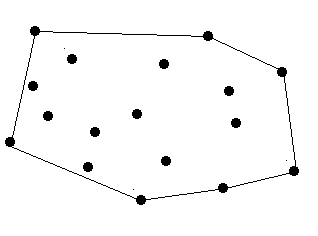
9 12 7 24 9 30 5 41 9 80 7 50 87 22 9 45 1 50 7 0
243.06
n=1和n=2的时候要特判。 #include <iostream> #include <string.h> #include <algorithm> #include <math.h> using namespace std; #define M 1000 int top; struct node { double x,y; }p[M],stack[M]; double L(node a,node b) { return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } double multi(node a,node b,node c) { return (a.x-c.x)*(b.y-c.y)-(b.x-c.x)*(a.y-c.y); } int cmp(node a,node b) { if(multi(a,b,p[0])>0) return 1; if(multi(a,b,p[0])==0&&L(a,p[0])<L(b,p[0])) return 1; return 0; } void GS(node p[],node stack[],int n) { int i,k=0; node temp; for(i=0;i<n;i++) { if(p[i].y<p[k].y||((p[i].y==p[k].y)&&(p[i].x<p[k].x))) k=i; } temp=p[0]; p[0]=p[k]; p[k]=temp; sort(p+1,p+n,cmp); top=2; stack[0]=p[0],stack[1]=p[1],stack[2]=p[2]; for(i=3;i<n;i++) { while(top>1&&multi(p[i],stack[top],stack[top-1])>=0) top--; stack[++top]=p[i]; } } int main() { double t; int n,i,m; while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n) { t=0; memset(p,0,sizeof(p)); memset(stack,0,sizeof(stack)); for(i=0;i<n;i++) { scanf("%lf %lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); } if(n==1) { printf("0.00\n"); continue; } if(n==2) { printf("%.2lf\n",L(p[0],p[1])); continue; } GS(p,stack,n); stack[top+1]=stack[0]; for(i=0;i<=top;i++) { t+=L(stack[i],stack[i+1]); } if(n>2) printf("%.2lf\n",t); } return 0; }
Surround the Trees,布布扣,bubuko.com
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/qq2256420822/article/details/37728873