关键词:分组聚合
物理上一张表,逻辑上是两张表 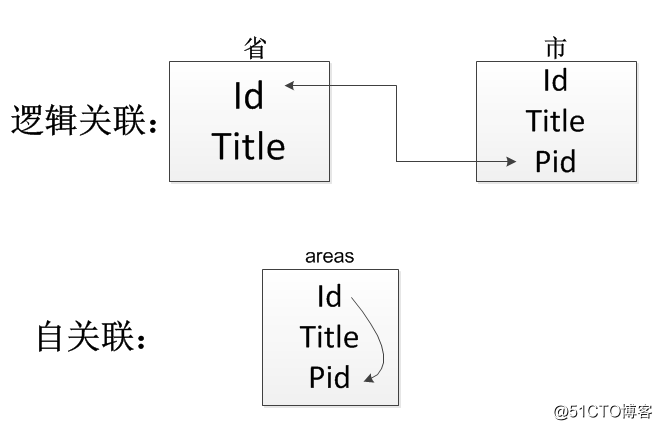
create table areas(
id int primary key,
atitle varchar(20),
pid int,
foreign key(pid) references areas(id)
); 导入sql文件
source areas.sql; 示例图
示例语句
select sheng.id as sid,sheng.title as stile,shi.id as shiid,shi.title as shititle from areas as sheng
inner join areas as shi on sheng.id=shi.pid
where sheng.pid is null and sheng.title=‘山西省‘
limit 0,100;create view stuscore as + 查询语句
四个特性(ACID)
引擎类型:engine=innodb/bdb 支持事务,默认innodb
查看表创建的语句: show create table students;
修改表类型 : alter table students engine=innodb;
事务语句
begin; //开启
commit; //提交
rollback; // 回滚操作查看索引
show index from 表名;创建索引
create index indexName on areas(title(20)); 删除索引
drop index [indexName] on 表名; 执行时间
set profiling=1; show profiles;每一个python会话都是一次事务
Connec类
connection = connect(host,port,db,user,passwd,charset)connection对象的方法
close() 关闭连接
commit() 事务提交,所以需要提交才会生效
rollback() 事务回滚,放弃之前的操作
cursor() 返回Cursor对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果 Cursor
执行SQL语句
cursor1=connection.cursor() // 调用cursor方法 返回一个cursor对象 cursor对象的常用方法
execute(operation ,[ parameters ]) //执行语句,返回受影响的行数
fetchone() //获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组
fetchall() //获取查询结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,返回一个大元组import MySQLdb
try:
connection=MySQLdb.connect(host=‘localhost‘,port=3306,db=‘python3‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘***‘,charset=‘utf8‘)
cursor1=connection.cursor()
sql=‘SQL语句增删查改‘
count=cs1.execute(sql)
connection.commit()
cursor1.close()
connection.close()
except Exception,e:
print (e.message)防止SQL注入
from MySQLdb import *
try:
name = raw_input(‘请输入一个名字‘)
connection = connect(host=‘localhost‘,port=3306,db=‘python3‘,user=‘root‘,passwd=‘***‘,charset=‘utf8‘)
#sql = ‘insert into students(name) values("小乖巧")‘
#sql = ‘update students set name=‘乖巧‘ where id=3‘
#sql = ‘delete from students where id = 3‘
sql = ‘insert into students(name) values(%s)‘
cursor1.execute(sql,[name])
connection.commit()
cursor1.close()
connection.close()
except Exception,e:
print (e.message)class MYSQL:
def __init__(self,host,port=3306,db,user,passwd,charset=‘uft8‘):
self.host = host
self.port = port
self.db = db
self.user = user
self.passwd = passwd
self.charset = charset
def open(self):
self.connection = connect(host=self.host,port=self.port,db=self.db,user=self.user,passwd=self.passwd,charset=self.charset)
self.cursor = self.connection.cursor()
def close(self):
self.cursor.close()
self.connection.close()
def curd(self):
try:
self.open()
self.cursor(sql,param)
self.commit()
self.close()
except Exception,e:
print(e.message)
def all(self,sql,param=[]):
try:
self.open()
self.cursor(sql,param)
result = self.cursor.fetchall()
self.commit()
self.close()
return result
except Exception,e:
print(e.message)5/13/2018 9:57:42 PM
原文:http://blog.51cto.com/13736429/2115790