应用层协议http,发展至今已经是http2.0了,拥有以下特点:
(1) CS模式的协议
(2) 简单 - 只需要服务URL,携带必要的请求参数或者消息体
(3) 灵活 - 任意类型,传输内容类型由HTTP消息头中的Content-Type加以标记
(4) 无状态 - 必须借助额外手段,比如session或者cookie来保持状态
客户端发送一个HTTP请求到服务器的请求消息包括以下格式:请求行(request line)、请求头部(header)、空行和请求数据四个部分组成,下图给出了请求报文的一般格式。

举个例子:
GET /hello.txt HTTP/1.1
User-Agent: curl/7.16.3 libcurl/7.16.3 OpenSSL/0.9.7l zlib/1.2.3
Host: www.example.com
Accept-Language: en, mi
根据HTTP标准,HTTP请求可以使用多种请求方法。
HTTP1.0定义了三种请求方法: GET, POST 和 HEAD方法。
HTTP1.1新增了五种请求方法:OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE, TRACE 和 CONNECT 方法。
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GET | 请求指定的页面信息,并返回实体主体。 |
| 2 | HEAD | 类似于get请求,只不过返回的响应中没有具体的内容,用于获取报头 |
| 3 | POST | 向指定资源提交数据进行处理请求(例如提交表单或者上传文件)。数据被包含在请求体中。POST请求可能会导致新的资源的建立和/或已有资源的修改。 |
| 4 | PUT | 从客户端向服务器传送的数据取代指定的文档的内容。 |
| 5 | DELETE | 请求服务器删除指定的页面。 |
| 6 | CONNECT | HTTP/1.1协议中预留给能够将连接改为管道方式的代理服务器。 |
| 7 | OPTIONS | 允许客户端查看服务器的性能。 |
| 8 | TRACE | 回显服务器收到的请求,主要用于测试或诊断。 |
GET方法:参数在请求行,不安全且有一定限制
POST方法:要求在服务器接受后面的数据,常用于提交表单。
一般GET用于获取/查询信息,而POST一般用于创建,更新信息。二者主要区别如下:
(1) 根据HTTP规范,GET用于获取,应该是安全和幂等的,而POST则表示可能改变服务器上的资源;
(2) GET请求数据会附在URL上,即请求行中,以"?"分隔URL和传输数据,多个参数用&连接;而POST会把数据放在HTTP消息的报体中,地址栏中没有
(3) 传输数据的大小不同,特定浏览器有限制,例如IE对URL限制是2083字节,POST理论上没有限制
(4) POST更安全,使用GET还有可能受到Cross-site request forgery攻击等等。
| Header | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Accept | 指定客户端能够接收的内容类型 | Accept: text/plain, text/html |
| Accept-Charset | 浏览器可以接受的字符编码集。 | Accept-Charset: iso-8859-5 |
| Accept-Encoding | 指定浏览器可以支持的web服务器返回内容压缩编码类型。 | Accept-Encoding: compress, gzip |
| Accept-Language | 浏览器可接受的语言 | Accept-Language: en,zh |
| Accept-Ranges | 可以请求网页实体的一个或者多个子范围字段 | Accept-Ranges: bytes |
| Authorization | HTTP授权的授权证书 | Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== |
| Cache-Control | 指定请求和响应遵循的缓存机制 | Cache-Control: no-cache |
| Connection | 表示是否需要持久连接。(HTTP 1.1默认进行持久连接) | Connection: close |
| Cookie | HTTP请求发送时,会把保存在该请求域名下的所有cookie值一起发送给web服务器。 | Cookie: $Version=1; Skin=new; |
| Content-Length | 请求的内容长度 | Content-Length: 348 |
| Content-Type | 请求的与实体对应的MIME信息 | Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| Date | 请求发送的日期和时间 | Date: Tue, 15 Nov 2010 08:12:31 GMT |
| Expect | 请求的特定的服务器行为 | Expect: 100-continue |
| From | 发出请求的用户的Email | From: user@email.com |
| Host | 指定请求的服务器的域名和端口号 | Host: www.zcmhi.com |
| If-Match | 只有请求内容与实体相匹配才有效 | If-Match: “737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d” |
| If-Modified-Since | 如果请求的部分在指定时间之后被修改则请求成功,未被修改则返回304代码 | If-Modified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 2010 19:43:31 GMT |
| If-None-Match | 如果内容未改变返回304代码,参数为服务器先前发送的Etag,与服务器回应的Etag比较判断是否改变 | If-None-Match: “737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d” |
| If-Range | 如果实体未改变,服务器发送客户端丢失的部分,否则发送整个实体。参数也为Etag | If-Range: “737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d” |
| If-Unmodified-Since | 只在实体在指定时间之后未被修改才请求成功 | If-Unmodified-Since: Sat, 29 Oct 2010 19:43:31 GMT |
| Max-Forwards | 限制信息通过代理和网关传送的时间 | Max-Forwards: 10 |
| Pragma | 用来包含实现特定的指令 | Pragma: no-cache |
| Proxy-Authorization | 连接到代理的授权证书 | Proxy-Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== |
| Range | 只请求实体的一部分,指定范围 | Range: bytes=500-999 |
| Referer | 先前网页的地址,当前请求网页紧随其后,即来路 | Referer: http://www.zcmhi.com/archives/71.html |
| TE | 客户端愿意接受的传输编码,并通知服务器接受接受尾加头信息 | TE: trailers,deflate;q=0.5 |
| Upgrade | 向服务器指定某种传输协议以便服务器进行转换(如果支持) | Upgrade: HTTP/2.0, SHTTP/1.3, IRC/6.9, RTA/x11 |
| User-Agent | User-Agent的内容包含发出请求的用户信息 | User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; X11) |
| Via | 通知中间网关或代理服务器地址,通信协议 | Via: 1.0 fred, 1.1 nowhere.com (Apache/1.1) |
| Warning | 关于消息实体的警告信息 | Warn: 199 Miscellaneous warning |
HTTP响应也由四个部分组成,分别是:状态行、消息报头、空行和响应正文。
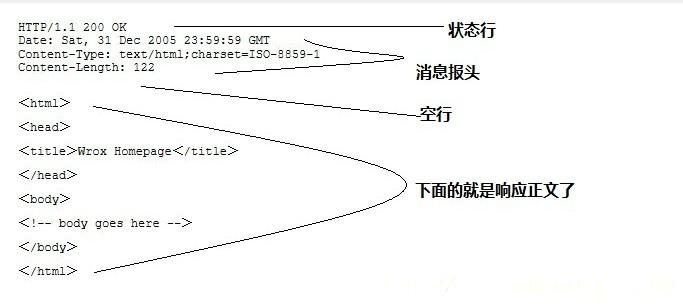
当浏览者访问一个网页时,浏览者的浏览器会向网页所在服务器发出请求。当浏览器接收并显示网页前,此网页所在的服务器会返回一个包含HTTP状态码的信息头(server header)用以响应浏览器的请求。
HTTP状态码的英文为HTTP Status Code。
下面是常见的HTTP状态码:
HTTP状态码由三个十进制数字组成,第一个十进制数字定义了状态码的类型,后两个数字没有分类的作用。HTTP状态码共分为5种类型:
| 分类 | 分类描述 |
|---|---|
| 1** | 信息,服务器收到请求,需要请求者继续执行操作 |
| 2** | 成功,操作被成功接收并处理 |
| 3** | 重定向,需要进一步的操作以完成请求 |
| 4** | 客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或无法完成请求 |
| 5** | 服务器错误,服务器在处理请求的过程中发生了错误 |
HTTP状态码列表:
| 状态码 | 状态码英文名称 | 中文描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | Continue | 继续。客户端应继续其请求 |
| 101 | Switching Protocols | 切换协议。服务器根据客户端的请求切换协议。只能切换到更高级的协议,例如,切换到HTTP的新版本协议 |
| 200 | OK | 请求成功。一般用于GET与POST请求 |
| 201 | Created | 已创建。成功请求并创建了新的资源 |
| 202 | Accepted | 已接受。已经接受请求,但未处理完成 |
| 203 | Non-Authoritative Information | 非授权信息。请求成功。但返回的meta信息不在原始的服务器,而是一个副本 |
| 204 | No Content | 无内容。服务器成功处理,但未返回内容。在未更新网页的情况下,可确保浏览器继续显示当前文档 |
| 205 | Reset Content | 重置内容。服务器处理成功,用户终端(例如:浏览器)应重置文档视图。可通过此返回码清除浏览器的表单域 |
| 206 | Partial Content | 部分内容。服务器成功处理了部分GET请求 |
| 300 | Multiple Choices | 多种选择。请求的资源可包括多个位置,相应可返回一个资源特征与地址的列表用于用户终端(例如:浏览器)选择 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | 永久移动。请求的资源已被永久的移动到新URI,返回信息会包括新的URI,浏览器会自动定向到新URI。今后任何新的请求都应使用新的URI代替 |
| 302 | Found | 临时移动。与301类似。但资源只是临时被移动。客户端应继续使用原有URI |
| 303 | See Other | 查看其它地址。与301类似。使用GET和POST请求查看 |
| 304 | Not Modified | 未修改。所请求的资源未修改,服务器返回此状态码时,不会返回任何资源。客户端通常会缓存访问过的资源,通过提供一个头信息指出客户端希望只返回在指定日期之后修改的资源 |
| 305 | Use Proxy | 使用代理。所请求的资源必须通过代理访问 |
| 306 | Unused | 已经被废弃的HTTP状态码 |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | 临时重定向。与302类似。使用GET请求重定向 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 客户端请求的语法错误,服务器无法理解 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 请求要求用户的身份认证 |
| 402 | Payment Required | 保留,将来使用 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 服务器理解请求客户端的请求,但是拒绝执行此请求 |
| 404 | Not Found | 服务器无法根据客户端的请求找到资源(网页)。通过此代码,网站设计人员可设置"您所请求的资源无法找到"的个性页面 |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | 客户端请求中的方法被禁止 |
| 406 | Not Acceptable | 服务器无法根据客户端请求的内容特性完成请求 |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required | 请求要求代理的身份认证,与401类似,但请求者应当使用代理进行授权 |
| 408 | Request Time-out | 服务器等待客户端发送的请求时间过长,超时 |
| 409 | Conflict | 服务器完成客户端的PUT请求是可能返回此代码,服务器处理请求时发生了冲突 |
| 410 | Gone | 客户端请求的资源已经不存在。410不同于404,如果资源以前有现在被永久删除了可使用410代码,网站设计人员可通过301代码指定资源的新位置 |
| 411 | Length Required | 服务器无法处理客户端发送的不带Content-Length的请求信息 |
| 412 | Precondition Failed | 客户端请求信息的先决条件错误 |
| 413 | Request Entity Too Large | 由于请求的实体过大,服务器无法处理,因此拒绝请求。为防止客户端的连续请求,服务器可能会关闭连接。如果只是服务器暂时无法处理,则会包含一个Retry-After的响应信息 |
| 414 | Request-URI Too Large | 请求的URI过长(URI通常为网址),服务器无法处理 |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type | 服务器无法处理请求附带的媒体格式 |
| 416 | Requested range not satisfiable | 客户端请求的范围无效 |
| 417 | Expectation Failed | 服务器无法满足Expect的请求头信息 |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务器内部错误,无法完成请求 |
| 501 | Not Implemented | 服务器不支持请求的功能,无法完成请求 |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | 充当网关或代理的服务器,从远端服务器接收到了一个无效的请求 |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | 由于超载或系统维护,服务器暂时的无法处理客户端的请求。延时的长度可包含在服务器的Retry-After头信息中 |
| 504 | Gateway Time-out | 充当网关或代理的服务器,未及时从远端服务器获取请求 |
| 505 | HTTP Version not supported | 服务器不支持请求 |
| Header | 解释 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Accept-Ranges | 表明服务器是否支持指定范围请求及哪种类型的分段请求 | Accept-Ranges: bytes |
| Age | 从原始服务器到代理缓存形成的估算时间(以秒计,非负) | Age: 12 |
| Allow | 对某网络资源的有效的请求行为,不允许则返回405 | Allow: GET, HEAD |
| Cache-Control | 告诉所有的缓存机制是否可以缓存及哪种类型 | Cache-Control: no-cache |
| Content-Encoding | web服务器支持的返回内容压缩编码类型。 | Content-Encoding: gzip |
| Content-Language | 响应体的语言 | Content-Language: en,zh |
| Content-Length | 响应体的长度 | Content-Length: 348 |
| Content-Location | 请求资源可替代的备用的另一地址 | Content-Location: /index.htm |
| Content-MD5 | 返回资源的MD5校验值 | Content-MD5: Q2hlY2sgSW50ZWdyaXR5IQ== |
| Content-Range | 在整个返回体中本部分的字节位置 | Content-Range: bytes 21010-47021/47022 |
| Content-Type | 返回内容的MIME类型 | Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 |
| Date | 原始服务器消息发出的时间 | Date: Tue, 15 Nov 2010 08:12:31 GMT |
| ETag | 请求变量的实体标签的当前值 | ETag: “737060cd8c284d8af7ad3082f209582d” |
| Expires | 响应过期的日期和时间 | Expires: Thu, 01 Dec 2010 16:00:00 GMT |
| Last-Modified | 请求资源的最后修改时间 | Last-Modified: Tue, 15 Nov 2010 12:45:26 GMT |
| Location | 用来重定向接收方到非请求URL的位置来完成请求或标识新的资源 | Location: http://www.zcmhi.com/archives/94.html |
| Pragma | 包括实现特定的指令,它可应用到响应链上的任何接收方 | Pragma: no-cache |
| Proxy-Authenticate | 它指出认证方案和可应用到代理的该URL上的参数 | Proxy-Authenticate: Basic |
| refresh | 应用于重定向或一个新的资源被创造,在5秒之后重定向(由网景提出,被大部分浏览器支持) |
Refresh: 5; url=
http://www.zcmhi.com/archives/94.html
|
| Retry-After | 如果实体暂时不可取,通知客户端在指定时间之后再次尝试 | Retry-After: 120 |
| Server | web服务器软件名称 | Server: Apache/1.3.27 (Unix) (Red-Hat/Linux) |
| Set-Cookie | 设置Http Cookie | Set-Cookie: UserID=JohnDoe; Max-Age=3600; Version=1 |
| Trailer | 指出头域在分块传输编码的尾部存在 | Trailer: Max-Forwards |
| Transfer-Encoding | 文件传输编码 | Transfer-Encoding:chunked |
| Vary | 告诉下游代理是使用缓存响应还是从原始服务器请求 | Vary: * |
| Via | 告知代理客户端响应是通过哪里发送的 | Via: 1.0 fred, 1.1 nowhere.com (Apache/1.1) |
| Warning | 警告实体可能存在的问题 | Warning: 199 Miscellaneous warning |
| WWW-Authenticate | 表明客户端请求实体应该使用的授权方案 | WWW-Authenticate: Basic |
netty天生异步事件驱动的架构,无论是在性能上还是在可靠性上,都表现优异,非常适合在非Web容器的场景下应用,相比于传统的Tomcat,Jetty等Web容器,更加的轻量和小巧、灵活性和定制性也更好。
我们以文件服务器为例学习Netty的HTTP服务端入门开发,例程场景如下:
1 import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; 2 import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; 3 import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; 4 import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; 5 import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; 6 import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; 7 import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; 8 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; 9 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder; 10 import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder; 11 import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedWriteHandler; 12 13 /** 14 * @author lilinfeng 15 * @version 1.0 16 * @date 2014年2月14日 17 */ 18 public class HttpFileServer { 19 20 private static final String DEFAULT_URL = "/"; 21 22 public void run(final int port, final String url) throws Exception { 23 EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 24 EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); 25 try { 26 ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); 27 b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) 28 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) 29 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { 30 @Override 31 protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) 32 throws Exception { 33 ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", 34 new HttpRequestDecoder()); // 请求消息解码器 35 ch.pipeline().addLast("http-aggregator", 36 new HttpObjectAggregator(65536));// 目的是将多个消息转换为单一的request或者response对象 37 ch.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", 38 new HttpResponseEncoder());//响应解码器 39 ch.pipeline().addLast("http-chunked", 40 new ChunkedWriteHandler());//目的是支持异步大文件传输() 41 ch.pipeline().addLast("fileServerHandler", 42 new HttpFileServerHandler(url));// 业务逻辑 43 } 44 }); 45 ChannelFuture future = b.bind("127.0.0.1", port).sync(); 46 System.out.println("HTTP文件目录服务器启动,网址是 : " + "http://127.0.0.1:" 47 + port + url); 48 future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); 49 } catch (Exception e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 } finally { 52 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 53 workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); 54 } 55 } 56 57 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 58 int port = 8080; 59 if (args.length > 0) { 60 try { 61 port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); 62 } catch (NumberFormatException e) { 63 e.printStackTrace(); 64 } 65 } 66 String url = DEFAULT_URL; 67 if (args.length > 1) 68 url = args[1]; 69 new HttpFileServer().run(port, url); 70 } 71 }
重点在于编解码器,首先添加的HTTP请求消息解码器HttpRequestDecoder,然后是HttpObjectAggregator解码器,它的作用是将多个消息转换为单一的FullHttpRequest或者FullHttpResponse,原因是HTTP解码器在每个HTTP消息中会生成多个消息对象。
(1) HttpRequest/HttpResponse;
(2) HttpContent;
(3) LastHttpContent;
下面是FileServerHandler:
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.*; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*; import io.netty.handler.stream.ChunkedFile; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; import javax.activation.MimetypesFileTypeMap; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.net.URLDecoder; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpMethod.GET; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.*; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1; /** * @author lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年2月14日 */ public class HttpFileServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<FullHttpRequest> { private final String url; public HttpFileServerHandler(String url) { this.url = url; } @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest request) throws Exception { /*如果无法解码400*/ if (!request.decoderResult().isSuccess()) { sendError(ctx, BAD_REQUEST); return; } /*只支持GET方法*/ if (request.method() != GET) { sendError(ctx, METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED); return; } final String uri = request.uri(); /*格式化URL,并且获取路径*/ final String path = sanitizeUri(uri); if (path == null) { sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN); return; } File file = new File(path); /*如果文件不可访问或者文件不存在*/ if (file.isHidden() || !file.exists()) { sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND); return; } /*如果是目录*/ if (file.isDirectory()) { //1. 以/结尾就列出所有文件 if (uri.endsWith("/")) { sendListing(ctx, file); } else { //2. 否则自动+/ sendRedirect(ctx, uri + ‘/‘); } return; } if (!file.isFile()) { sendError(ctx, FORBIDDEN); return; } RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = null; try { randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(file, "r");// 以只读的方式打开文件 } catch (FileNotFoundException fnfe) { sendError(ctx, NOT_FOUND); return; } long fileLength = randomAccessFile.length(); //创建一个默认的HTTP响应 HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK); //设置Content Length HttpUtil.setContentLength(response, fileLength); //设置Content Type setContentTypeHeader(response, file); //如果request中有KEEP ALIVE信息 if (HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(request)) { response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaderValues.KEEP_ALIVE); } ctx.write(response); ChannelFuture sendFileFuture; //通过Netty的ChunkedFile对象直接将文件写入发送到缓冲区中 sendFileFuture = ctx.write(new ChunkedFile(randomAccessFile, 0, fileLength, 8192), ctx.newProgressivePromise()); sendFileFuture.addListener(new ChannelProgressiveFutureListener() { @Override public void operationProgressed(ChannelProgressiveFuture future, long progress, long total) { if (total < 0) { // total unknown System.err.println("Transfer progress: " + progress); } else { System.err.println("Transfer progress: " + progress + " / " + total); } } @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelProgressiveFuture future) throws Exception { System.out.println("Transfer complete."); } }); ChannelFuture lastContentFuture = ctx .writeAndFlush(LastHttpContent.EMPTY_LAST_CONTENT); //如果不支持keep-Alive,服务器端主动关闭请求 if (!HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(request)) { lastContentFuture.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); if (ctx.channel().isActive()) { sendError(ctx, INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } } private static final Pattern INSECURE_URI = Pattern.compile(".*[<>&\"].*"); private String sanitizeUri(String uri) { try { uri = URLDecoder.decode(uri, "UTF-8"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { try { uri = URLDecoder.decode(uri, "ISO-8859-1"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e1) { throw new Error(); } } if (!uri.startsWith(url)) { return null; } if (!uri.startsWith("/")) { return null; } uri = uri.replace(‘/‘, File.separatorChar); if (uri.contains(File.separator + ‘.‘) || uri.contains(‘.‘ + File.separator) || uri.startsWith(".") || uri.endsWith(".") || INSECURE_URI.matcher(uri).matches()) { return null; } return System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + uri; } private static final Pattern ALLOWED_FILE_NAME = Pattern .compile("[A-Za-z0-9][-_A-Za-z0-9\\.]*"); private static void sendListing(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, File dir) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/html; charset=UTF-8"); StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(); String dirPath = dir.getPath(); buf.append("<!DOCTYPE html>\r\n"); buf.append("<html><head><title>"); buf.append(dirPath); buf.append(" 目录:"); buf.append("</title></head><body>\r\n"); buf.append("<h3>"); buf.append(dirPath).append(" 目录:"); buf.append("</h3>\r\n"); buf.append("<ul>"); buf.append("<li>链接:<a href=\"../\">..</a></li>\r\n"); for (File f : dir.listFiles()) { if (f.isHidden() || !f.canRead()) { continue; } String name = f.getName(); if (!ALLOWED_FILE_NAME.matcher(name).matches()) { continue; } buf.append("<li>链接:<a href=\""); buf.append(name); buf.append("\">"); buf.append(name); buf.append("</a></li>\r\n"); } buf.append("</ul></body></html>\r\n"); ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(buf, CharsetUtil.UTF_8); response.content().writeBytes(buffer); buffer.release(); ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } private static void sendRedirect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String newUri) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, FOUND); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.LOCATION, newUri); ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } private static void sendError(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, status, Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Failure: " + status.toString() + "\r\n", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8"); ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } private static void setContentTypeHeader(HttpResponse response, File file) { MimetypesFileTypeMap mimeTypesMap = new MimetypesFileTypeMap(); response.headers().set(HttpHeaderNames.CONTENT_TYPE, mimeTypesMap.getContentType(file.getPath())); } }
上面的代码注释相对详细,这里大致梳理一下。
(1) 不能解码返回400,只支持GET请求,否则返回405.
(2) 对url包装,使用UTF-8字符集,转换为绝对path
(3) 如果是目录,创建一个html页面
(4) 如果是文件,设置content-type和content-length,使用netty的chunkedfile直接写到缓冲,异步的方式
(5) 如果是非keepalived的,服务器端主动关闭,否则等待客户端主动关闭。
说明:原书是使用XML协议开发,XML框架用的是JiBX,这里用的是Json。
我们模拟一个简单的用户订购系统。
| 字段名称 | 类型 | 备注 |
| 订购数量 | Int64 | 订购的商品数量 |
| 客户信息 | Customer | 客户信息,负责POJO对象 |
| 账单地址 | Address | 账单的地址 |
| 寄送方式 | Shipping |
枚举类型如下: 普通邮寄 宅急送 国际邮递 国内快递 国际快递 |
| 送货地址 | Address | 送货地址 |
| 总价 | float | 商品总价 |
| 字段名称 | 类型 | 备注 |
| 客户ID | Int64 | 客户ID,长整型 |
| 姓 | String | 客户姓氏,字符串 |
| 名 | String | 客户名字,字符串 |
| 全名 | List<String> | 客户全称,字符列表 |
| 字段名称 | 类型 | 备注 |
| 街道1 | String | |
| 街道2 | String | |
| 城市 | String | |
| 省份 | String | |
| 邮编 | String | |
| 国家 | String |
| 字段名称 | 类型 | 备注 |
| 普通邮递 | 枚举类型 | |
| 宅急送 | 枚举类型 | |
| 国际邮递 | 枚举类型 | |
| 国内快递 | 枚举类型 | |
| 国际快递 | 枚举类型 |
涉及的类比较多:

netty开发的关键在于各种编解码器。
首先定义自己的请求类和响应类:
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest; /** * @author Lilinfeng * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月1日 */ public class HttpJsonRequest { private FullHttpRequest request; private Object body; public HttpJsonRequest(FullHttpRequest request, Object body) { this.request = request; this.body = body; } /** * @return the request */ public final FullHttpRequest getRequest() { return request; } /** * @param request the request to set */ public final void setRequest(FullHttpRequest request) { this.request = request; } /** * @return the object */ public final Object getBody() { return body; } /** * @param object the object to set */ public final void setBody(Object body) { this.body = body; } /* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString() { return "HttpJsonRequest [request=" + request + ", body =" + body + "]"; } }
import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse; /** * @author Administrator * @version 1.0 * @date 2014年3月1日 */ public class HttpJsonResponse { private FullHttpResponse httpResponse; private Object result; public HttpJsonResponse(FullHttpResponse httpResponse, Object result) { this.httpResponse = httpResponse; this.result = result; } /** * @return the httpResponse */ public final FullHttpResponse getHttpResponse() { return httpResponse; } /** * @param httpResponse the httpResponse to set */ public final void setHttpResponse(FullHttpResponse httpResponse) { this.httpResponse = httpResponse; } /** * @return the body */ public final Object getResult() { return result; } /** * @param body the body to set */ public final void setResult(Object result) { this.result = result; } /* * (non-Javadoc) * * @see java.lang.Object#toString() */ @Override public String toString() { return "HttpJsonResponse [httpResponse=" + httpResponse + ", result=" + result + "]"; } }
根据这2个类来设计流程,我们可以使用netty对http协议支持的编解码器,首先我们使用了FastJson来作为json的框架,因此先定义2个抽象类,其中封装了json的转换方法,虽然看上去有点复杂,但是仅仅封装了json化和反json化方法。
import demo.protocol.http.json.FastJsonUtils; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageEncoder; import java.nio.charset.Charset; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public abstract class AbstractHttpJsonEncoder<T> extends MessageToMessageEncoder<T> { final static Charset UTF_8 = Charset.forName("utf-8"); protected ByteBuf encode0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object body) { String jsonStr = FastJsonUtils.convertObjectToJSON(body); ByteBuf encodeBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(jsonStr, UTF_8); return encodeBuf; } }
import demo.protocol.http.json.FastJsonUtils; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.MessageToMessageDecoder; import java.nio.charset.Charset; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public abstract class AbstractHttpJsonDecoder<T> extends MessageToMessageDecoder<T> { private Class<?> clazz; private boolean isPrint; private final static Charset UTF_8 = Charset.forName("UTF-8"); protected AbstractHttpJsonDecoder(Class<?> clazz) { this(clazz, false); } protected AbstractHttpJsonDecoder(Class<?> clazz, boolean isPrint) { this.clazz = clazz; this.isPrint = isPrint; } protected Object decode0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf body) { String content = body.toString(UTF_8); if (isPrint) System.out.println("The body is : " + content); Object result = FastJsonUtils.convertJSONToObject(content, clazz); return result; } }
(1) HttpRequestDecoder:请求消息解码器,转换为消息对象。
(2) HttpObjectAggregator: 目的是将多个消息转换为单一的request或者response对象,最终得到的是FullHttpRequest对象
(3) 需要自定义的解码器HttpJsonRequestDecoder,将FullHttpRequest转换为HttpJsonRequest对象
(1) HttpResponseEncoder:响应消息编码器,已经是一个HTTP消息了
(2) 自定义编码器 HttpJsonResponseEncoder:由于Netty的DefaultFullHttpResponse没有提供动态设置消息体content的接口。因此我们只能复制一个新的HTTP消息,将动态内容加入,生成一个DefaultFullHttpResponse对象。
上面涉及到的类如下:
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.DefaultFullHttpResponse; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpRequest; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; import java.util.List; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonRequestDecoder extends AbstractHttpJsonDecoder<FullHttpRequest> { public HttpJsonRequestDecoder(Class<?> clazz) { this(clazz, false); } /** * 构造器 * * @param clazz 解码的对象信息 * @param isPrint 是否需要打印 */ public HttpJsonRequestDecoder(Class<?> clazz, boolean isPrint) { super(clazz, isPrint); } /** * @param ctx channel上下文 * @param msg 消息 * @param out 输出集合 * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpRequest msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { if (!msg.decoderResult().isSuccess()) { sendError(ctx, HttpResponseStatus.BAD_REQUEST); return; } HttpJsonRequest request = new HttpJsonRequest(msg, decode0(ctx, msg.content())); out.add(request); } /** * 测试的话,直接封装,实战中需要更健壮的处理 */ private static void sendError(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, status, Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Failure: " + status.toString() + "\r\n", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8"); ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } }
/** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonResponseEncoder extends AbstractHttpJsonEncoder<HttpJsonResponse> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpJsonResponse msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { //编码 ByteBuf body = encode0(ctx, msg.getResult()); FullHttpResponse response = msg.getHttpResponse(); if (response == null) { response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, OK, body); } else { response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(msg.getHttpResponse() .protocolVersion(), msg.getHttpResponse().status(), body); } response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/json"); HttpUtil.setContentLength(response, body.readableBytes()); out.add(response); } }
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.util.List; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonRequestEncoder extends AbstractHttpJsonEncoder<HttpJsonRequest> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpJsonRequest msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { //(1)调用父类的encode0,将业务需要发送的对象转换为Json ByteBuf body = encode0(ctx, msg.getBody()); //(2) 如果业务自定义了HTTP消息头,则使用业务的消息头,否则在这里构造HTTP消息头 // 这里使用硬编码的方式来写消息头,实际中可以写入配置文件 FullHttpRequest request = msg.getRequest(); if (request == null) { request = new DefaultFullHttpRequest(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpMethod.GET, "/do", body); HttpHeaders headers = request.headers(); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.HOST, InetAddress.getLocalHost() .getHostAddress()); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.CONNECTION, HttpHeaders.Values.CLOSE); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_ENCODING, HttpHeaderValues.GZIP.toString() + ‘,‘ + HttpHeaderValues.DEFLATE.toString()); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_CHARSET, "ISO-8859-1,utf-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7"); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT_LANGUAGE, "zh"); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.USER_AGENT, "Netty json Http Client side"); headers.set(HttpHeaderNames.ACCEPT, "text/html,application/json;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8"); } HttpUtil.setContentLength(request, body.readableBytes()); // (3) 编码后的对象 out.add(request); } }
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.FullHttpResponse; import java.util.List; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonResponseDecoder extends AbstractHttpJsonDecoder<FullHttpResponse> { public HttpJsonResponseDecoder(Class<?> clazz) { this(clazz, false); } /** * 构造器 * * @param clazz 解码的对象信息 * @param isPrint 是否需要打印 */ public HttpJsonResponseDecoder(Class<?> clazz, boolean isPrint) { super(clazz, isPrint); } /** * @param ctx channel上下文 * @param msg 消息 * @param out 输出集合 * @throws Exception */ @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, FullHttpResponse msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { System.out.println("开始解码..."); out.add( new HttpJsonResponse(msg, decode0(ctx, msg.content())) ); } }
import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonRequestDecoder; import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonResponseEncoder; import demo.protocol.http.json.pojo.Order; import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestDecoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseEncoder; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonServer { public void run(final int port) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { //接收HttpJsonRequest,需要对应解码器 //ByteBuf->FullHttpRequest-> HttpJsonRequestDecoder //输出HttpJsonResponse,需要对应编码器 //HttpResponseEncoder->FullHttpResponse-> HttpJsonResponseEncoder ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpRequestDecoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("http-aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)); ch.pipeline().addLast("json-decoder", new HttpJsonRequestDecoder(Order.class, true)); ch.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", new HttpResponseEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("json-encoder", new HttpJsonResponseEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("jsonServerHandler", new HttpJsonServerHandler()); } }); ChannelFuture future = b.bind(new InetSocketAddress(port)).sync(); System.out.println("HTTP订购服务器启动,网址是 : " + "http://localhost:" + port); future.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int port = 8080; if (args.length > 0) { try { port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } new HttpJsonServer().run(port); } }
import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonRequest; import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonResponse; import demo.protocol.http.json.pojo.Address; import demo.protocol.http.json.pojo.Order; import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.*; import io.netty.util.CharsetUtil; import io.netty.util.concurrent.Future; import io.netty.util.concurrent.GenericFutureListener; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR; import static io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<HttpJsonRequest> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpJsonRequest msg) throws Exception { HttpRequest request = msg.getRequest(); Order order = (Order) msg.getBody(); System.out.println("Http server receive request : " + order); dobusiness(order); ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(new HttpJsonResponse(null, order)); if (!HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(request)) { future.addListener(new GenericFutureListener<Future<? super Void>>() { public void operationComplete(Future future) throws Exception { ctx.close(); } }); } } private void dobusiness(Order order) { order.getCustomer().setFirstName("狄"); order.getCustomer().setLastName("仁杰"); List<String> midNames = new ArrayList<String>(); midNames.add("李元芳"); order.getCustomer().setMiddleNames(midNames); Address address = order.getBillTo(); address.setCity("洛阳"); address.setCountry("大唐"); address.setState("河南道"); address.setPostCode("123456"); order.setBillTo(address); order.setShipTo(address); } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception { cause.printStackTrace(); if (ctx.channel().isActive()) { sendError(ctx, INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } } private static void sendError(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpResponseStatus status) { FullHttpResponse response = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HTTP_1_1, status, Unpooled.copiedBuffer("失败: " + status.toString() + "\r\n", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); response.headers().set(CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8"); ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); } }
import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonRequestEncoder; import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonResponseDecoder; import demo.protocol.http.json.pojo.Order; import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap; import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer; import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption; import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup; import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel; import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpObjectAggregator; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpRequestEncoder; import io.netty.handler.codec.http.HttpResponseDecoder; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonClient { public void connect(int port) throws Exception { // 配置客户端NIO线程组 EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true) .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpResponseDecoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("http-aggregator", new HttpObjectAggregator(65536)); // json解码器 ch.pipeline().addLast("json-decoder", new HttpJsonResponseDecoder(Order.class, true)); ch.pipeline().addLast("http-encoder", new HttpRequestEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("json-encoder", new HttpJsonRequestEncoder()); ch.pipeline().addLast("jsonClientHandler", new HttpJsonClientHandler()); } }); // 发起异步连接操作 ChannelFuture f = b.connect(new InetSocketAddress(port)).sync(); // 当代客户端链路关闭 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { // 优雅退出,释放NIO线程组 group.shutdownGracefully(); } } /** * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int port = 8080; if (args != null && args.length > 0) { try { port = Integer.valueOf(args[0]); } catch (NumberFormatException e) { // 采用默认值 } } new HttpJsonClient().connect(port); } }
import demo.protocol.http.json.codec.HttpJsonRequest; import demo.protocol.http.json.pojo.OrderFactory; import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext; import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter; /** * Created by carl.yu on 2016/12/16. */ public class HttpJsonClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { System.out.println("连接上服务器..."); HttpJsonRequest request = new HttpJsonRequest(null, OrderFactory.create(123)); ctx.writeAndFlush(request); } @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception { System.out.println(msg.getClass().getName()); System.out.println("接收到了数据..." + msg); } /*@Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, HttpJsonResponse msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("The client receive response of http header is : " + msg.getHttpResponse().headers().names()); System.out.println("The client receive response of http body is : " + msg.getResult()); }*/ @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
运行即可。
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/carl10086/p/6185095.html