Pipes have no names, and their biggest disadvantage is that they can be used only between processes that have a parent process in common. Two unrelated processes can-
not create a pipe between them and use it for IPC
FIFO stands for first in, first out, and a Unix FIFO is similar to a pipe. It is a one-way (half-duplex) flow of data. But unlike pipes, a FIFO has a pathname associated with it, allowing unrelated processes to access a single FIFO.
FIFO是有名管道,有一个路径与之关联,允许无亲缘关系的进程通信,单向。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mkfifo (const char *pathname, mode-t mode)
Returns: 0 if OK, -1 on error
创建一个新的fifo或者返回错误,如果返回错误使用open或fopen打开,FIFO是半双工,不能同时读和写
#include "unpipc.h"
#define FIFO1 "/tmp/fifo.1"
#define FIFO2 "/tmp/fifo.2"
void client(int, int), server(int, int);
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int readfd, writefd;
pid_t childpid;
/* 4create two FIFOs; OK if they already exist */
if ((mkfifo(FIFO1, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
err_sys("can‘t create %s", FIFO1);
if ((mkfifo(FIFO2, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST)) {
unlink(FIFO1);
err_sys("can‘t create %s", FIFO2);
}
if ( (childpid = Fork()) == 0) { /* child */
readfd = Open(FIFO1, O_RDONLY, 0);
writefd = Open(FIFO2, O_WRONLY, 0);
server(readfd, writefd);
exit(0);
}
/* 4parent */
writefd = Open(FIFO1, O_WRONLY, 0);
readfd = Open(FIFO2, O_RDONLY, 0);
client(readfd, writefd);
Waitpid(childpid, NULL, 0); /* wait for child to terminate */
Close(readfd);
Close(writefd);
Unlink(FIFO1);
Unlink(FIFO2);
exit(0);
}

server_main.c
#include "fifo.h"
void server(int, int);
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int readfd, writefd;
/* 4create two FIFOs; OK if they already exist */
if ((mkfifo(FIFO1, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST))
err_sys("can‘t create %s", FIFO1);
if ((mkfifo(FIFO2, FILE_MODE) < 0) && (errno != EEXIST)) {
unlink(FIFO1);
err_sys("can‘t create %s", FIFO2);
}
readfd = Open(FIFO1, O_RDONLY, 0);
writefd = Open(FIFO2, O_WRONLY, 0);
server(readfd, writefd);
exit(0);
}
fifo.h
#include "unpipc.h" #define FIFO1 "./fifo.1" #define FIFO2 "./fifo.2"
client_main.c
#include "unpipc.h"
void
client(int readfd, int writefd)
{
size_t len;
ssize_t n;
char buff[MAXLINE];
/* 4read pathname */
Fgets(buff, MAXLINE, stdin);
len = strlen(buff); /* fgets() guarantees null byte at end */
if (buff[len-1] == ‘\n‘)
len--; /* delete newline from fgets() */
/* 4write pathname to IPC channel */
Write(writefd, buff, len);
/* 4read from IPC, write to standard output */
while ( (n = Read(readfd, buff, MAXLINE)) > 0)
Write(STDOUT_FILENO, buff, n);
}
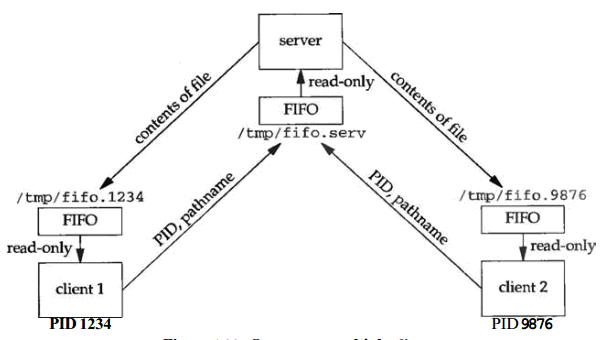
单个服务器,多个客户:服务器以一个众所周知的路径名创建一个FIFO,从这个FIFO读入客户的请求。每个客户在启动时创建自己的FIFO,所用的路径名包含有自己的进程id。每个客户把自己的请求写入服务器的众所周知的FIFO中,请求中包含客户的进程id以及一个路径名。具有该路径名的文件就是客户希望服务器打开并发回的文件。
原文:http://my.oschina.net/hnuweiwei/blog/292480