
..WO.... ..WO.... BBOYGGWR BBOYGGWR ..YR.... ..YR.... ..GY.... ..BY.... ROYWRRBB GWOWRBOW ..YG.... ..OG.... ........ ........ ........ ........ ........ ........
X YZXXXZYZXYXYZZYZZYZXYY
题目虽长,可是题意非常easy。就是一个拼魔方的游戏,要求输出步骤
事实上代码的思路也不难,仅仅是写起来非常麻烦蛋疼
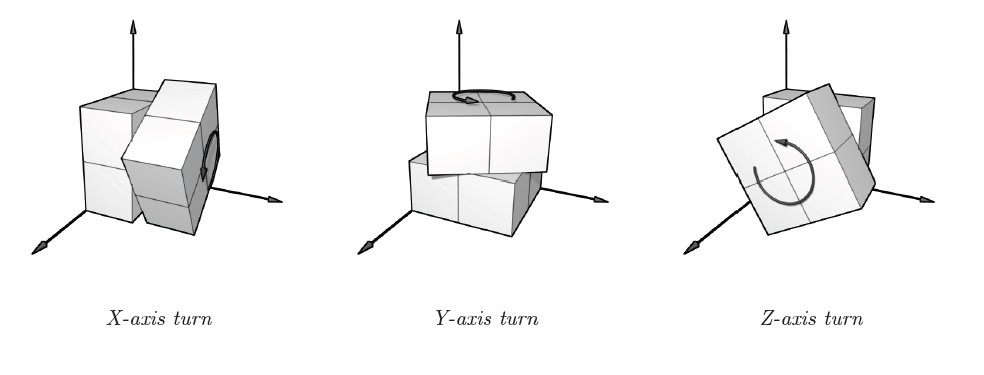
从图中不难看出。不管魔方怎么旋转,与原点相接的那个小方块是不动的,那么我们能够由原点的小方块得出三个面的终于颜色,然后再通过这三个面去确定其它三个面的颜色
然后就是IDA的剪枝估測函数的h值,因为每次旋转可以改变8个小面,那么仅仅要求出如今不在其位的面总数SUM,得出(sum+7)/8就可以,加7是保证sum+7>=8得出步数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int x,y;
} cube[10][10],side[10][10];
char color[10],rubik[10][10];
int ans[1000];
int flag,step;
void init()//cube代表每一个小立方体的3个面相应字符数字的哪个位置,side则是6个面,每一个面的四个元素各自是什么
{
cube[0][0].x=3,cube[0][0].y=2;
cube[0][1].x=3,cube[0][1].y=1;
cube[0][2].x=4,cube[0][2].y=2;
cube[1][0].x=3,cube[1][0].y=3;
cube[1][1].x=3,cube[1][1].y=4;
cube[1][2].x=4,cube[1][2].y=3;
cube[2][0].x=2,cube[2][0].y=2;
cube[2][1].x=2,cube[2][1].y=1;
cube[2][2].x=1,cube[2][2].y=2;
cube[3][0].x=2,cube[3][0].y=3;
cube[3][1].x=1,cube[3][1].y=3;
cube[3][2].x=2,cube[3][2].y=4;
cube[4][0].x=3,cube[4][0].y=0;
cube[4][1].x=5,cube[4][1].y=2;
cube[4][2].x=3,cube[4][2].y=7;
cube[5][0].x=5,cube[5][0].y=3;
cube[5][1].x=3,cube[5][1].y=5;
cube[5][2].x=3,cube[5][2].y=6;
cube[6][0].x=0,cube[6][0].y=2;
cube[6][1].x=2,cube[6][1].y=7;
cube[6][2].x=2,cube[6][2].y=0;
cube[7][0].x=0,cube[7][0].y=3;
cube[7][1].x=2,cube[7][1].y=5;
cube[7][2].x=2,cube[7][2].y=6;
side[0][0].x=0,side[0][0].y=2;
side[0][1].x=0,side[0][1].y=3;
side[0][2].x=1,side[0][2].y=2;
side[0][3].x=1,side[0][3].y=3;
side[1][0].x=2,side[1][0].y=0;
side[1][1].x=2,side[1][1].y=1;
side[1][2].x=3,side[1][2].y=0;
side[1][3].x=3,side[1][3].y=1;
side[2][0].x=2,side[2][0].y=2;
side[2][1].x=2,side[2][1].y=3;
side[2][2].x=3,side[2][2].y=2;
side[2][3].x=3,side[2][3].y=3;
side[3][0].x=2,side[3][0].y=4;
side[3][1].x=2,side[3][1].y=5;
side[3][2].x=3,side[3][2].y=4;
side[3][3].x=3,side[3][3].y=5;
side[4][0].x=2,side[4][0].y=6;
side[4][1].x=2,side[4][1].y=7;
side[4][2].x=3,side[4][2].y=6;
side[4][3].x=3,side[4][3].y=7;
side[5][0].x=4,side[5][0].y=2;
side[5][1].x=4,side[5][1].y=3;
side[5][2].x=5,side[5][2].y=2;
side[5][3].x=5,side[5][3].y=3;
}
char get_color(int A,int B,int C) //通过小格子的颜色获得每一个面的颜色
{
for(int i=0; i<8; i++)
{
if(rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y];
if(rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y];
if(rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y];
if(rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y];
if(rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y];
if(rubik[cube[i][2].x][cube[i][2].y]==color[A]&&rubik[cube[i][1].x][cube[i][1].y]==color[B]&&rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y]!=color[C])
return rubik[cube[i][0].x][cube[i][0].y];
}
}
void turn_x(char maze[10][10]) //x轴
{
char tmp;
tmp=maze[2][4];
maze[2][4]=maze[2][5];
maze[2][5]=maze[3][5];
maze[3][5]=maze[3][4];
maze[3][4]=tmp;
tmp=maze[1][3];
maze[1][3]=maze[2][6];
maze[2][6]=maze[5][3];
maze[5][3]=maze[3][3];
maze[3][3]=tmp;
tmp=maze[0][3];
maze[0][3]=maze[3][6];
maze[3][6]=maze[4][3];
maze[4][3]=maze[2][3];
maze[2][3]=tmp;
}
void turn_y(char maze[10][10]) //y轴
{
char tmp;
tmp=maze[2][0];
maze[2][0]=maze[2][6];
maze[2][6]=maze[2][4];
maze[2][4]=maze[2][2];
maze[2][2]=tmp;
tmp=maze[2][1];
maze[2][1]=maze[2][7];
maze[2][7]=maze[2][5];
maze[2][5]=maze[2][3];
maze[2][3]=tmp;
tmp=maze[0][2];
maze[0][2]=maze[0][3];
maze[0][3]=maze[1][3];
maze[1][3]=maze[1][2];
maze[1][2]=tmp;
}
void turn_z(char maze[10][10]) //z轴
{
char tmp;
tmp=maze[2][1];
maze[2][1]=maze[1][3];
maze[1][3]=maze[3][4];
maze[3][4]=maze[4][2];
maze[4][2]=tmp;
tmp=maze[3][1];
maze[3][1]=maze[1][2];
maze[1][2]=maze[2][4];
maze[2][4]=maze[4][3];
maze[4][3]=tmp;
tmp=maze[2][2];
maze[2][2]=maze[2][3];
maze[2][3]=maze[3][3];
maze[3][3]=maze[3][2];
maze[3][2]=tmp;
}
int get_h(char mid[10][10])
{
int i,j,sum = 0;
for(i = 0; i<6; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j<4; j++)
{
if(mid[side[i][j].x][side[i][j].y]!=color[i])
sum++;
}
}
return (sum+7)/8;
}
int IDA(char mid[10][10],int cnt)
{
if(cnt+get_h(mid)>step)
return 0;
if(cnt == step)
return 1;
for(int i = 0; i<3; i++)
{
char tem[10][10];
for(int x = 0; x<6; x++)
for(int y = 0; y<8; y++)
tem[x][y]=mid[x][y];
if(i == 0)
turn_x(tem);
else if(i == 1)
turn_y(tem);
else
turn_z(tem);
ans[cnt] = i;
if(IDA(tem,cnt+1))
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int i;
init();
while(~scanf("%s",rubik[0]))
{
for(i = 1; i<6; i++)
scanf("%s",rubik[i]);
if(!strcmp(rubik[0],"........"))
break;
color[1]=rubik[3][0];
color[5]=rubik[5][2];
color[4]=rubik[3][7];
color[0]=get_color(1,4,5);
color[2]=get_color(1,5,4);
color[3]=get_color(4,5,1);
step = 0;
while(1)
{
if(IDA(rubik,0)) break;
step++;
}
for(i = 0; i<step; i++)
printf("%c",ans[i]+‘X‘);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
HDU3459:Rubik 2×2×2(IDA)
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/brucemengbm/p/7207515.html