一、注解解释
Spring的@PostConstruct注解在方法上,表示此方法是在Spring实例化该Bean之后马上执行此方法,之后才会去实例化其他Bean,并且一个Bean中@PostConstruct注解的方法可以有多个。
二、示例代码
1. spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd "> <!-- 引入属性文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:config.properties" /> <!-- 自动扫描dao和service包(自动注入) --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.wbf.bean" /> </beans>
2. Bean1.java
1 package com.wbf.bean; 2 3 import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; 4 5 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 7 8 @Service("bean1") 9 public class Bean1 { 10 11 private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Bean1.class); 12 13 public Bean1() { 14 log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": Bean1 Constructor"); 15 } 16 17 @PostConstruct 18 public void test() { 19 log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": bean1-->test()"); 20 Bean2.uniqueInstance().test(); 21 22 } 23 24 @PostConstruct 25 public void print() { 26 log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": bean1-->print()"); 27 } 28 }
3. Bean2.java
package com.wbf.bean; import org.apache.log4j.Logger; public class Bean2 { private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Bean2.class); private static Bean2 instance = uniqueInstance(); public static Bean2 uniqueInstance() { if (instance == null) instance = new Bean2(); return instance; } public Bean2() { log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": Bean2 Construtor"); } public void test() { log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": bean2-->test()"); } }
4. Bean3.java
1 package com.wbf.bean; 2 3 import org.apache.log4j.Logger; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; 5 6 @Service("bean3") 7 public class Bean3 { 8 9 private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Bean3.class); 10 11 public Bean3() { 12 log.info(System.currentTimeMillis() + ": Bean3 Construtor"); 13 } 14 15 }
5. SpringTest.java
1 package com.wbf.bean; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 5 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 6 7 public class SpringTest { 8 9 @Test 10 public void test() { 11 //加载/解析spring.xml, 得到BeanFactory, 实例化所有IOC容器中的Bean 12 //在实例化每一个Bean之后,如果当前Bean包含@PostConstruct注解的方法则会马上执行该方法,之后才会去实例化其他的Bean 13 //每一个Bean中可以有多个包含@PostConstruct注解的方法 14 ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[]{"classpath:spring.xml"}); 15 } 16 17 }
运行结果:
[org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext]Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@b0f2b2: startup date [Thu Jun 11 11:51:17 CST 2015]; root of context hierarchy [org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader]Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [spring.xml] [org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer]Loading properties file from class path resource [config.properties] [org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor]JSR-330 ‘javax.inject.Inject‘ annotation found and supported for autowiring [org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory]Pre-instantiating singletons in org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory@1b8dc93: defining beans [org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer#0,bean1,bean3,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.internalPersistenceAnnotationProcessor,org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.importAwareProcessor]; root of factory hierarchy [com.wbf.bean.Bean1]1433994678340: Bean1 Constructor [com.wbf.bean.Bean1]1433994678347: bean1-->print() [com.wbf.bean.Bean1]1433994678347: bean1-->test() [com.wbf.bean.Bean2]1433994678348: Bean2 Construtor [com.wbf.bean.Bean3]1433994678348: Bean3 Construtor
从运行结果可以看出Spring在实例化Bean1之后马上执行了它的@PostConstruct注解的方法print()和test(),之后才去实例化Bean3。其中Bean2没有被Spring IOC容器管理。
三、补充说明
1.@PostConstruct说明
被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servlet(bean)的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Serclet的inti()方法。被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在构造函数之后,init()方法之前运行。
2.@PreDestroy说明
被@PreDestroy修饰的方法会在服务器卸载Servlet(bean)的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Servlet的destroy()方法。被@PreDestroy修饰的方法会在destroy()方法之后运行,在Servlet被彻底卸载之前
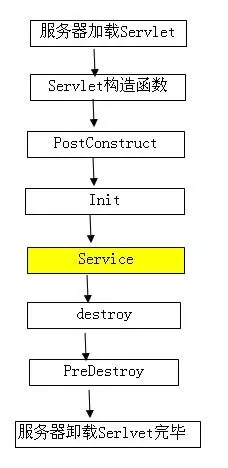
另外,spring中Constructor、@Autowired、@PostConstruct的顺序
其实从依赖注入的字面意思就可以知道,要将对象p注入到对象a,那么首先就必须得生成对象a和对象p,才能执行注入。所以,如果一个类A中有个成员变量p被@Autowried注解,那么@Autowired注入是发生在A的构造方法执行完之后的。
如果想在生成对象时完成某些初始化操作,而偏偏这些初始化操作又依赖于依赖注入,那么久无法在构造函数中实现。为此,可以使用@PostConstruct注解一个方法来完成初始化,@PostConstruct注解的方法将会在依赖注入完成后被自动调用。
Constructor >> @Autowired >> @PostConstruct
举个例子:
1 public Class AAA{ 2 @Autowired 3 private BBB b; 4 5 public AAA() { 6 System.out.println("此时b还未被注入: b = " + b); 7 } 8 @PostConstruct 9 private void init () { 10 System.out.println("@PostConstruct将在依赖注入完成后被自动调用: b = " + b); 11 } 12 }
pring注解之@PostConstruct在项目启动时执行指定方法
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/fnlingnzb-learner/p/10758848.html