2 1 2 3 4 1 3 5 7 4 2 1 2 3 4 1 4 4 1 1 2 3 4 1 3 5 7 4 1 1 2 3 10 1 4
Case 1: The minimum cost between station 1 and station 4 is 3. The minimum cost between station 4 and station 1 is 3. Case 2: Station 1 and station 4 are not attainable.
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define INF 1e18
const int N = 110;
__int64 x[510], w[N][N], d[N];
__int64 abs(__int64 x)
{
return x >= 0 ? x : -x;
}
void Dijkstra(__int64 n, __int64 u)
{
int vis[N];
__int64 i;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
d[i] = INF;
d[u] = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
__int64 x = u, temp = INF;
for(__int64 y = 1; y <= n; y++)
if(!vis[y] && d[y] < temp)
temp = d[x = y];
if(temp == INF) break;
vis[x] = 1;
for(__int64 y = 1; y <= n; y++)
if(d[y] > d[x] + w[x][y])
d[y] = d[x] + w[x][y];
}
}
int main()
{
__int64 T, n, m, i, j, cas = 0;
__int64 l[5], c[5];
scanf("%I64d",&T);
while(T--)
{
for(i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&l[i]);
for(i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&c[i]);
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&n,&m);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%I64d",&x[i]);
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(i == j)
w[i][j] = 0;
else
{
int temp = abs(x[i] - x[j]);
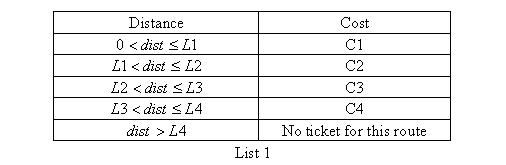
if(temp > 0 && temp <= l[1])
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = c[1];
else if(temp > l[1] && temp <= l[2])
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = c[2];
else if(temp > l[2] && temp <= l[3])
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = c[3];
else if(temp > l[3] && temp <= l[4])
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = c[4];
else if(temp > l[4])
w[i][j] = w[j][i] = INF;
}
}
__int64 u, v;
printf("Case %I64d:\n",++cas);
for(i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%I64d%I64d",&u, &v);
Dijkstra(n, u);
if(d[v] == INF)
printf("Station %I64d and station %I64d are not attainable.\n", u, v);
else
printf("The minimum cost between station %I64d and station %I64d is %I64d.\n",u, v, d[v]);
}
}
return 0;
}Java学习从菜鸟变大鸟之三 多线程中Thread 和Runnable的区别与运用
原文:http://blog.csdn.net/lishehe/article/details/19171659