

--initial-advertise-peer-urls http://${THIS_IP}:2380 \
--listen-peer-urls http://${THIS_IP}:2380 \
--advertise-client-urls http://${THIS_IP}:2379 \
--listen-client-urls http://${THIS_IP}:2379 \
--initial-cluster ${CLUSTER} \
--initial-cluster-state ${CLUSTER_STATE} \
--initial-cluster-token ${TOKEN}
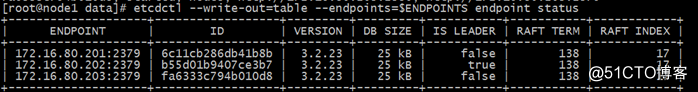
我们做一个测试,是否主节点写入或删除,其余两个节点也会写入或删除,结果如下(表示正确)
[root@node2 ~]# etcdctl --endpoints=${HOST_1}:2379,${HOST_2}:2379,${HOST_3}:2379 put foo "a"
OK
[root@node2 ~]# etcdctl --endpoints=${HOST_1}:2379,${HOST_2}:2379,${HOST_3}:2379 get foo
foo
a
[root@node3 ~]# etcdctl --endpoints=${HOST_1}:2379,${HOST_2}:2379,${HOST_3}:2379 get foo
foo
a
[root@node2 ~]# etcdctl --endpoints=${HOST_1}:2379,${HOST_2}:2379,${HOST_3}:2379 del foo
1
创建snapshot
etcdctl --endpoints=$ENDPOINTS snapshot save my.db
etcdctl --write-out=table --endpoints=$ENDPOINTS snapshot status my.db
数据迁移:(一般不用,因为etcd是集群,可以添加节点的方式来实现数据迁移,然后删除原有的节点)
etcdctl --endpoints=$ENDPOINT migrate --data-dir="default.etcd" --wal-dir="default.etcd/member/wal"
权限
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} role add root
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} role grant-permission root readwrite foo
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} role get root
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} user add root
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} user grant-role root root
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} user get root
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} auth enable
#now all client requests go through auth
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} --user=root:123 put foo bar
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} get foo
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} --user=root:123 get foo
etcdctl --endpoints=${ENDPOINTS} --user=root:123 get foo1
参考文章:https://coreos.com/etcd/docs/latest
原文:http://blog.51cto.com/laodou/2160545