上一节我们看了系统参数的主界面,大家应该还有印象,如下

那本节我们来看一下修改和删除。
上节我已经介绍了系统参数修改以及删除的WebService,如下
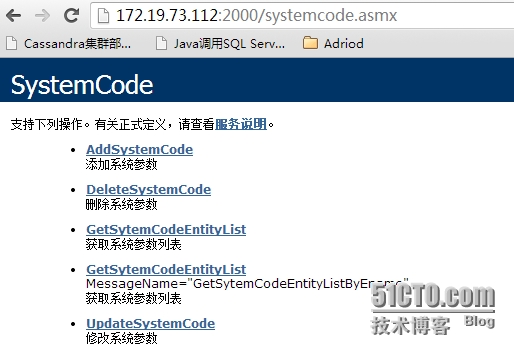
其中系统参数修改的描述如下

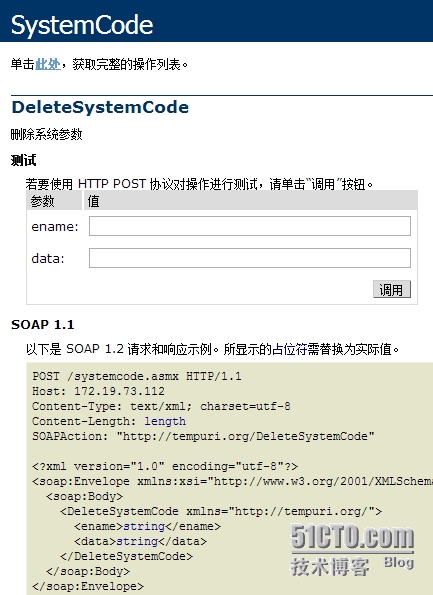
系统参数删除的定义如下
接下来我们需要知道的是如何实现修改和删除按钮的功能。记得上节我们使用系统提供的SimpleAdapter去展示listview的数据。这样是无法实现按钮的响应的。所以在实现这两个按钮的功能之前,首先需要让他们能够响应点击事件。所以需要我们自己定义Adapter。
public class customAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private List<Map<String, Object>> dataList;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
private Context context;
private String[] keyString;
private int[] valueViewID;
Holder holder;
public customAdapter(Context context,
List<Map<String, Object>> dataList, int resource,
String[] from, int[] to) {
this.dataList = dataList;
this.context = context;
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) this.context
.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
keyString = new String[from.length];
valueViewID = new int[to.length];
System.arraycopy(from, 0, keyString, 0, from.length);
System.arraycopy(to, 0, valueViewID, 0, to.length);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return dataList.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return dataList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
public void removeItem(int position) {
dataList.remove(position);
this.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
if (convertView != null) {
holder = (Holder) convertView.getTag();
} else {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(
R.layout.systemcodedetailtemplate, null);
holder = new Holder();
holder.labCname = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[0]);
holder.labData = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[1]);
holder.labDisplay = (TextView) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[2]);
holder.btnUpdate = (Button) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[3]);
holder.btnDelete = (Button) convertView
.findViewById(valueViewID[4]);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
Map<String, Object> appInfo = dataList.get(position);
if (appInfo != null) {
String cname = appInfo.get(keyString[0]).toString();
String data = appInfo.get(keyString[1]).toString();
String displayContent = appInfo.get(keyString[2]).toString();
holder.labCname.setText(cname);
holder.labData.setText(data);
holder.labDisplay.setText(displayContent);
holder.btnDelete.setOnClickListener(new ViewButtonListener(
position));
holder.btnUpdate.setOnClickListener(new ViewButtonListener(
position));
}
return convertView;
}在构造函数中我们传入了数据源,得到加载xml布局文件的实例化对象mInflater,以及传递进来的数据源Map<String, Object>中的key值,页面中的元素的id,用来和key值取到的value作对应匹配。
然后再覆盖BaseAdapter的一些方法。在这里主要看这个getView。
首先判断是否已经加载了根布局模版,如果已加载,则获取Holder,否则实例化holder,并将模版内的元素赋给Holder。这个Holder怎么理解呢,我觉得是xml布局模版上元素的载体。通过Holder可以拿到该模版上的任何元素。接下来这个appInfo就是当前界面上listview所选择的行的数据Map<String, Object>,所以在这里我们可以通过key值拿到value。难道以后将值赋给Holder载体中的各个对应元素
String cname = appInfo.get(keyString[0]).toString(); String data = appInfo.get(keyString[1]).toString(); String displayContent = appInfo.get(keyString[2]).toString(); holder.labCname.setText(cname); holder.labData.setText(data); holder.labDisplay.setText(displayContent);
OK,这个其实就是重写实现listView的展示。接下来我们来看这次的重点
holder.btnDelete.setOnClickListener(new ViewButtonListener( position)); holder.btnUpdate.setOnClickListener(new ViewButtonListener( position));
这两个按钮是我们第一幅图中的最右边的两个操作按钮。我们分别为其注册了单击事件监听,它的监听实现类是ViewButtonListener,我们看一下
class ViewButtonListener implements OnClickListener {
private int position;
Object cname;
Object data;
Object displayContent;
EditText txtEname;
EditText txtCname;
EditText txtData;
EditText txtDisplayContent;
EditText txtRemark;
View layout;
ViewButtonListener(int position) {
this.position = position;
cname = dataList.get(position).get("cname");
data = dataList.get(position).get("data");
displayContent = dataList.get(position).get("displaycontent");
LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater();
layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.systemcodemodify,
(ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.modifyDialog));
txtEname = (EditText) layout.findViewById(R.id.txtEname);
txtCname = (EditText) layout.findViewById(R.id.txtCname);
txtData = (EditText) layout.findViewById(R.id.txtData);
txtDisplayContent = (EditText) layout
.findViewById(R.id.txtDisplay);
txtRemark = (EditText) layout.findViewById(R.id.txtRemark);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
int vid = view.getId();
if (vid == holder.btnUpdate.getId()) {
txtEname.setText(owner.ename);
txtCname.setText(cname.toString());
txtData.setText(data.toString());
txtDisplayContent.setText(displayContent.toString());
txtEname.setEnabled(false);
txtCname.setEnabled(false);
txtData.setEnabled(false);
final AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(
owner);
builder.setIcon(R.drawable.info);
builder.setTitle(R.string.titleSystemCodeModifyName);
builder.setView(layout);
builder.setPositiveButton(R.string.btnSave, null);
builder.setNegativeButton(R.string.btnClose,null);
final AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
dialog.show();
dialog.getButton(AlertDialog.BUTTON_POSITIVE)
.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (txtDisplayContent.getText().toString()
.trim().length() == 0) {
ShowMessage("显示值不能为空!");
return;
}
SoapObject soapObject = new systemcodedetail()
.ModifySystemCode(ename, data
.toString(), txtDisplayContent.getText().toString().trim()
.toString(), txtRemark
.getText().toString());
Boolean isSuccess = Boolean
.valueOf(soapObject.getProperty(
"IsSuccess").toString());
if (isSuccess) {
ShowMessage(R.string.SaveSuccess);
dialog.dismiss();
} else {
String errorMsg = soapObject
.getProperty("ErrorMessage")
.toString();
ShowMessage(errorMsg);
}
}
});
} else if (vid == holder.btnDelete.getId()) {
SoapObject soapObject = new systemcodedetail()
.DeleteSystemCode(ename, data.toString());
Boolean isSuccess = Boolean.valueOf(soapObject.getProperty(
"IsSuccess").toString());
if (isSuccess) {
ShowMessage(R.string.DeleteSuccess);
} else {
String errorMsg = soapObject
.getProperty("ErrorMessage").toString();
ShowMessage(errorMsg);
}
}
}
}
class Holder {
public TextView labCname;
public TextView labDisplay;
public TextView labData;
public Button btnUpdate;
public Button btnDelete;
}
}OK,我们看到了,在构造函数中,我们拿到了各个元素,因为我们的保存和删除按钮的监听那个实现类都是ViewButtonListener。因此在Onclick事件中,我们需要得知是哪个按钮触发了事件。所以先获取一下id,如果id是btnUpdate。那么就走修改逻辑,否则走删除逻辑。
首先来看一下修改逻辑,创建一个dialog,这个dialog加载的是一个activity,弹出的界面是什么呢,在构造函数中有这样一段
layout = inflater.inflate(R.layout.systemcodemodify, (ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.modifyDialog));
在创建dialog的时候我们也看到了这句
builder.setView(layout);
所以弹出的界面就是R.layout.systemcodemodfy。我们来看一下这个界面
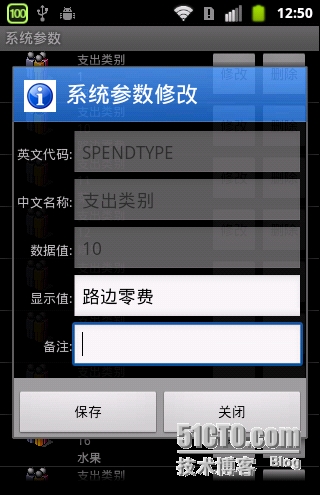
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:id="@+id/modifyDialog" android:orientation="vertical"> <TableLayout android:id="@+id/tabMain" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:padding="3dip" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/labEname" android:textSize="6pt" android:gravity="right" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtEname" android:maxLength="25" android:singleLine="true"></EditText> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/labCname" android:textSize="6pt" android:gravity="right" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtCname" android:maxLength="50" android:singleLine="true"></EditText> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/labData" android:textSize="6pt" android:gravity="right" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtData" android:singleLine="true"></EditText> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/labDisplay" android:textSize="6pt" android:gravity="right" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtDisplay" android:singleLine="true"></EditText> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/labRemark" android:textSize="6pt" android:gravity="right" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/txtRemark" android:maxLines="4"></EditText> </TableRow> </TableLayout> <!-- <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal"--> <!-- android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent"--> <!-- android:layout_height="wrap_content">--> <!-- <Button android:id="@+id/btnSave" android:layout_width="110dp"--> <!-- android:layout_height="45dp" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"--> <!-- android:text="@string/btnSave" android:textStyle="bold"--> <!-- android:textColor="@color/blue"></Button>--> <!-- <Button android:id="@+id/btnClose" android:layout_width="110dp"--> <!-- android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:layout_height="45dp"--> <!-- android:text="@string/btnClose" android:textStyle="bold"--> <!-- android:textColor="@color/blue"></Button>--> <!-- </LinearLayout>--> </LinearLayout>
OK,就是这个界面,table布局。
再往下看,就是这个setIcon(设置弹出页图标),setTitle(弹出页标题),setPostiveButton和setNegativeButton。大家都知道弹出页在点击按钮的时候总是会自动关闭掉,为了解决这一问题,我们的按钮点击事件进行了重写
dialog.getButton(AlertDialog.BUTTON_POSITIVE)
.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {}}在点击事件中,如果说验证没通过,界面不会关闭,否则关闭。我们来看一下效果,界面并没有关闭。
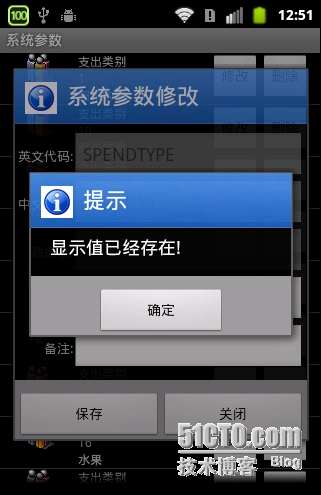
如果保存成功,则关闭界面
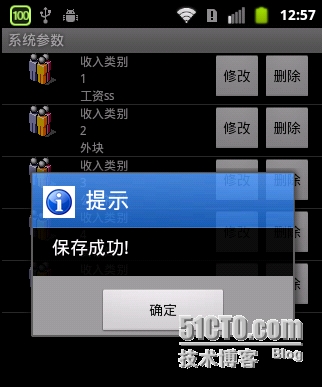
OK,我们接下来看看修改的调用
private SoapObject ModifySystemCode(String ename, String data,
String display, String remark) {
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME_PUT);
SystemCodeEntity codeEntity = new SystemCodeEntity();
codeEntity.setProperty(0, ename);
codeEntity.setProperty(2, data);
codeEntity.setProperty(3, display);
codeEntity.setProperty(4, remark);
PropertyInfo pi = new PropertyInfo();
pi.setName("systemCodeEntity");
pi.setValue(codeEntity);
pi.setType(codeEntity.getClass());
request.addProperty(pi);
SoapSerializationEnvelope soapEnvelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(
SoapEnvelope.VER11);
soapEnvelope.dotNet = true;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
HttpTransportSE httpTS = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
soapEnvelope.bodyOut = httpTS;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);// 设置请求参数
soapEnvelope.addMapping(NAMESPACE, "SystemCodeEntity", codeEntity
.getClass());
try {
httpTS.call(SOAP_ACTION_PUT, soapEnvelope);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SoapObject result = null;
try {
result = (SoapObject) soapEnvelope.getResponse();
} catch (SoapFault e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}在这里就不多讲了。再看一下删除的代码
private SoapObject DeleteSystemCode(String ename, String data) {
SoapObject request = new SoapObject(NAMESPACE, METHOD_NAME_DELETE);
PropertyInfo pi = new PropertyInfo();
pi.setName("ename");
pi.setType(String.class);
pi.setValue(ename);
request.addProperty(pi);
pi = new PropertyInfo();
pi.setName("data");
pi.setType(String.class);
pi.setValue(data);
SoapSerializationEnvelope soapEnvelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(
SoapEnvelope.VER11);
soapEnvelope.dotNet = true;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);
HttpTransportSE httpTS = new HttpTransportSE(URL);
soapEnvelope.bodyOut = httpTS;
soapEnvelope.setOutputSoapObject(request);// 设置请求参数
try {
httpTS.call(SOAP_ACTION_DELETE, soapEnvelope);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (XmlPullParserException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
SoapObject result = null;
try {
result = (SoapObject) soapEnvelope.getResponse();
} catch (SoapFault e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}OK,本篇到此为止。
本文出自 “技术创造价值” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://leelei.blog.51cto.com/856755/1416819
原文:http://leelei.blog.51cto.com/856755/1416819