? 为了回顾关于django的文件上传和分页功能,打算写一个微型的小说网站练练手。花了一个下午的时间,写了个小项目,发现其中其实遇到了许多问题,不过大部分通过debug之后就解决了,其他部分通过阅读了Pagination插件以及Bootstrap-FileInput插件的官方文档。
? 省去小说网站的用户模块的功能,小说网站主要的功能就是上传文件,在线阅读小说。针对这两个功能,
? 主要用到dajngo内置的Pagination模块,以及选择一个上传文件插件即可。因为用的是Bootsrap前端框架,所以就选择了Bootsrap比较多人用的FileInput插件。
? 大致的流程:
- 在首页可以选择上传本地的txt文件到服务器上,然后首页上同时会异步更新已上传的txt文本文件列表。
- 并且可以在上面选择阅读或者删除的操作。阅读则跳转到另外一个页面,后台会读取该文本文件,并且进行分页操作,返回到前端。主要的流程就是这样。接下来讲讲Pagination和FileInput插件和核心代码。
?Django内置的Pagination实现分页功能,这个不用多说,用Django做web开发分页功能都会用到。
?Bootstrap本身自带upload file文件上传插件太丑了,加上功能也不够完善。所以选择了Bootstrap FileInput插件。
- Python 3.6.6
- Django==2.1.7
- Bootstrap v4.3.1
- bootstrap-fileinput v4.5.2
首先代码主要分为两块,一块为文件上传后,接收文件对象,保存到指定的目录下;第二块为读取txt文本文件内容,分页展示到前端页面。
?首先讲讲文件上传的代码,主要涉及到前端的bootstrap-fileinputt插件。该插件将简单的HTML文件输入转换为高级文件选择器控件。对于不支持JQuery或Javascript的浏览器,将有助于回退到正常的HTML文件输入。

?以上这段是官方的自我介绍,说说我个人感受吧。首先这个插件支持批量上传,异步上传等功能,简化大部分JS逻辑方面的代码,具体只要跟着官方的API文档看一看,修改一些参数即可。其次,对于上传时会显示一个进度条,用于显示上传的完成度,这样直观反映了完成度。
bootstrap-fileinput的github地址:
https://github.com/kartik-v/bootstrap-fileinput
bootstrap-fileinput的官方文档地址:
http://plugins.krajee.com/file-input
bootstrap-fileinput的官方DEMO:
http://plugins.krajee.com/file-basic-usage-demo
?HTML代码:
<div dir=rtl class="file-loading">
<input id="input-b8" name="input-b8" multiple type="file">
</div>?JS代码:
$(document).ready( function() {
$("#input-b8").fileinput({
rtl: true,
uploadUrl: ‘/file_receive/‘,
dropZoneEnabled: false,
showPreview: false,
allowedFileExtensions: [‘txt‘],
initialPreviewConfig: []
});
});代码说明:
?fileinput()方法里面传入的是一个json数据,里面有很多个属性,每个数值代表初始化上传控件时的特性,如果没有设置的属性则按照控件的默认属性设置。简单说下里面几个属性的设置:uploadUrl:上传文件地址;dropZoneEnabled:是否显示拖曳区域;showPreview:是否显示预览区域;allowedFileExtensions:允许上传的文件格式。
?后台代码
def file_receive(request):
# 接收File-Input空间传送的文件
if request.method == ‘POST‘:
file = request.FILES[‘input-b8‘]
file_path = "static/books/"+file.name
with open(file_path,"wb") as f:
for chunk in file.chunks():
f.write(chunk)
return JsonResponse({‘status‘:‘success‘})代码说明:
?以上是后台接收文件对象并且保存的代码。我这边省略判断上传文件大小的方法,感兴趣的可以在with open()中添加判断。最后接收文件后,会返回给前端一个json数据,前端插件接收到返回的JSON数据才会确定是否上传文件成功,bootstrap Fileinput才会先Done状态。
拓展:
?这里有点需要注意的就是,后台接收上传的文件,虽然是通过POST的方式上传,但是不能通过request.POST["filename"]或者request.POST.get("filename","None")两种方式来访问。
?而是需要用另外一种方式:
? request.FILES["filename"]或者request.FILES.get("filename","None")
?接下来已经得到文件对象,需要把在内存中的文件写入到硬盘中。读取文件的几个方法和属性:
- filename.read():从文件读取整个上传的数据,这个方法只适合小文件
- filename.chunks():按块返回文件,通过for循环进行迭代,可以将大文件按块写入到服务器中
- filename.multiple_chunks():当filename文件大于2.5M时,该方法返回True,否则返回False。可以根据该方法来判断选择用1方法还是2方法。
?HTML代码:
<div style="padding-top: 20px">
<table id="book_list" class="table table-striped table-bordered table-hover">
<tr>
<th>上传书籍</th>
<th>上传时间</th>
<th>文件大小</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
{% for book in objects %}
<tr>
<td>{{ book.name}}</td>
<td>{{ book.book_time }}</td>
<td>{{ book.book_size }}</td>
<td><a href="/book_read/?book_name={{ book.name }}">阅读</a>
<a href="/book_del/?book_name={{ book.name }}">删除</a></td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</div>?JS代码:
$("#input-b8").on(‘fileuploaded‘,function(){
console.log(‘success‘);
$.get(‘/book_update/‘,function(data){
var book_html ="<tr>\n" +
"<th>上传书" +
"籍</th>" +
"<th>上传时间</th>" +
"<th>文件大小</th>" +
"<th>操作</th>"+
"</tr>";
console.log(data);
for (var i in data){
book_html += "<tr><td>"+ data[i][‘name‘]+"</td>" +
"<td>"+data[i][‘book_time‘]+"</td>" +
"<td>"+data[i][‘book_size‘]+"</td>" +
"<td><a href=\"/book_read/?book_name="+data[i][‘name‘]+"\">阅读</a>"+
"<a href=\"/book_del/?book_name="+data[i][‘name‘]+"\">删除</a></td>"+
"</tr>"
}
$("#book_list").html(book_html)
console.log(book_html)
});
});代码说明:
?$("#input-b8").on(‘fileuploaded‘,function(){})这个方法时在上传完文件后进行回调事件的函数;就是指上传一个文件成功后就会调用该方法;所以我将异步更新上传文件列表的代码放在这个回调事件中。当每个文件上传后,就会请求后台,查询指定目录下的文件列表,生成json格式的数据返回前台,前台再通过遍历的形式拿到其中的数据,进行展示,具体效果如下:
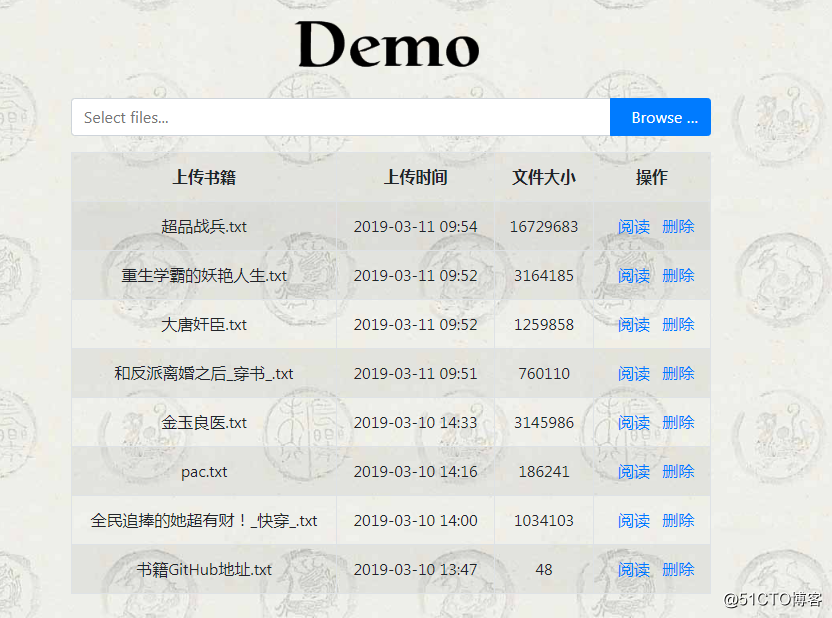
?后台代码
def book_list():
# 获取books目录下的书籍
file_list = []
filedir_path = "static/books/"
list_file = os.listdir(filedir_path)
for book in list_file:
book_info = {}
book_path = filedir_path + book
book_info[‘name‘] = book
book_info[‘timestamp‘] = os.path.getctime(book_path)
book_info[‘book_time‘] = time_format(book_info[‘timestamp‘])
book_info[‘book_size‘] = os.path.getsize(book_path)
file_list.append(book_info)
books = sorted(file_list,key= lambda x:x[‘timestamp‘],reverse=True)
return books
def time_format(timestamp):
# 格式化时间戳成指定的时间
time_struct = time.localtime(timestamp)
time_string = time.strftime(‘%Y-%m-%d %H:%M‘,time_struct)
return time_string 代码说明:
?代码其实很简单,主要是对通过os模块获取静态目录static下的books目录下的文件列表,然后在获取每个文件的时间戳,通过列表推导式,按时间戳为key值进行逆向排序。
?HTML代码:
<div class="header text-center ">
<a href="/index/" style="float: left;">
<i class="fa fa-home fa-2x" aria-hidden="true">Home</i>
</a>
<h3>{{ book_name }}</h3>
</div>
<div class="col-md-12 col-sm-offset-1 main">
{% for content in book_content %}
<span>{{ content }}</span>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<div class="pagination">
<div class="col-md-4 ">
{% if book_content.has_previous %}
<i class="fa fa-arrow-left" aria-hidden="true">
<a href="?book_name={{ book_name }}&page={{ book_content.previous_page_number }}">
上一页
</a>
</i>
{% endif %}
</div>
<div class="col-md-4 ">
<h5>
第{{ book_content.number }}页/共{{ book_content.paginator.num_pages }}页
</h5>
</div>
{% if book_content.has_next %}
<div class="col-md-4 ">
<a href="?book_name={{book_name}}&page={{ book_content.next_page_number }}">
下一页
</a>
<i class="fa fa-arrow-right" aria-hidden="true">
</i>
</div>
{% endif %}
</div>?JS代码:
def book_read(request):
# 获取上传书籍的内容
if request.method == ‘GET‘:
book_name = request.GET[‘book_name‘] # 书籍名称
file_path = "static/books/" + book_name # 书籍路径
with open(file_path,encoding=‘gbk‘, errors=‘ignore‘) as f:
book_contents = f.readlines()
paginator = Paginator(book_contents, 50)
try:
page = int(request.GET[‘page‘]) # 页码
book_content = paginator.page(page)
except Exception as e:
book_content = paginator.page(1)
return render_to_response(‘book.html‘,{‘book_content‘: book_content, ‘book_name‘: book_name})代码说明:
?读取文件的所有行,保存在一个列表中(list),每行作为一个元素。然后实例化一个Paginator对象,并且在实例化中传入一个需要分页的对象列表,以及一页包含多少个数据。再从接收前端传送过来的页码,取特定页码的数据,再传回前端。
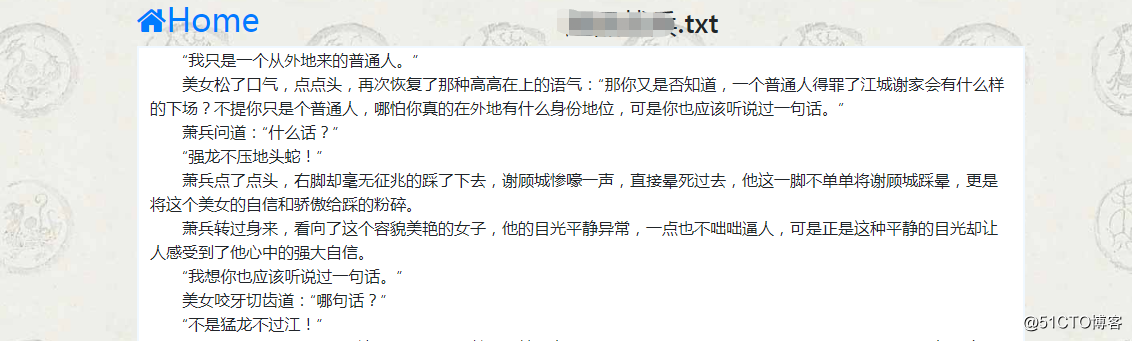

拓展:
1、分页功能有Django内置的Paginator类提供的,该类位于django/core/paginator,需要用的地方导入即可:
from django.core.paginator improt Paginator2、read()、readline()、readlines()方法的区别:
三者都是读取文件内容:
read([size]):从当前位置其读取size字节,如果方法里面没有参数size,读取至文件结束为止。返回的是一个字符串对象。
readline():方法调用一次就读文件一行,该方法返回一个字符串。
readlines():读取整个文件所有行,保存在一个列表中,每行作为一个元素
3、Paginator对象操作:
实例化对象:
book_list = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
book_content = Paginator(book_list,3)
取特定页的数据
content = book_content.page(2)
查特定页当前页码数:
content.number
查分页后的总页数
content.num_pages
查询某一页是否有上一页或者查询上一页页码:
content.has_previous()
content.previous_page_number()
查询某一页是否有下一页或者查询下一页页码:
content.has_next()
content.next_page_number()感兴趣的同学可以上我GitHub上,项目代码的地址:
https://github.com/libuliduobuqiuqiu/noval_test
原文:https://blog.51cto.com/mbb97/2363772