编程语言提供了各种控制结构,同意更复杂的运行路径。
循环语句同意我们运行一个语句或语句组多次。以下是在大多数编程语言中的循环语句的一般形式:
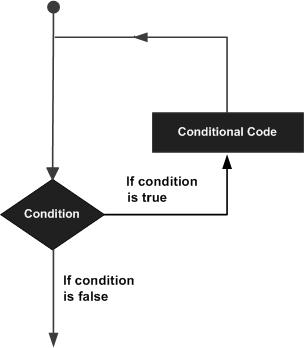
Python提供了for循环和while循环(在Python中没有do..while循环):
| 循环类型 | 描写叙述 |
|---|---|
| while 循环 | 在给定的推断条件为 true 时运行循环体,否则退出循环体。 |
| for 循环 | 反复运行语句 |
| 嵌套循环 | 你能够在while循环体中嵌套for循环 |
循环控制语句
循环控制语句能够更改语句运行的顺序。Python支持下面循环控制语句:
| 控制语句 | 描写叙述 |
|---|---|
| break 语句 | 在语句块运行过程中终止循环。而且跳出整个循环 |
| continue 语句 | 在语句块运行过程中终止当前循环,跳出该次循环。运行下一次循环。 |
| pass 语句 | pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。 |
二、Python While循环语句
Python 编程中 while 语句用于循环运行程序,即在某条件下,循环运行某段程序。以处理须要反复处理的同样任务。其基本形式为:
while 推断条件: 运行语句……
运行语句能够是单个语句或语句块。
推断条件能够是不论什么表达式。不论什么非零、或非空(null)的值均为true。
当推断条件假false时,循环结束。
运行流程图例如以下:
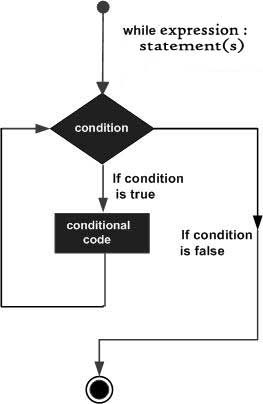
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while (count < 9): print ‘The count is:‘, count count = count + 1 print "Good bye!"
以上代码运行输出结果:
The count is: 0 The count is: 1 The count is: 2 The count is: 3 The count is: 4 The count is: 5 The count is: 6 The count is: 7 The count is: 8 Good bye!
while 语句时还有另外两个重要的命令 continue,break 来跳过循环。continue 用于跳过该次循环,break 则是用于退出循环,此外"推断条件"还能够是个常值,表示循环必然成立,详细使用方法例如以下:
# continue 和 break 使用方法 i = 1 while i < 10: i += 1 if i%2 > 0: # 非双数时跳过输出 continue print i # 输出双数2、4、6、8、10 i = 1 while 1: # 循环条件为1必然成立 print i # 输出1~10 i += 1 if i > 10: # 当i大于10时跳出循环 break
无限循环
假设条件推断语句永远为 true,循环将会无限的运行下去,例如以下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- var = 1 while var == 1 : # 该条件永远为true,循环将无限运行下去 num = raw_input("Enter a number :") print "You entered: ", num print "Good bye!"
以上实例输出结果:
Enter a number :20 You entered: 20 Enter a number :29 You entered: 29 Enter a number :3 You entered: 3 Enter a number between :Traceback (most recent call last): File "test.py", line 5, in <module> num = raw_input("Enter a number :") KeyboardInterrupt
注意:以上的无限循环你能够使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中,for … else 表示这种意思。for 中的语句和普通的没有差别。else 中的语句会在循环正常运行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下运行。while … else 也是一样。
#!/usr/bin/python count = 0 while count < 5: print count, " is less than 5" count = count + 1 else: print count, " is not less than 5"
以上实例输出结果为:
0 is less than 5 1 is less than 5 2 is less than 5 3 is less than 5 4 is less than 5 5 is not less than 5
简单语句组
类似if语句的语法。假设你的while循环体中仅仅有一条语句,你能够将该语句与while写在同一行中。 例如以下所看到的:
#!/usr/bin/python flag = 1 while (flag): print ‘Given flag is really true!‘ print "Good bye!"
注意:以上的无限循环你能够使用 CTRL+C 来中断循环。
三、Python for 循环语句
Python for循环能够遍历不论什么序列的项目。如一个列表或者一个字符串。
语法:
for循环的语法格式例如以下:
for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s)
流程图:
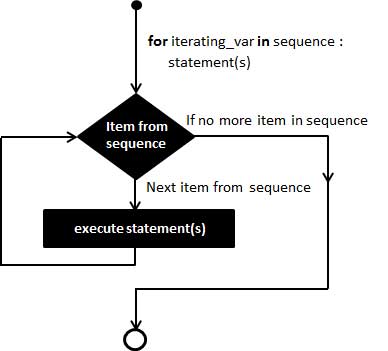
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in ‘Python‘: # 第一个实例 print ‘当前字母 :‘, letter fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘] for fruit in fruits: # 第二个实例 print ‘当前字母 :‘, fruit print "Good bye!"
以上实例输出结果:
当前字母 : P 当前字母 : y 当前字母 : t 当前字母 : h 当前字母 : o 当前字母 : n 当前字母 : banana 当前字母 : apple 当前字母 : mango Good bye!
通过序列索引迭代
第二种运行循环的遍历方式是通过索引,例如以下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- fruits = [‘banana‘, ‘apple‘, ‘mango‘] for index in range(len(fruits)): print ‘当前水果 :‘, fruits[index] print "Good bye!"
以上实例输出结果:
当前水果 : banana 当前水果 : apple 当前水果 : mango Good bye!
以上实例我们使用了内置函数 len() 和 range(),函数 len() 返回列表的长度,即元素的个数。 range返回一个序列的数。
循环使用 else 语句
在 python 中。for … else 表示这种意思,for 中的语句和普通的没有差别。else 中的语句会在循环正常运行完(即 for 不是通过 break 跳出而中断的)的情况下运行,while … else 也是一样。
例如以下实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for num in range(10,20): # 迭代 10 到 20 之间的数字 for i in range(2,num): # 依据因子迭代 if num%i == 0: # 确定第一个因子 j=num/i # 计算第二个因子 print ‘%d 等于 %d * %d‘ % (num,i,j) break # 跳出当前循环 else: # 循环的 else 部分 print num, ‘是一个质数‘
以上实例输出结果:
10 等于 2 * 5 11 是一个质数 12 等于 2 * 6 13 是一个质数 14 等于 2 * 7 15 等于 3 * 5 16 等于 2 * 8 17 是一个质数 18 等于 2 * 9 19 是一个质数
四、Python 循环嵌套
Python 语言同意在一个循环体里面嵌入还有一个循环。
Python for 循环嵌套语法:
for iterating_var in sequence: for iterating_var in sequence: statements(s) statements(s)
Python while 循环嵌套语法:
while expression: while expression: statement(s) statement(s)
你能够在循环体内嵌入其它的循环体,如在while循环中能够嵌入for循环。 反之,你能够在for循环中嵌入while循环。
实例:
下面实例使用了嵌套循环输出2~100之间的素数:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- i = 2 while(i < 100): j = 2 while(j <= (i/j)): if not(i%j): break j = j + 1 if (j > i/j) : print i, " 是素数" i = i + 1 print "Good bye!"
以上实例输出结果:
2 是素数 3 是素数 5 是素数 7 是素数 11 是素数 13 是素数 17 是素数 19 是素数 23 是素数 29 是素数 31 是素数 37 是素数 41 是素数 43 是素数 47 是素数 53 是素数 59 是素数 61 是素数 67 是素数 71 是素数 73 是素数 79 是素数 83 是素数 89 是素数 97 是素数 Good bye!
五、Python break 语句
Python break语句,就像在C语言中。打破了最小封闭for或while循环。
break语句用来终止循环语句,即循环条件没有False条件或者序列还没被全然递归完,也会停止运行循环语句。
break语句用在while和for循环中。
假设您使用嵌套循环,break语句将停止运行最深层的循环,并開始运行下一行代码。
Python语言 break 语句语法:
break
流程图:
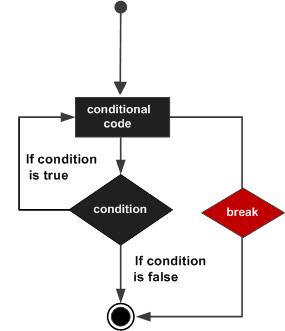
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python for letter in ‘Python‘: # First Example if letter == ‘h‘: break print ‘Current Letter :‘, letter var = 10 # Second Example while var > 0: print ‘Current variable value :‘, var var = var -1 if var == 5: break print "Good bye!"
以上实例运行结果:
Current Letter : P Current Letter : y Current Letter : t Current variable value : 10 Current variable value : 9 Current variable value : 8 Current variable value : 7 Current variable value : 6 Good bye!
六、Python continue 语句
Python continue 语句跳出本次循环,而break跳出整个循环。
continue 语句用来告诉Python跳过当前循环的剩余语句,然后继续进行下一轮循环。
continue语句用在while和for循环中。
Python 语言 continue 语句语法格式例如以下:
continue
流程图:
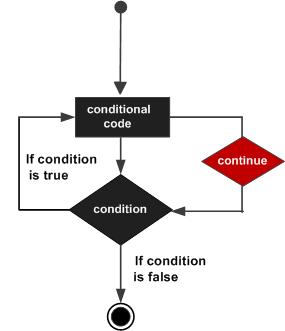
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- for letter in ‘Python‘: # 第一个实例 if letter == ‘h‘: continue print ‘当前字母 :‘, letter var = 10 # 第二个实例 while var > 0: var = var -1 if var == 5: continue print ‘当前变量值 :‘, var print "Good bye!"
以上实例运行结果:
当前字母 : P 当前字母 : y 当前字母 : t 当前字母 : o 当前字母 : n 当前变量值 : 9 当前变量值 : 8 当前变量值 : 7 当前变量值 : 6 当前变量值 : 4 当前变量值 : 3 当前变量值 : 2 当前变量值 : 1 当前变量值 : 0 Good bye!
七、Python pass 语句
Python pass是空语句,是为了保持程序结构的完整性。
pass 不做不论什么事情。一般用做占位语句。
Python 语言 pass 语句语法格式例如以下:
pass
实例:
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 输出 Python 的每一个字母 for letter in ‘Python‘: if letter == ‘h‘: pass print ‘这是 pass 块‘ print ‘当前字母 :‘, letter print "Good bye!"
以上实例运行结果:
当前字母 : P 当前字母 : y 当前字母 : t 这是 pass 块 当前字母 : h 当前字母 : o 当前字母 : n Good bye!
