1.连接插件connetion plugins:负责和被监控端实现通讯;
2.host inventory:指定操作的主机,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机;
3.各种模块核心模块,command模块,自定义模块;
4.借助于插件完成纪录日志邮件等功能;
5.playbook:剧本执行多个任务时,非必需可以让节点一次性运行多个任务。ansible架构图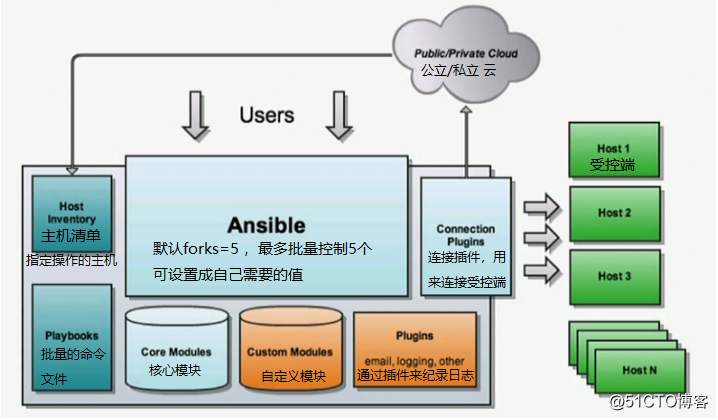
Ansible有很多配置参数,以下是几个默认的配置参数:
inventory = /root/ansible/hosts
library = /usr/share/my_modules/
forks = 5
sudo_user = root
remote_port = 22
host_key_checking = False
timeout = 20
log_path = /var/log/ansible.loginventory:该参数表示inventory文件的位置,资源清单(inventory)就是Ansible需要连接管理的一些主机列表。
library:Ansible的所有操作都使用模块来执行实现,这个library参数就是指向存放Ansible模块的目录。
forks:设置默认情况下Ansible最多能有多少个进程同时工作,默认5个进程并行处理。具体需要设置多少个,可以根据控制端性能和被管理节点的数量来确定。
sudo_user:设置默认执行命令的用户,也可以在playbook中重新设置这个参数。
remote_port:指定连接被管理节点的管理端口,默认是22,除非设置了特殊的SSH端口,否则不需要修改此参数。
host_key_checking:设置是否检查SSH主机的密钥。可以设置为True或False。即ssh的主机再次验证。
timeout:设置SSH连接的超时间隔,单位是秒。
log_path:Ansible默认不记录日志,如果想把Ansible系统的输出记录到日志文件中,需要设置log_path。需要注意,模块将会调用被管节点的(r)syslog来记录,执行Ansible的用户需要有写入日志的权限。ansible安装
配置安装163的源
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
//创建备份目录
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mkdir /etc/repo-bf
//将原yum仓库的文件备份到repo-bf
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# mv * /etc/repo-bf
//下载163的源到yum仓库
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# curl -o 163.repo http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
//将改为版本的7
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# sed -i ‘s/\$releasever/7/g‘ /etc/yum.repos.d/163.repo
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# sed -i ‘s/enabled=0/enabled=1/g‘ /etc/yum.repos.d/163.repo
//自动配置yum的软件仓库,也可以自己配置
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum -y install epel-release
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum -y install ansible ansible-doc
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum clean all
//查看ansible版本
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ansible --version
ansible 2.6.3
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = [u‘/root/.ansible/plugins/modules‘, u‘/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules‘]
ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible
executable location = /usr/bin/ansible
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Aug 4 2017, 00:39:18) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16)]
//设置环境
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# yum -y install wget
[root@localhost yum.repos.d]# cdansible配置
配置文件:
ansible主配置文件 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
受控主机清单 /etc/ansible/hosts
受控主机清单配置方式
* 分组配置 一个组下添加多个ip
* ip配置 也可以网段,例:192.168.56.[1-254]
* 域名配置
* 通配符配置 [001:006], 1到6 (例:www.001.xxx.com ...)分组设置,例:
[abc]
192.168.56.123
192.168.56.138ansible通过ssh来控制远程主机,所以要配置ssh互信,否则将会提示你输入密码。
ssh-keygen -t rsa //生成密钥
[root@localhost ~]# ls .ssh/
id_rsa id_rsa.pub
ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@(需要免密的受控端ip)ansible如何获取帮助
ansible通过ansible-doc命令来获取帮助信息,可以使用此命令的-s选项来获取指定模块的帮助信息
//查询ping模块的帮助文档
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc -s ping
- name: Try to connect to host, verify a usable python and return `pong‘ on success
ping:
data: # Data to return for the `ping‘ return value. If this parameter is set
to `crash‘, the module will cause an
exception.ansible常用模块使用详解
ansible常用模块有:
* ping
* yum
* template
* copy
* user
* group
* service
* raw
* command
* shell
* scriptansible常用模块raw,command,shell的区别:
* shell模块调用的/bin/sh指令执行
* command模块不是调用的shell的指令,所以没有bash的环境变量
* raw很多地方和shell类似,更多地方建议使用shell和conmmand模块。但是如果是使用老版本python,需要用到raw,又后者是客户端是路由器,因为没有安装python模块,那就需要使用raw模块了ansible常用之ping
ping模块常用于检查指定节点机器是否连通,用法简单,不涉及参数,主机如果在线,则回复pong
[root@localhost ~]# ansible [all或你设置组,ip等] -m ping
例:
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m ping
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}ansible常用模块之command
command模块用于在远程主机上执行命令,ansible默认就是使用command模块
command模块有一个缺陷就是不能使用管道符和重定向功能,这里不做示范
//查看受控机的/tmp目录内容
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -a ‘ls /tmp‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
ansible_bWbAQA
ks-script-FJMsU1
systemd-private-d64c48c29b014817892ff2b800ef4fdf-chronyd.service-SQE1dO
systemd-private-d64c48c29b014817892ff2b800ef4fdf-httpd.service-REOrV8
systemd-private-d64c48c29b014817892ff2b800ef4fdf-vgauthd.service-AEDF9T
systemd-private-d64c48c29b014817892ff2b800ef4fdf-vmtoolsd.service-7FRejI
systemd-private-e09517bf16f64a2fbe7372b98204716d-chronyd.service-nkIAuP
systemd-private-e09517bf16f64a2fbe7372b98204716d-vgauthd.service-r1RS7D
systemd-private-e09517bf16f64a2fbe7372b98204716d-vmtoolsd.service-QXRPMs
yum.log
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
ansible__mXwII
ks-script-Q6MuAp
systemd-private-5895f3e39f304700829d55b9a5234b36-chronyd.service-O9f5LP
systemd-private-5895f3e39f304700829d55b9a5234b36-vgauthd.service-bfquyZ
systemd-private-5895f3e39f304700829d55b9a5234b36-vmtoolsd.service-Z2u8r9
yum.log
//在受控主机上新建个文件
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -a ‘touch /tmp/123‘
//受控机上查看
[root@localhost ~]# ls /tmp/
123**ansible常用模块之raw
raw模块用于在远程主机上执行命令,支持管道符与重定向***
//查看
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m raw -a ‘cat /tmp/123‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
123456
Shared connection to 192.168.56.123 closed.
...
//支持管道符
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m raw -a ‘cat /tmp/123|grep 123‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
123456
Shared connection to 192.168.56.123 closed.ansible常用模块之shell
shell模块用于在受控机上执行受控机上的脚本,也可直接在受控机上执行命令
支持管道和重定向
//查看受控机的脚本(自编)
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/aaa.sh
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..10};do
echo $i
done
使用shell模块在受控机上执行的脚本
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘bash /etc/aaa.sh|grep 1 &>/tmp/123‘
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘cat /tmp/123‘
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
1
10
...ansible常用模块之script
scrip模块在受控机上执行主控上的脚本
[root@localhost ~]# scp root@192.168.56.138:/etc/aaa.sh /root
[root@localhost ~]# mv aaa.sh a123.sh
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m script -a ‘a123.sh &> /tmp/123‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"rc": 0,
"stderr": "Shared connection to 192.168.56.123 closed.\r\n",
"stderr_lines": [
"Shared connection to 192.168.56.123 closed."
],
"stdout": "",
"stdout_lines": []
}
...
//受控机查看
[root@localhost ~]# cat /tmp/123
1
2
3
...
可见在受控机上执行了主控机上的脚本,并纪录到了受控机。ansible常用模块之template
template模块用于生成一个模板,并可将其传输至远程主机上
//下载并设置163的源
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
[root@localhost ~]# curl -o CentOS7-Base-163.repo http://mirrors.163.com/.help/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
[root@localhost ~]# sed -i ‘s/\$releasever/7/g‘ /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
[root@localhost ~]# sed -i ‘s/^enabled=.*/enabled=1/g‘ /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo
//将设置好的163源传到受控机
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m template -a ‘src=/etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS7-Base-163.repo dest=/etc/yum.repos.d/163.repo‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "60b8868e0599489038710c45025fc11cbccf35f2",
"dest": "/etc/yum.repos.d/163.repo",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "5a3e688854d9ceccf327b953dab55b21",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 1462,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536578876.83-251571075139699/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
...
//受控机查看
[root@localhost ~]# ls /etc/yum.repos.d/
163.repo ansible常用模板之yum
yum模板用于在指定节点机器上通过yum管理软件,其支持的参数主要有两个
* name:要管理的包名
* state:要进行的操作state常用的值:
若想使用yum来管理软件,请确保受控机上的yum源无异常
//在受控和机上查询vsftpd软件是否安装
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -qa|grep vsftpd
在ansible主机上使用yum模块在受控机上安装vsftpd
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m yum -a ‘name=vsftpd state=present‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"msg": "",
"rc": 0,
"results": [
"vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64 providing vsftpd is already installed"
]
}
...
//检查vsftpd
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘rpm -qa|grep vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
vsftpd-3.0.2-22.el7.x86_64ansible常用模块之copy
copy模块用于复制文件至远程受控机
[root@localhost ~]# ls
a123.sh
将主控机root下的a123.sh复制到受控机的root/
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m copy -a ‘src=a123.sh dest=root/‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"checksum": "dd788902d7b36afedee8f2087a3e93b4047d33de",
"dest": "root/a123.sh",
"gid": 0,
"group": "root",
"md5sum": "84f03ff2c65a9b9bfea41587ad43e533",
"mode": "0644",
"owner": "root",
"size": 45,
"src": "/root/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1536584403.91-155709823063677/source",
"state": "file",
"uid": 0
}
...
//受控机查看
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘ls root/‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
a123.sh
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
a123.shansible常用模块之group
group模块用于在受控机上添加或者删除组
//在受控机上添加一个系统组,gid为306,组名mysql
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m group -a ‘name=mysql gid=306 state=present‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"gid": 306,
"name": "mysql",
"state": "present",
"system": false
}
...
在/etc/group里过滤初mysql
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘grep mysql /etc/group‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mysql:x:306:
...
//删除受控机上的mysql组
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m group -a ‘name=mysql state=absent‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"name": "mysql",
"state": "absent"
}
...
//受控机查看
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘grep mysql /etc/group‘
192.168.56.123 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return codeansible常用模块之user
user模块用于管理受控机的用户账号
//在受控机上添加一个系统账户,用户名为mysql,uid为306,设置shell为/sbin/nologin,无家目录
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m user -a ‘name=mysql uid=306 system=yes create_home=no shell=/sbin/nologin state=present‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"create_home": false,
"group": 306,
"home": "/home/mysql",
"name": "mysql",
"shell": "/sbin/nologin",
"state": "present",
"system": true,
"uid": 306
}
...
//检查受控机
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘grep mysql /etc/group‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mysql:x:306:
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mysql:x:306:
查看用户
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘ls /home‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
1
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
1
//修改mysql用户的uid为366
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m user -a ‘name=mysql uid=366‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"append": false,
"changed": true,
"comment": "",
"group": 306,
"home": "/home/mysql",
"move_home": false,
"name": "mysql",
"shell": "/sbin/nologin",
"state": "present",
"uid": 366
}
...
//受控机查看用户
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘grep mysql /etc/passwd‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mysql:x:366:306::/home/mysql:/sbin/nologin
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
mysql:x:366:306::/home/mysql:/sbin/nologin
//删除受控机上的mysql用户
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m user -a ‘name=mysql state=absent‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"force": false,
"name": "mysql",
"remove": false,
"state": "absent"
}
...
//受控机查看用户
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘grep mysql /etc/passwd‘
192.168.56.123 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
non-zero return code
...ansible常用模块之service
service模块用于管理受控机上的服务
//查看受控机上的vsftp服务是否启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘systemctl is-active vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | FAILED | rc=3 >>
unknownnon-zero return code
//启动受控机上的vsftp服务
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m service -a ‘name=vsftpd state=started‘
...
//查看受控机上的vsftpd服务是否启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘systemctl is-active vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
active
192.168.56.138 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
active
//查看受控机上的vsftpd服务是否开机自启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘systemctl is-enabled vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
disablednon-zero return code
//设置受控机上的vsftpd服务开机自动启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m service -a ‘name=vsftpd enabled=yes‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"enabled": true,
"name": "vsftpd",
"status": {
...
//查看受控机上的vsftpd服务是否开机自启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘systemctl is-enabled vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
enabled
...
//停止受控机上的vsftpd服务
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m service -a ‘name=vsftpd state=stopped‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": true,
"name": "vsftpd",
"state": "stopped",
"status": {
...
//查看受控机上的vsftpd服务是否启动
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘systemctl is-active vsftpd‘
192.168.56.123 | FAILED | rc=3 >>
inactivenon-zero return code
//查看端口
[root@localhost ~]# ansible abc -m shell -a ‘ss -anlt‘
192.168.56.123 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:*
LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::* LINUX——关于ansible批量控制,批量命令及部署的使用
原文:http://blog.51cto.com/13859004/2173972