下为常用变量: Embedded Variables $http_user_agent $http_cookie $connection #connection serial number (1.3.8, 1.2.5) $connection_requests #current number of requests made through a connection (1.3.8, 1.2.5) $content_length #“Content-Length” request header field $content_type #“Content-Type” request header field $cookie_name #the name cookie $host #in this order of precedence: host name from the request line, or host name from the “Host” request header field, or the server name matching a request $hostname #host name $nginx_version #nginx version $pid #PID of the worker process $remote_addr #client address $remote_port #client port $remote_user #user name supplied with the Basic authentication $time_local #local time in the Common Log Format (1.3.12, 1.2.7) $server_name #name of the server which accepted a request $server_port #port of the server which accepted a request $server_protocol #request protocol, usually “HTTP/1.0”, “HTTP/1.1”, or “HTTP/2.0” 详见:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html
示例(11):valid_referers:定义防盗链
======防盗链=====
valid_referers none blocked server_names
*.example.com example.* www.example.org/galleries/
~\.google\.;
if ($invalid_referer) { #invalid_referer表示该用户是从哪个位置链接过来本网站的
return 403;
}
示例:
server {
listen 80;
server_name web1.samlee.com;
location / {
root /htdocs/web1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location ~* \.(jpg|png|gif|jpeg)$ {
root /htdocs/web1;
valid_referers none blocked web1.samlee.com *.samlee.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
rewrite ^/ http://web1.samlee.com/403.html;
}
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name web2.test.com;
location / {
root /htdocs/web2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
web2.test.com--index.html文件内容如下:
<h1>
<font color=‘red‘ size="10">
web2.test.com
</font>
</h1>
<img src="测试如下:
以上为nginx常用应用详解。
本文出自 “Opensamlee” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://gzsamlee.blog.51cto.com/9976612/1845630
原文:http://gzsamlee.blog.51cto.com/9976612/1845630