 http://os.51cto.com/art/201209/355490.htm
http://os.51cto.com/art/201209/355490.htm http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jGGdExK
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1jGGdExK10.11 Linux网络相关
介绍

ifconfig查看网卡ip(yum install net-tools)
[root@centos7 ~]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.189.128 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.189.255
inet6 fe80::243c:86d7:d85e:224d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:15:53:53 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 44 bytes 6786 (6.6 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 78 bytes 9431 (9.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 64 bytes 5344 (5.2 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 64 bytes 5344 (5.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ifup ens33/ifdown ens33 开启、关闭端口
注意,这里如果是远程登录(xhsell,putty)的话,在远程登录处down了ens33端口的话,会使远程登录中断,
需要在本机(虚拟机,linux本机)再up起来。
单独针对一个网卡去做更改需要用到ifup/ifdown命令。
指定更改端口设置后可以使用此命令。
添加&&并且条件命令,可以让端口断掉马上再次开启起来,此时不会断掉远程终端。
[root@centos7 ~]# ifdown ens33 && ifup ens33
成功断开设备 'ens33'。
连接已成功激活(D-Bus 活动路径:/org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/2)
设定虚拟网卡ens33:1
[root@centos7 ~]# cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
[root@centos7 network-scripts]# cp ifcfg-ens33 ifcfg-ens33\:0
复制ens33网卡配置文件,改名ifcfg-ens33\:0 (\是脱义)
更改33:0文件,把name,device,和dns更改,添加对应参数:0,其他不变。
[root@centos7 network-scripts]# vi ifcfg-ens33:0
NAME=ens33:0
DEVICE=ens33:0
IPADDR=192.168.189.150
[root@centos7 ~]# ifdown ens33 && ifup ens33
[root@centos7 ~]# ifconfig
ens33: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.189.128 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.189.255
inet6 fe80::243c:86d7:d85e:224d prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:15:53:53 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 629 bytes 61934 (60.4 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 512 bytes 64012 (62.5 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
ens33:0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.189.150 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.189.255
ether 00:0c:29:15:53:53 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 64 bytes 5344 (5.2 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 64 bytes 5344 (5.2 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
由此可见,多了ens33:0的网卡信息。
还在可以windows上面ping通ens33:0的ip,并且可以利用Xshell等远程工具去远程连接它的22端口,
查看网卡连接状态
mii-tool ens33 查看网卡是否连接
此用法,用在检查机房端口是否亮。
[root@centos7 ~]# mii-tool ens33
ens33: negotiated 1000baseT-FD flow-control, link ok
link ok表示连接状态。如果现实no link,说明网卡坏了或者没有连接网线。
如果上述命令不能使用,可以使用#ethtool
#ethtool ens33
[root@centos7 ~]# ethtool ens33
Settings for ens33:
Supported ports: [ TP ]
Supported link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Full
Supported pause frame use: No
Supports auto-negotiation: Yes
Advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Full
Advertised pause frame use: No
Advertised auto-negotiation: Yes
Speed: 1000Mb/s
Duplex: Full
Port: Twisted Pair
PHYAD: 0
Transceiver: internal
Auto-negotiation: on
MDI-X: off (auto)
Supports Wake-on: d
Wake-on: d
Current message level: 0x00000007 (7)
drv probe link
Link detected: yes
如果网卡没有连接,link detected 会显示no.
更改主机名 hostnamectl set-hostname hostname 此命令不适用与CentOS7之前的系统
[root@centos7 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname centos7-01
[root@centos7 ~]# hostname 查看hostname名字
centos7-01
[root@centos7 ~]# bash 如果想使设置生效,可以重新登进登出。或者#bash进入子shell
[root@centos7-01 ~]# exit 生效退出子shell
exit
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/hostname hostname的配置文件
centos7-01
DNS配置文件/etc/resolv.conf 此文件的参数可以在网卡配置文件发生更改而更改。
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
# Generated by NetworkManager
nameserver 114.114.114.114
如果#vi /etc/resolv.conf,更改了resolv.conf的参数之后,重启了服务器或者服务,参数都会被网卡配置文件的参数所覆盖掉。所以resolv.conf只适用于临时更改。
/etc/hosts文件 作用是临时解析某个域名,只在本机下生效。
格式是 左边ip 右边域名
一个IP可以跟多个域名,可以是几十个,甚至上百个,用空格分隔。
每一行只能有一个IP,也就是说一个域名不能对应多个IP。
如果有多行中出现相同的域名(对应IP不一样),会按最近出现的记录来解析。
示例:
# vim /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.189.128 www.qq.com
[root@centos7 ~]# ping www.qq.com
PING www.qq.com (192.168.189.128) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from www.qq.com (192.168.189.128): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.054 ms
64 bytes from www.qq.com (192.168.189.128): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.055 ms
64 bytes from www.qq.com (192.168.189.128): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.432 ms
10.12 firewalld和netfilter

selinux临时关闭 setenforce 0
#setenforce 0
selinux永久关闭 vi /etc/selinux/config
更改配置文件/etc/selinux/config,把SELINUX=enforcing改成SELINUX=disabled,
#vim /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
更改完成该配置文件后,重启系统方可生效。可以使用getenforce命令获得SELINUX的状态,
[root@centos7 ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@centos7 ~]# setenforce 0
[root@centos7 ~]# getenforce
Permissive
Enforcing与Permissive的区别在于,
Permissive selinux开启,遇到需要发送阻断的时候,不需要真正阻断,它只是一个提醒。
!!!!!SELINUX一般都处于关闭状态。因为开启SELINUX会增加很多运维成本,很多服务受限于SELINUX。
把SELINUX关闭不会有太多安全问题。
centos7之前使用netfilter防火墙
centos7防火墙改名,firewalld
俩基制不一样,但是内部工具iptables是一样的,可以通过iptables去添加一些规则。例如把80端口开放,把22端口开放,把8080端口关闭,这时候可以使用iptables去实现,增加一定的规则即可。
不管是firewalld还是netfilter,他们都主持iptables命令的。
在centos7上,firewalld是默认开启的。所以我们需要把firewalld关闭掉,再开启netfilter。
#systemctl stop firewalld 关闭firewalld服务
#systemctl disable firewalled 禁止firewalld服务开机启动
#yum install -y iptables-services 安装iptables-services,这样就可以之前版本的iptables了
#systemctl enable iptables 让iptables开机启动
#systemctl start iptables 启动iptables服务
10.13 netfilter5表5链介绍

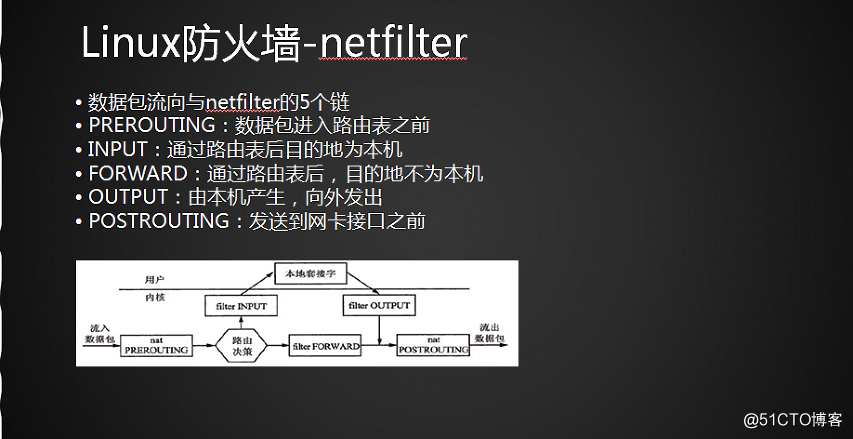
netfilter的5个表
filter表用于过滤包,最常用的表,有INPUT、FORWARD、OUTPUT三个链
默认的表,内置3个链
INPUT链作用于进入本机的包。数据包进入本机,之后做的相关操作。
OUTPUT链作用于本机送出的包。本本机产生数据包,出去之前做的操作。
FORWARE链作用于那些根本机无关的包。把目标地址进行更改,转发等等操作。
nat表用于网络地址转换,有PREROUTING、OUTPUT、POSTROUTING三个链
PREROUTING链 在进来的那一刻更改数据包
OUTPUT链与filter的OUTPUT是一样的
POSTROUTING链 在出的的那一刻更改数据包
nat用法实例
有ABC三台机器,
A机器a网卡,公网连接。B机器b网卡公网,c网卡私网。C机器d卡,私网。
此时A想访问C的80端口,应该怎么做?
因为B可以跟C进行通讯,所以可以在B机器上面做iptables,做个映射端口8088,映射到C的80端口
当A访问B的8088端口时候,可以直接映射到C的80端口上。
这时候,需要用到PREROUTING和POSTROUTING。
managle表用于给数据包做标记,几乎用不到
raw表可以实现不追踪某些数据包,阿铭从来不用
security表在centos6中并没有,用于强制访问控制(MAC)的网络规则,阿铭没用过
参考文章 http://www.cnblogs.com/metoy/p/4320813.html
总结:
如果是本机的数据包会经过PREROUTING,INPUT,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING,
如果不是本机的,PREROUTING,FORWARD,POSTROUTING.
10.14 Linux防火墙-netfilter
查看iptables规则:iptables -nvL
[root@centos7 ~]# service iptables restart 重启iptables服务。
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart iptables.service
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
31 2124 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED
0 0 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0
0 0 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW tcp dpt:22
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 18 packets, 1736 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
[root@centos7 ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables 规则文件,默认规则。
cat /etc/sysconfig/iptables
# sample configuration for iptables service
# you can edit this manually or use system-config-firewall
# please do not ask us to add additional ports/services to this default configuration
*filter
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
-A INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
COMMIT
iptables -F 清空规则
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -F
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 5 packets, 388 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 4 packets, 448 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
service iptables save
把配置好的规则保存到配置文件里面。
#service iptables save
# service iptables restart 重启服务,会重新加载配置文件的规则。
iptables -t nat //-t指定表
!
iptables -Z 可以把计数器清零
!
#iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -j DROP
如果没有-t 指的是针对filter表来操作。
此命令的意思就是,添加一条规则,针对INPUT的链。指定来源IP 来源IP 来源端口 目的IP 目的端口 -j 丢包
-A 表示增加一条规则。
-D 表示删除一条规则
-I 表示插入一条规则,效果跟-A一样。只是顺序不同,-I会比-A的位置要前。所以-I会被优先过 滤
-P 表示指定协议,可以是tcp udp或者icmp
--dport 跟-p一起使用,表示指定目标端口
--sport 跟-p一起使用,表示指定源端口
-s 表示源IP(可以是一个IP段)
-d 表示指定目的IP(可以是一个IP段)
-j 后面跟动作,其中ACCEPT表示允许包,DROP表示丢掉包,REJECT表示拒绝包。
-i 表示指定网卡(少用)
DROP把数据包扔掉,不会再看数据包,直接丢掉。(常用)
REJECT拒绝数据包,数据包来了先看一下,然后反馈信息,再扔掉。
两效果一样,相当于把IP封掉。
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -j DROP
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 25 packets, 1744 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.188.1 192.168.188.128 tcp spt:1234 dpt:80
-I插入规则,对比-A不同的是,-I的位置比-A前,会被优先过滤。
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP
删除规则
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -D INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -j DROP
删除规则还有另一个方法,
首先添加和插入规则-A和-I
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.188.1 -p tcp --sport 1234 -d 192.168.188.128 --dport 80 -j DROP
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j DROP
添加首选行编号表示
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL --line-numbers
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 72 packets, 5160 bytes)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
2 0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 192.168.188.1 192.168.188.128 tcp spt:1234 dpt:80
删除第2条规则,利用编号删除
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -D INPUT 2
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL --line-numbers
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 27 packets, 1840 bytes)
num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
1 0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
iptables -I/-A/-D INPUT -s 1.1.1.1 -j DROP
iptables -I INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -i eth0 -j ACCEPT
插入规则
iptables -nvL --line-numbers
编号显示规则
iptables -D INPUT 1
删除规则
iptables -P INPUT DROP
默认规则
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -nvL
Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 61 packets, 4381 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
0 0 DROP tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 34 packets, 4104 bytes)
pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
链一般有默认的policy,policy ACCEPT表示这个链,不加规则的话,例如OUTPUT链没有任何规则,所以OUTPUT的数据包,它就由默认的策略来决定,这个默认的策略就是ACCEPT。
*所有的数据包,只要是没有具体的规则来匹配,那它就走默认的策略。
默认策略改成DROP
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -P OUTPUT DROP
这个一般不要在远程终端执行,因为如果执行了此命令。 因为默认的规则一旦被DROP掉,那么当前窗口就会被禁掉。因为数据包和22端口通信,通信完后,需要反馈数据给客户端(Xshell),结果Xshell OUTPUT出来的包到达不了Xshell 所以它接收不了数据,最终导致断开。
如果断开了 在本机(虚拟机、服务器)给OUTPUT的默认策略改回ACCEPT即可。
[root@centos7 ~]# iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
10.11-10.14 网络相关 firewall,netfilter,5表5链,iptables
原文:http://blog.51cto.com/13578154/2089563