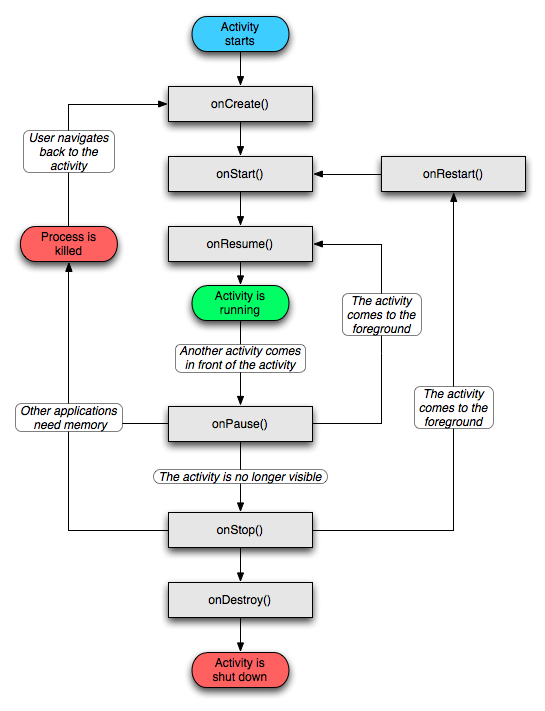
首先看一下Android api中所提供的Activity生命周期图(不明白的,可以看完整篇文章,在回头看一下这个图,你会明白的):
Activity其实是继承了ApplicationContext这个类,我们可以重写以下方法,如下代码:
1 |
public class Activity extends ApplicationContext { |
2 |
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState); |
3 |
protected void onStart(); |
4 |
protected void onRestart(); |
5 |
protected void onResume(); |
6 |
protected void onPause(); |
7 |
protected void onStop(); |
8 |
protected void onDestroy(); |
为了便于大家更好的理解,我简单的写了一个Demo,不明白Activity周期的朋友们,可以亲手实践一下,大家按照我的步骤来。
第一步:新建一个Android工程,我这里命名为ActivityDemo.
第二步:修改ActivityDemo.java(我这里重新写了以上的七种方法,主要用Log打印),代码如下:
01 |
package com.tutor.activitydemo; |
02 |
import android.app.Activity; |
03 |
import android.os.Bundle; |
04 |
import android.util.Log; |
05 |
public class ActivityDemo extends Activity { |
07 |
private static final String TAG = "ActivityDemo"; |
09 |
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { |
10 |
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); |
11 |
setContentView(R.layout.main); |
13 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~"); |
17 |
protected void onStart() { |
19 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~"); |
23 |
protected void onRestart() { |
25 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onRestart~~~"); |
29 |
protected void onResume() { |
31 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onResume~~~"); |
35 |
protected void onPause() { |
37 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onPause~~~"); |
41 |
protected void onStop() { |
43 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onStop~~~"); |
47 |
protected void onDestroy() { |
49 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~"); |
第三步:运行上述工程,效果图如下(没什么特别的):
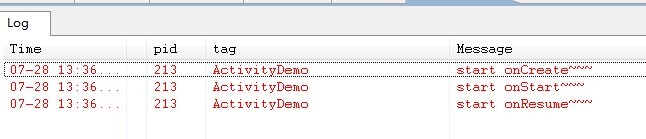
核心在Logcat视窗里,如果你还不会用Logcat你可以看一下我的这篇文章 Log图文详解(Log.v,Log.d,Log.i,Log.w,Log.e) ,我们打开应用时先后执行了onCreate()->onStart()->onResume三个方法,看一下LogCat视窗如下:
BACK键:
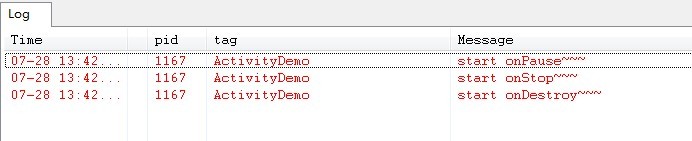
当我们按BACK键时,我们这个应用程序将结束,这时候我们将先后调用onPause()->onStop()->onDestory()三个方法,如下图所示:
HOME键:
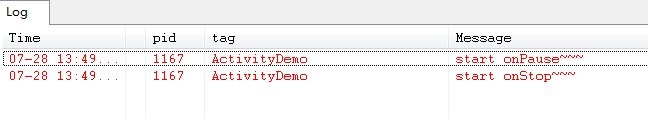
当我们打开应用程序时,比如浏览器,我正在浏览NBA新闻,看到一半时,我突然想听歌,这时候我们会选择按HOME键,然后去打开音乐应用程序,而 当我们按HOME的时候,Activity先后执行了onPause()->onStop()这两个方法,这时候应用程序并没有销毁。如下图所示:
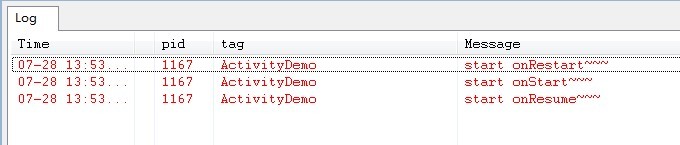
而当我们再次启动ActivityDemo应用程序时,则先后分别执行了onRestart()->onStart()->onResume()三个方法,如下图所示:
这里我们会引出一个问题,当我们按HOME键,然后再进入ActivityDemo应用时,我们的应用的状态应该是和按HOME键之前的状态是一样的,同样为了方便理解,在这里我将ActivityDemo的代码作一些修改,就是增加一个EditText。
第四步:修改main.xml布局文件(增加了一个EditText),代码如下:
01 |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> |
02 |
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" |
03 |
android:orientation="vertical" |
04 |
android:layout_width="fill_parent" |
05 |
android:layout_height="fill_parent" |
08 |
android:layout_width="fill_parent" |
09 |
android:layout_height="wrap_content" |
10 |
android:text="@string/hello" |
13 |
android:id="@+id/editText" |
14 |
android:layout_width="fill_parent" |
15 |
android:layout_height="wrap_content" |
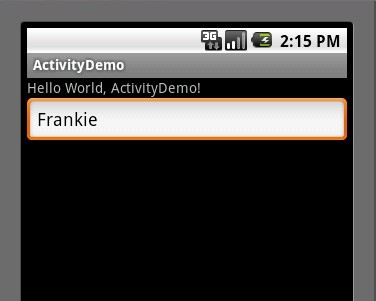
第五步:然后其他不变,运行ActivityDemo程序,在EditText里输入如"Frankie"字符串(如下图:)
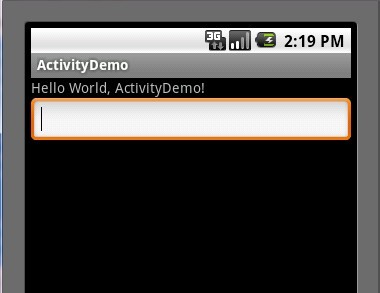
这时候,大家可以按一下HOME键,然后再次启动ActivityDemo应用程序,这时候EditText里并没有我们输入的"Frankie"字样,如下图:
这显然不能称得一个合格的应用程序,所以我们需要在Activity几个方法里自己实现,如下第六步所示:
第六步修改ActivityDemo.java代码如下:
01 |
package com.tutor.activitydemo; |
02 |
import android.app.Activity; |
03 |
import android.os.Bundle; |
04 |
import android.util.Log; |
05 |
import android.widget.EditText; |
06 |
public class ActivityDemo extends Activity { |
08 |
private static final String TAG = "ActivityDemo"; |
09 |
private EditText mEditText; |
11 |
private String mString; |
12 |
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { |
13 |
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); |
14 |
setContentView(R.layout.main); |
15 |
mEditText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText); |
16 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onCreate~~~"); |
20 |
protected void onStart() { |
22 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onStart~~~"); |
26 |
protected void onRestart() { |
28 |
mEditText.setText(mString); |
29 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onRestart~~~"); |
33 |
protected void onResume() { |
35 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onResume~~~"); |
40 |
protected void onPause() { |
42 |
mString = mEditText.getText().toString(); |
43 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onPause~~~"); |
47 |
protected void onStop() { |
49 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onStop~~~"); |
53 |
protected void onDestroy() { |
55 |
Log.e(TAG, "start onDestroy~~~"); |
第七步:重新运行ActivityDemo程序,重复第五步操作,当我们按HOME键时,再次启动应用程序时,EditText里有上次输入的"Frankie"字样,如下图如示:
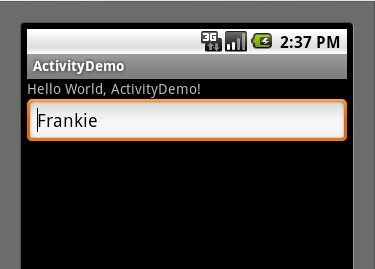
OK,大功基本告成,这时候大家可以在回上面看一下Activity生命周期图,我想大家应该完全了解了Activity的生命周期了,不知道你了解了没?
原文转自:http://blog.csdn.net/android_tutor/article/details/5772285
两分钟彻底让你明白Android Activity生命周期(图文)!,布布扣,bubuko.com
两分钟彻底让你明白Android Activity生命周期(图文)!
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/kevincode/p/3818282.html