本文是对基于Kubernetes V1.5的代码,对ResourceQuotaController的原理分析和源码分析,给出了对应的源码目录结构分析,内部实现原理图,及其完整流程的源码分析,希望能帮助你对Kubernetes ResourceQuota和ResourceQuotaController有更深入的了解。
关于ResoureQuota和ResourceController的介绍和使用请参见如下官方文档。这是你理解这篇博客的基础。
ResourceQuota Controller作为Kubernetes Controller Manager管理的众多Controller中的一员,其主要的源码位于目录k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/quota和k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller/resourcequota,具体分析如下:
k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/quota
.
├── evaluator // 负责各种资源使用的统计
│ └── core
│ ├── configmap.go // ConfigMapEvaluator的实现,负责ConfigMap资源的统计
│ ├── doc.go
│ ├── persistent_volume_claims.go // PVCEvaluator的实现,负责PVC资源的统计
│ ├── persistent_volume_claims_test.go
│ ├── pods.go //PodEvaluator的实现,负责Pod资源的统计
│ ├── pods_test.go
│ ├── registry.go // 创建Registry时注册所有的Evaluators
│ ├── replication_controllers.go // RCEvaluator的实现,负责ReplicationController资源的统计
│ ├── resource_quotas.go // ResourceQuotaEvaluator的实现,负责ResourceQuota资源的统计
│ ├── secrets.go // SecretEvaluator的实现,负责Secret资源的统计
│ ├── services.go // ServiceEvaluator的实现,负责Service资源的统计
│ └── services_test.go
├── generic // genericEvaluator的定义和实现
│ ├── evaluator.go // 实现了genericEvaluator的接口,包括最重要的CalculateUsageStats接口
│ └── registry.go // 定义GenericRegistry
├── install
│ └── registry.go // 定义了startResourceQuotaController时会调用创建ResourceQuota Registry的方法
├── interfaces.go // 定义了Registry和Evaluator Interface
├── resources.go // 定义Resources的集合操作以及CalculateUsage方法
└── resources_test.gok8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller/resourcequota
.
├── doc.go
├── replenishment_controller.go // 定义replenishmentControllerFactory,用来创建replenishmentController
├── replenishment_controller_test.go
├── resource_quota_controller.go // 定义ResourceQuotaController及其Run方法,syncResourceQuota方法等,属于核心文件。
└── resource_quota_controller_test.go请下载到本地放大查看。
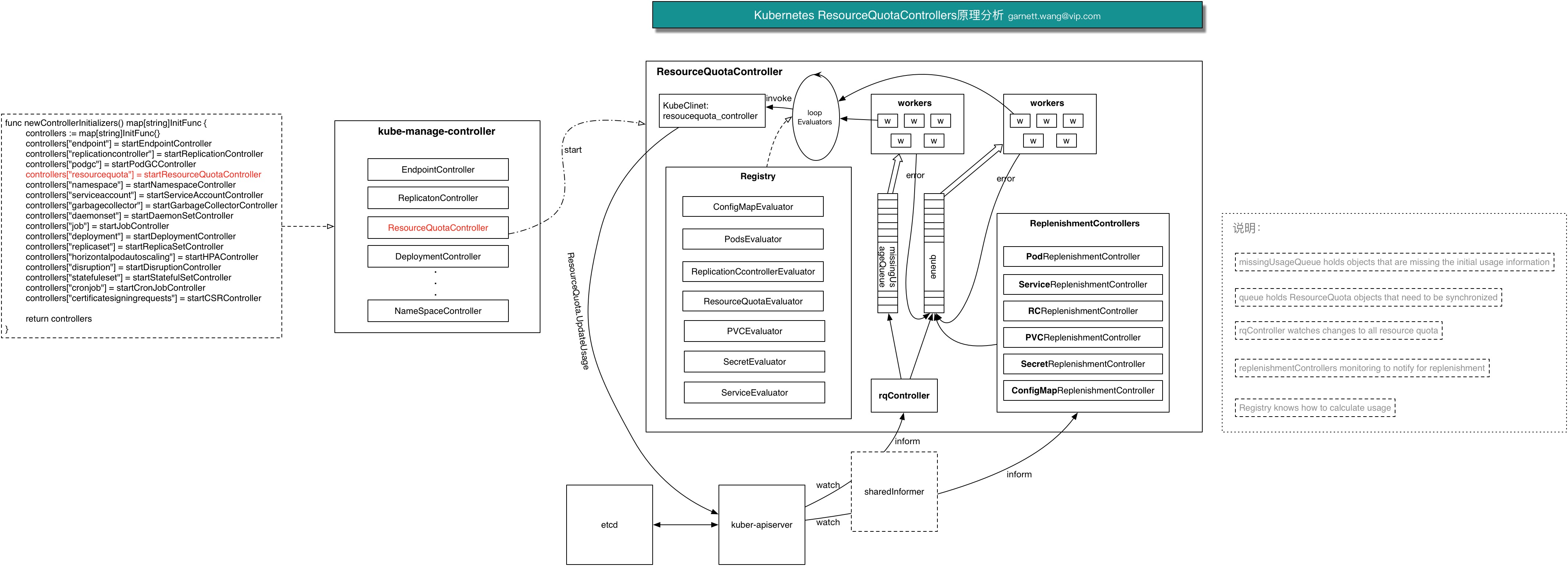
具体各个模块的功能和交互请看下面的源码分析。
上面的内部实现原理图显示,ResourceQuotaController是Kubenetes Controller Manager启动进行初始化众多Controllers的时候,通过调用startResourceQuotaController来完成ResourceQuotaController的启动。
cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/core.go:76
func startResourceQuotaController(ctx ControllerContext) (bool, error) {
resourceQuotaControllerClient := ctx.ClientBuilder.ClientOrDie("resourcequota-controller")
resourceQuotaRegistry := quotainstall.NewRegistry(resourceQuotaControllerClient, ctx.InformerFactory)
// 定义ReplenishmentController需要监控的资源对象
groupKindsToReplenish := []schema.GroupKind{
api.Kind("Pod"),
api.Kind("Service"),
api.Kind("ReplicationController"),
api.Kind("PersistentVolumeClaim"),
api.Kind("Secret"),
api.Kind("ConfigMap"),
}
...
go resourcequotacontroller.NewResourceQuotaController(
resourceQuotaControllerOptions,
).Run(int(ctx.Options.ConcurrentResourceQuotaSyncs), ctx.Stop)
return true, nil
}startResourceQuotaController启动一个goroutine,通过NewResourceQuotaController创建一个ResourceQuotaController并执行其Run方法开始提供ResourceQuotaController。
下面是ResourceQuotaController和ResourceQuotaControllerOptions结构体的定义。ResourceQuotaController中定义了几个关键Entity,分别是rqController、queue、missingUsageQueue、registry、replenishmentControllers,在上一节中的原理图中也能看到它们的身影。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:40
// ResourceQuotaControllerOptions holds options for creating a quota controller
type ResourceQuotaControllerOptions struct {
// Must have authority to list all quotas, and update quota status
KubeClient clientset.Interface
// Controls full recalculation of quota usage
ResyncPeriod controller.ResyncPeriodFunc
// Knows how to calculate usage
Registry quota.Registry
// Knows how to build controllers that notify replenishment events
ControllerFactory ReplenishmentControllerFactory
// Controls full resync of objects monitored for replenihsment.
ReplenishmentResyncPeriod controller.ResyncPeriodFunc
// List of GroupKind objects that should be monitored for replenishment at
// a faster frequency than the quota controller recalculation interval
GroupKindsToReplenish []schema.GroupKind
}
// ResourceQuotaController is responsible for tracking quota usage status in the system
type ResourceQuotaController struct {
// Must have authority to list all resources in the system, and update quota status
kubeClient clientset.Interface
// An index of resource quota objects by namespace
rqIndexer cache.Indexer
// Watches changes to all resource quota
rqController *cache.Controller
// ResourceQuota objects that need to be synchronized
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
// missingUsageQueue holds objects that are missing the initial usage informatino
missingUsageQueue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
// To allow injection of syncUsage for testing.
syncHandler func(key string) error
// function that controls full recalculation of quota usage
resyncPeriod controller.ResyncPeriodFunc
// knows how to calculate usage
registry quota.Registry
// controllers monitoring to notify for replenishment
replenishmentControllers []cache.ControllerInterface
}接下来,我们看看startResourceQuotaController调用的NewRegistry、NewResourceQuotaController以及ResourceQuotaController的Run方法。
pkg/quota/evaluator/core/registry.go:29
// NewRegistry returns a registry that knows how to deal with core kubernetes resources
// If an informer factory is provided, evaluators will use them.
func NewRegistry(kubeClient clientset.Interface, f informers.SharedInformerFactory) quota.Registry {
pod := NewPodEvaluator(kubeClient, f)
service := NewServiceEvaluator(kubeClient)
replicationController := NewReplicationControllerEvaluator(kubeClient)
resourceQuota := NewResourceQuotaEvaluator(kubeClient)
secret := NewSecretEvaluator(kubeClient)
configMap := NewConfigMapEvaluator(kubeClient)
persistentVolumeClaim := NewPersistentVolumeClaimEvaluator(kubeClient, f)
return &generic.GenericRegistry{
InternalEvaluators: map[schema.GroupKind]quota.Evaluator{
pod.GroupKind(): pod,
service.GroupKind(): service,
replicationController.GroupKind(): replicationController,
secret.GroupKind(): secret,
configMap.GroupKind(): configMap,
resourceQuota.GroupKind(): resourceQuota,
persistentVolumeClaim.GroupKind(): persistentVolumeClaim,
},
}
}可见,NewRegistry负责这些资源对象(pod,service,rc,secret,configMap,resourceQuota,PVC)的的Evaluator的创建和注册,供后面Worker中执行quota.CalculateUsage(…)对这些资源对象进行使用统计。
NewRegistry执行完后,开始创建ResourceQuotaController,代码如下。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:78
func NewResourceQuotaController(options *ResourceQuotaControllerOptions) *ResourceQuotaController {
// build the resource quota controller
rq := &ResourceQuotaController{
kubeClient: options.KubeClient,
queue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "resourcequota_primary"),
missingUsageQueue: workqueue.NewNamedRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter(), "resourcequota_priority"),
resyncPeriod: options.ResyncPeriod,
registry: options.Registry,
replenishmentControllers: []cache.ControllerInterface{},
}
...
// set the synchronization handler
rq.syncHandler = rq.syncResourceQuotaFromKey
// build the controller that observes quota
rq.rqIndexer, rq.rqController = cache.NewIndexerInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return rq.kubeClient.Core().ResourceQuotas(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return rq.kubeClient.Core().ResourceQuotas(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.ResourceQuota{},
rq.resyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: rq.addQuota,
UpdateFunc: func(old, cur interface{}) {
oldResourceQuota := old.(*v1.ResourceQuota)
curResourceQuota := cur.(*v1.ResourceQuota)
if quota.V1Equals(oldResourceQuota.Spec.Hard, curResourceQuota.Spec.Hard) {
return
}
rq.addQuota(curResourceQuota)
},
DeleteFunc: rq.enqueueResourceQuota,
},
cache.Indexers{"namespace": cache.MetaNamespaceIndexFunc},
)
for _, groupKindToReplenish := range options.GroupKindsToReplenish {
controllerOptions := &ReplenishmentControllerOptions{
GroupKind: groupKindToReplenish,
ResyncPeriod: options.ReplenishmentResyncPeriod,
ReplenishmentFunc: rq.replenishQuota,
}
replenishmentController, err := options.ControllerFactory.NewController(controllerOptions)
if err != nil {
glog.Warningf("quota controller unable to replenish %s due to %v, changes only accounted during full resync", groupKindToReplenish, err)
} else {
rq.replenishmentControllers = append(rq.replenishmentControllers, replenishmentController)
}
}
return rq
}NewResourceQuotaController负责创建ResourceQuotaController,包括queue, missingUsageQueue, syncHandler,rqIndexer, rqController,replenishmentControllers的Entity填充。重点关注
rq.rqIndexer, rq.rqController = cache.NewIndexerInformer(...)
进行了rqController中注册ResourceEventHandlerFuncs:addQuota和enqueueResourceQuota。另外,
replenishmentController, err := options.ControllerFactory.NewController(controllerOptions)
负责replenishmentController的创建,NewRegistry中注册了6种replenishmentSource,所以这里replenishmentControllers会添加对应的6中replenishmentController。
创建完ResourceQuotaController之后,就执行Run方法开始进行任务处理了。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:227
// Run begins quota controller using the specified number of workers
func (rq *ResourceQuotaController) Run(workers int, stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
...
// 启动rqController和rq.replenishmentControllers中的6中replenishmentController,开始watch对应的ResourceQuota加入到queue和missingUsageQueue。
go rq.rqController.Run(stopCh)
// the controllers that replenish other resources to respond rapidly to state changes
for _, replenishmentController := range rq.replenishmentControllers {
go replenishmentController.Run(stopCh)
}
// 启动workers数量的worker协程,分别对queue和missingUsageQueue中的Item。
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go wait.Until(rq.worker(rq.queue), time.Second, stopCh)
go wait.Until(rq.worker(rq.missingUsageQueue), time.Second, stopCh)
}
// 定期的进行全量的quotas计算。
go wait.Until(func() { rq.enqueueAll() }, rq.resyncPeriod(), stopCh)
<-stopCh
glog.Infof("Shutting down ResourceQuotaController")
rq.queue.ShutDown()
}接下来的主要处理都交给了workers进行处理了,默认配置是有5个worker对queue进行处理,有5个worker对missingUsageQuota进行处理。下面来看看worker是怎么对Queue中的Item进行处理的。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:199
// worker runs a worker thread that just dequeues items, processes them, and marks them done.
func (rq *ResourceQuotaController) worker(queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface) func() {
workFunc := func() bool {
// 从queue中获取Key
key, quit := queue.Get()
if quit {
return true
}
defer queue.Done(key)
// 执行NewResourceQuotaController时注册的syncHandler(流程跳转到syncResourceQuotaFromKey)
err := rq.syncHandler(key.(string))
...
}
return func() {
for {
if quit := workFunc(); quit {
glog.Infof("resource quota controller worker shutting down")
return
}
}
}
}流程进入到syncResourceQuotaFromKey,下面看看它的实现:
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:247
// syncResourceQuotaFromKey syncs a quota key
func (rq *ResourceQuotaController) syncResourceQuotaFromKey(key string) (err error) {
...
obj, exists, err := rq.rqIndexer.GetByKey(key)
...
quota := *obj.(*v1.ResourceQuota)
return rq.syncResourceQuota(quota)
}syncResourceQuotaFromKey根据从queue中获得的key,从rqIndexer中得到该Object,然后执行rq.syncResourceQuota(quota)。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:268
// syncResourceQuota runs a complete sync of resource quota status across all known kinds
func (rq *ResourceQuotaController) syncResourceQuota(v1ResourceQuota v1.ResourceQuota) (err error) {
...
newUsage, err := quota.CalculateUsage(resourceQuota.Namespace, resourceQuota.Spec.Scopes, hardLimits, rq.registry)
...
// ensure set of used values match those that have hard constraints
hardResources := quota.ResourceNames(hardLimits)
used = quota.Mask(used, hardResources)
usage := api.ResourceQuota{
ObjectMeta: api.ObjectMeta{
Name: resourceQuota.Name,
Namespace: resourceQuota.Namespace,
ResourceVersion: resourceQuota.ResourceVersion,
Labels: resourceQuota.Labels,
Annotations: resourceQuota.Annotations},
Status: api.ResourceQuotaStatus{
Hard: hardLimits,
Used: used,
},
}
dirty = dirty || !quota.Equals(usage.Status.Used, resourceQuota.Status.Used)
// there was a change observed by this controller that requires we update quota
if dirty {
v1Usage := &v1.ResourceQuota{}
if err := v1.Convert_api_ResourceQuota_To_v1_ResourceQuota(&usage, v1Usage, nil); err != nil {
return err
}
_, err = rq.kubeClient.Core().ResourceQuotas(usage.Namespace).UpdateStatus(v1Usage)
return err
}
return nil
}syncResourceQuota中最关键的操作是:
newUsage, err := quota.CalculateUsage(resourceQuota.Namespace, resourceQuota.Spec.Scopes, hardLimits, rq.registry)
quota.CalculateUsage根据namespace, quota的Scope,hardLimits,registry对该Item(resourceQuota)进行CalculateUsage。
pkg/quota/resources.go:217
// CalculateUsage calculates and returns the requested ResourceList usage
func CalculateUsage(namespaceName string, scopes []api.ResourceQuotaScope, hardLimits api.ResourceList, registry Registry) (api.ResourceList, error) {
// find the intersection between the hard resources on the quota
// and the resources this controller can track to know what we can
// look to measure updated usage stats for
hardResources := ResourceNames(hardLimits)
potentialResources := []api.ResourceName{}
evaluators := registry.Evaluators()
for _, evaluator := range evaluators {
potentialResources = append(potentialResources, evaluator.MatchingResources(hardResources)...)
}
// NOTE: the intersection just removes duplicates since the evaluator match intersects wtih hard
matchedResources := Intersection(hardResources, potentialResources)
// sum the observed usage from each evaluator
newUsage := api.ResourceList{}
for _, evaluator := range evaluators {
// only trigger the evaluator if it matches a resource in the quota, otherwise, skip calculating anything
intersection := evaluator.MatchingResources(matchedResources)
if len(intersection) == 0 {
continue
}
usageStatsOptions := UsageStatsOptions{Namespace: namespaceName, Scopes: scopes, Resources: intersection}
stats, err := evaluator.UsageStats(usageStatsOptions)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
newUsage = Add(newUsage, stats.Used)
}
// mask the observed usage to only the set of resources tracked by this quota
// merge our observed usage with the quota usage status
// if the new usage is different than the last usage, we will need to do an update
newUsage = Mask(newUsage, matchedResources)
return newUsage, nil
}CalculateUsage中最重要的一步是循环registry中注册的所有Evaluators,执行对应Evaluator的UsageStats方法进资源使用统计。看到这里,你也许懵逼了,Evaluators又是个什么东西?
我们先来看看Registry和Evaluator的关系,以及Evaluator的定义。
pkg/quota/interfaces.go:62
// Registry holds the list of evaluators associated to a particular group kind
type Registry interface {
// Evaluators returns the set Evaluator objects registered to a groupKind
Evaluators() map[schema.GroupKind]Evaluator
}
pkg/quota/interfaces.go:43
// Evaluator knows how to evaluate quota usage for a particular group kind
type Evaluator interface {
// Constraints ensures that each required resource is present on item
Constraints(required []api.ResourceName, item runtime.Object) error
// GroupKind returns the groupKind that this object knows how to evaluate
GroupKind() schema.GroupKind
// Handles determines if quota could be impacted by the specified operation.
// If true, admission control must perform quota processing for the operation, otherwise it is safe to ignore quota.
Handles(operation admission.Operation) bool
// Matches returns true if the specified quota matches the input item
Matches(resourceQuota *api.ResourceQuota, item runtime.Object) (bool, error)
// MatchingResources takes the input specified list of resources and returns the set of resources evaluator matches.
MatchingResources(input []api.ResourceName) []api.ResourceName
// Usage returns the resource usage for the specified object
Usage(item runtime.Object) (api.ResourceList, error)
// UsageStats calculates latest observed usage stats for all objects
UsageStats(options UsageStatsOptions) (UsageStats, error)
}可见Evaluator就是一系列操作的集合,是一个Interface,而Registry就是资源类型到Evaluator的一个Map。
Kubernetes中定义了7种资源的Evaluator,都在pkg/quota/evaluator/core/*目录下,比如pods.go就是PodEvaluator的实现,里面实现了关键的UsageStats方法。除了PodEvaluator之外,其他的Evaluator的UsageStats实现,都是genericEvaluator来完成的,其代码在pkg/quota/generic/evaluator.go:177。
具体Evaluator的代码分析,请读者自行完成。
下面我给出Worker的内部流程图,供大家参考:
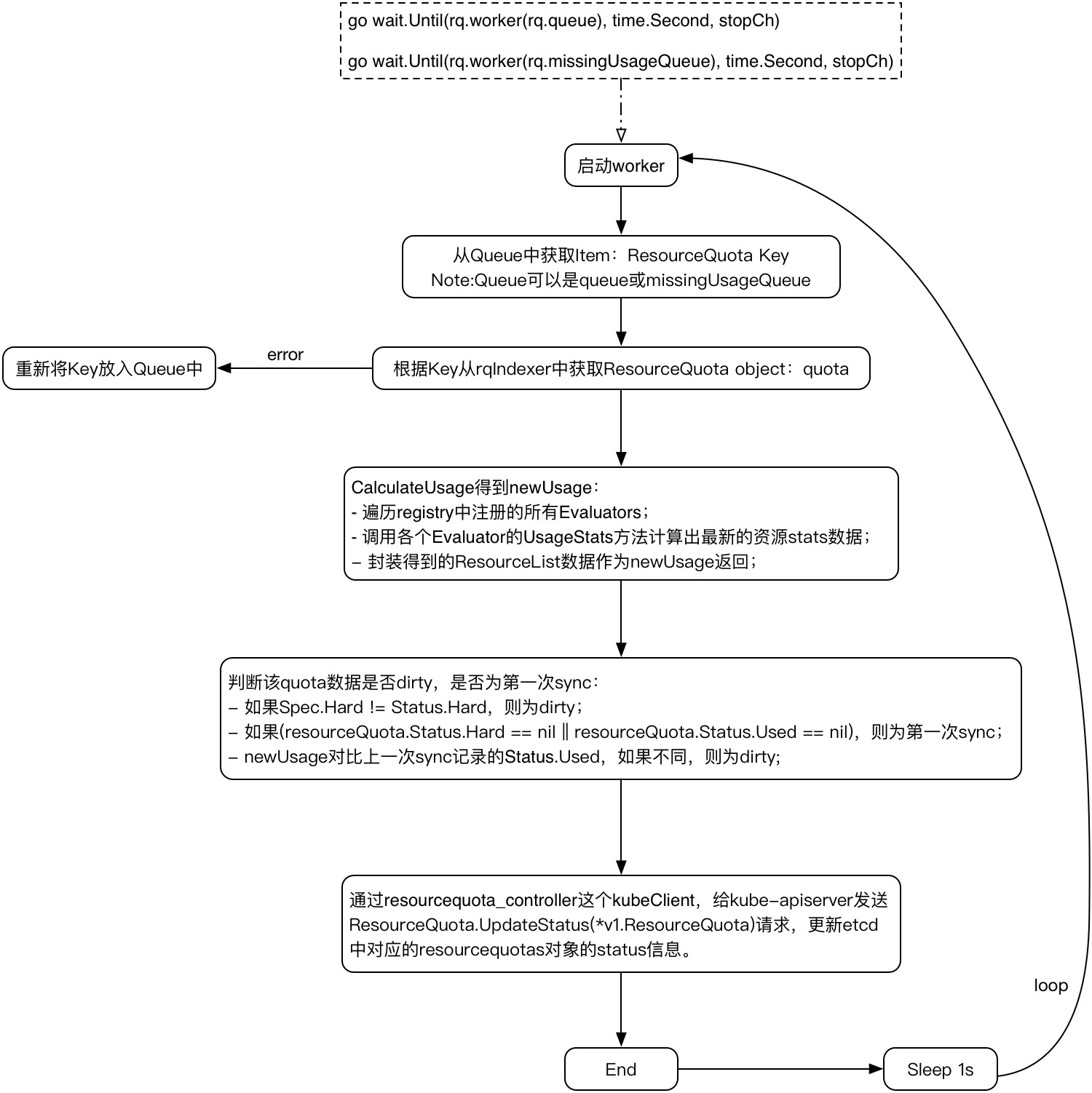
rqController负责watch待sync的ResourceQuota,并将其加入到queue和missingUsageQueue中,而上面分析NewResourceQuotaController代码时提到:
replenishmentController, err := options.ControllerFactory.NewController(controllerOptions)
负责replenishmentController的创建,那replenishmentController又是啥呢?我们有必要来看看replenishmentController的创建。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/replenishment_controller.go:131
func (r *replenishmentControllerFactory) NewController(options *ReplenishmentControllerOptions) (result cache.ControllerInterface, err error) {
...
switch options.GroupKind {
case api.Kind("Pod"):
if r.sharedInformerFactory != nil {
result, err = controllerFor(api.Resource("pods"), r.sharedInformerFactory, cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
UpdateFunc: PodReplenishmentUpdateFunc(options),
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
})
break
}
result = informers.NewPodInformer(r.kubeClient, options.ResyncPeriod())
case api.Kind("Service"):
// TODO move to informer when defined
_, result = cache.NewInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().Services(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().Services(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.Service{},
options.ResyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
UpdateFunc: ServiceReplenishmentUpdateFunc(options),
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
},
)
case api.Kind("ReplicationController"):
// TODO move to informer when defined
_, result = cache.NewInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().ReplicationControllers(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().ReplicationControllers(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.ReplicationController{},
options.ResyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
},
)
case api.Kind("PersistentVolumeClaim"):
if r.sharedInformerFactory != nil {
result, err = controllerFor(api.Resource("persistentvolumeclaims"), r.sharedInformerFactory, cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
})
break
}
// TODO (derekwaynecarr) remove me when we can require a sharedInformerFactory in all code paths...
_, result = cache.NewInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().PersistentVolumeClaims(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().PersistentVolumeClaims(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.PersistentVolumeClaim{},
options.ResyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
},
)
case api.Kind("Secret"):
// TODO move to informer when defined
_, result = cache.NewInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().Secrets(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().Secrets(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.Secret{},
options.ResyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
},
)
case api.Kind("ConfigMap"):
// TODO move to informer when defined
_, result = cache.NewInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().ConfigMaps(v1.NamespaceAll).List(options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options v1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
return r.kubeClient.Core().ConfigMaps(v1.NamespaceAll).Watch(options)
},
},
&v1.ConfigMap{},
options.ResyncPeriod(),
cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
DeleteFunc: ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options),
},
)
default:
return nil, NewUnhandledGroupKindError(options.GroupKind)
}
return result, err
}
整个代码结构非常清晰,就是根据不同的资源类型,返回对应的Controller。而每种资源的Controller的定义都是通过创建一个对应的Informer完成。Informer中注册对应的ResourceEventHandlerFuncs:UpdateFunc和DeleteFunc用来出watch的对象发生对应的change时需要调用的方法。
以Pod为例,看看Pod注册的UpdateFunc:PodReplenishmentUpdateFunc和DeleteFunc:ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc,你就知道replenishmentController是用来干啥的了。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/replenishment_controller.go:56
// PodReplenishmentUpdateFunc will replenish if the old pod was quota tracked but the new is not
func PodReplenishmentUpdateFunc(options *ReplenishmentControllerOptions) func(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
return func(oldObj, newObj interface{}) {
oldPod := oldObj.(*v1.Pod)
newPod := newObj.(*v1.Pod)
if core.QuotaV1Pod(oldPod) && !core.QuotaV1Pod(newPod) {
options.ReplenishmentFunc(options.GroupKind, newPod.Namespace, oldPod)
}
}
}
// ObjectReplenenishmentDeleteFunc will replenish on every delete
func ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc(options *ReplenishmentControllerOptions) func(obj interface{}) {
return func(obj interface{}) {
metaObject, err := meta.Accessor(obj)
if err != nil {
tombstone, ok := obj.(cache.DeletedFinalStateUnknown)
if !ok {
glog.Errorf("replenishment controller could not get object from tombstone %+v, could take up to %v before quota is replenished", obj, options.ResyncPeriod())
utilruntime.HandleError(err)
return
}
metaObject, err = meta.Accessor(tombstone.Obj)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("replenishment controller tombstone contained object that is not a meta %+v, could take up to %v before quota is replenished", tombstone.Obj, options.ResyncPeriod())
utilruntime.HandleError(err)
return
}
}
options.ReplenishmentFunc(options.GroupKind, metaObject.GetNamespace(), nil)
}
}在NewResourceQuotaController中创建replenishmentController时,已经指定了对应的ReplenishmentFunc为rq.replenishQuota,PodReplenishmentUpdateFunc和ObjectReplenishmentDeleteFunc最终都是调用ReplenishmentFunc(rq.replenishQuota)来进行quota recalculated。
pkg/controller/resourcequota/resource_quota_controller.go:330
// replenishQuota is a replenishment function invoked by a controller to notify that a quota should be recalculated
func (rq *ResourceQuotaController) replenishQuota(groupKind schema.GroupKind, namespace string, object runtime.Object) {
...
for i := range resourceQuotas {
resourceQuota := resourceQuotas[i].(*v1.ResourceQuota)
internalResourceQuota := &api.ResourceQuota{}
if err := v1.Convert_v1_ResourceQuota_To_api_ResourceQuota(resourceQuota, internalResourceQuota, nil); err != nil {
glog.Error(err)
continue
}
resourceQuotaResources := quota.ResourceNames(internalResourceQuota.Status.Hard)
if intersection := evaluator.MatchingResources(resourceQuotaResources); len(intersection) > 0 {
// 将该resourceQuota加入到队列queue
rq.enqueueResourceQuota(resourceQuota)
}
}
}因此replenishmentController就是用来捕获对应资源的Update/Delete事件,将其对应的ResourceQuota加入到queue中,然后worker再对其进行重新计算Usage。
--concurrent-resource-quota-syncs配置。--concurrent-resource-quota-syncs配置。--resource-quota-sync-periodKubernetes ResourceQuotaController内部实现原理及源码分析
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/waltonwang/article/details/54670584