Description
In mathematical terms, the sequence Fn of Fibonacci numbers is defined by the recurrence relation
DZY loves Fibonacci numbers very much. Today DZY gives you an array consisting of n integers: a1, a2, ..., an. Moreover, there arem queries, each query has one of the two types:
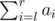 modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).
modulo 1000000009 (109 + 9).Help DZY reply to all the queries.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 300000). The second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — initial array a.
Then, m lines follow. A single line describes a single query in the format given in the statement. It is guaranteed that for each query inequality 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n holds.
Output
For each query of the second type, print the value of the sum on a single line.
Sample Input
4 4
1 2 3 4
1 1 4
2 1 4
1 2 4
2 1 3
17
12
Hint
After the first query, a = [2, 3, 5, 7].
For the second query, sum = 2 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 17.
After the third query, a = [2, 4, 6, 9].
For the fourth query, sum = 2 + 4 + 6 = 12.
解题思路:根据斐波那契数列的两个定义(任意区间适应,a为该区间的第一项,b为该区间的第二项):
(1)F(n)=b*fib[n-1]+a*fib[n-2] ;
(2)F[1]+F[2]+...+F[n]=F[n+2]-b;
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 #define lson i<<1 7 #define rson i<<1|1 8 #define mid ((l+r)>>1) 9 typedef __int64 LL; 10 const int maxn=300005; 11 const int mod=1e9+9; 12 int a[maxn],fib[maxn]; 13 14 struct Node 15 { 16 int f1,f2;//区间第一项和第二项的值 17 int sum; 18 }segtree[maxn<<2]; 19 20 void init()//斐波那契数列预处理 21 { 22 fib[1]=1;fib[2]=1; 23 for(int i=3;i<maxn;i++) 24 if((fib[i]=fib[i-1]+fib[i-2])>=mod) 25 fib[i]-=mod; 26 } 27 28 int get_fib(int a,int b,int n) 29 { 30 if(n==1) return a; 31 if(n==2) return b; 32 return ((LL)b*fib[n-1]+(LL)a*fib[n-2])%mod; 33 } 34 35 int get_sum(int a,int b,int n) 36 { 37 int sum=get_fib(a,b,n+2)-b; 38 return (sum+mod)%mod; 39 } 40 void add_fib(int i,int l,int r,int a,int b) 41 { 42 segtree[i].f1=(segtree[i].f1+a)%mod; 43 segtree[i].f2=(segtree[i].f2+b)%mod; 44 segtree[i].sum=(segtree[i].sum+get_sum(a,b,r-l+1))%mod; 45 } 46 47 void pushdown(int i,int l,int r) 48 { 49 add_fib(lson,l,mid,segtree[i].f1,segtree[i].f2); 50 add_fib(rson,mid+1,r,get_fib(segtree[i].f1,segtree[i].f2,mid+1-l+1) 51 ,get_fib(segtree[i].f1,segtree[i].f2,mid-l+3)); 52 segtree[i].f1=segtree[i].f2=0; 53 } 54 55 void pushup(int i) 56 { 57 segtree[i].sum=(segtree[lson].sum+segtree[rson].sum)%mod; 58 } 59 60 void build(int i,int l,int r) 61 { 62 if(l==r) 63 { 64 segtree[i].sum=a[l]; 65 segtree[i].f1=segtree[i].f2=0; 66 return ; 67 } 68 build(lson,l,mid); 69 build(rson,mid+1,r); 70 pushup(i); 71 } 72 73 void update(int i,int l,int r,int a,int b) 74 { 75 if(a<=l && r<=b) 76 { 77 add_fib(i,l,r,fib[l-a+1],fib[l-a+2]); 78 return ; 79 } 80 pushdown(i,l,r); 81 if(a<=mid) update(lson,l,mid,a,b); 82 if(b>mid) update(rson,mid+1,r,a,b); 83 pushup(i); 84 } 85 86 int query(int i,int l,int r,int a,int b) 87 { 88 if(a<=l && r<=b) 89 return segtree[i].sum; 90 pushdown(i,l,r); 91 int ans=0; 92 if(a<=mid) ans=(ans+query(lson,l,mid,a,b))%mod; 93 if(mid<b) ans=(ans+query(rson,mid+1,r,a,b))%mod; 94 return ans; 95 } 96 97 int main() 98 { 99 init(); 100 int i,n,m,op,l,r; 101 scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); 102 for(i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",a+i); 103 build(1,1,n); 104 while(m--) 105 { 106 scanf("%d%d%d",&op,&l,&r); 107 if(op==1) update(1,1,n,l,r); 108 if(op==2) printf("%d\n",query(1,1,n,l,r)); 109 } 110 return 0; 111 }
codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 数论+线段树成段更新,布布扣,bubuko.com
codeforces 446C DZY Loves Fibonacci Numbers 数论+线段树成段更新
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiong-/p/3853223.html