更多精彩内容请关注微信公众号:听潮庭。
综述:
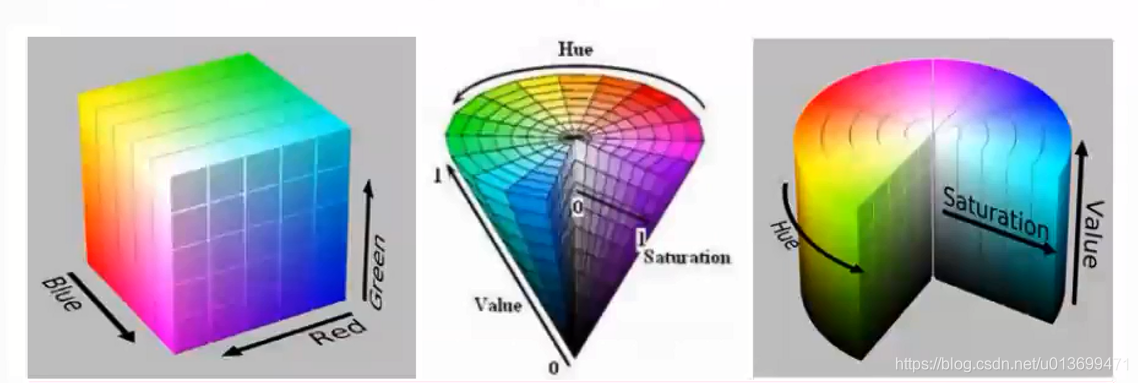




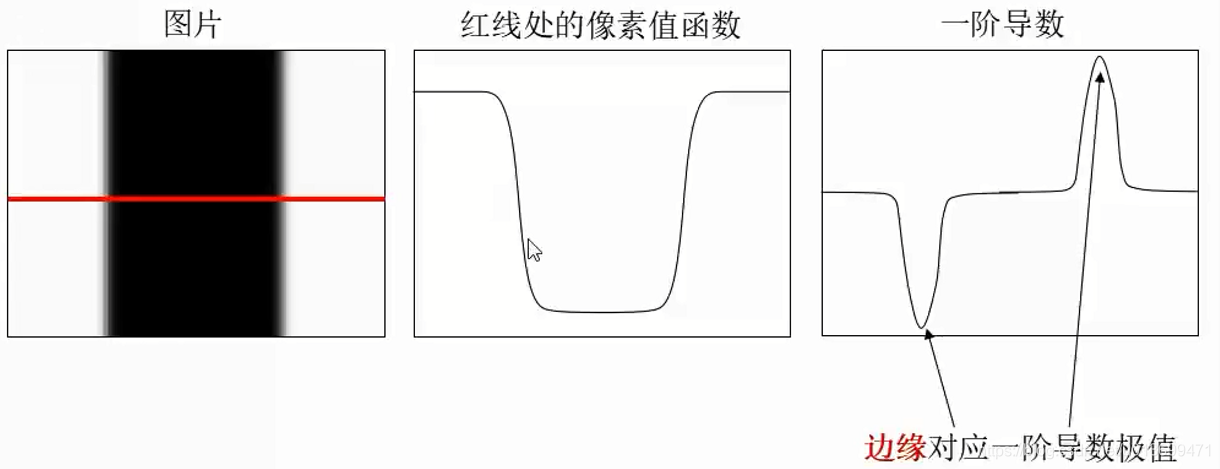
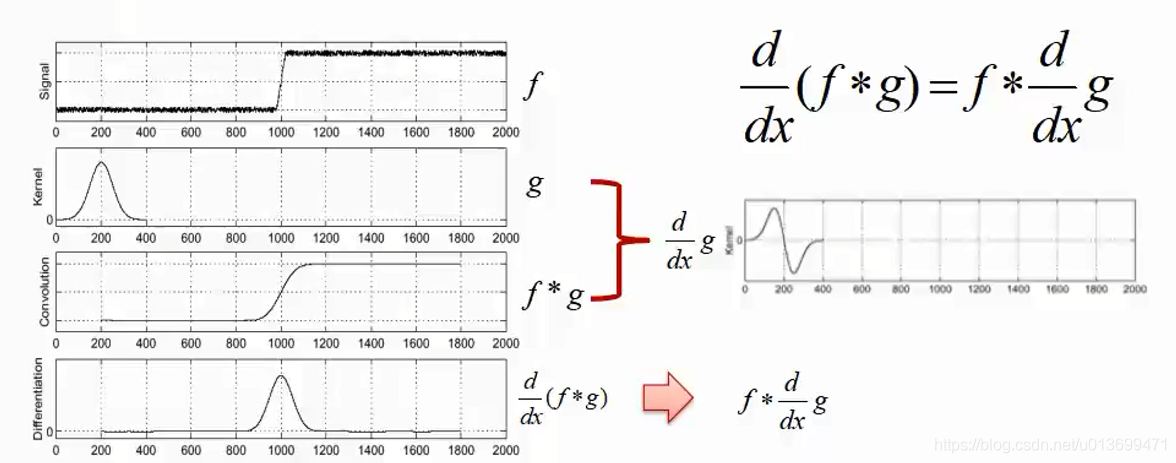
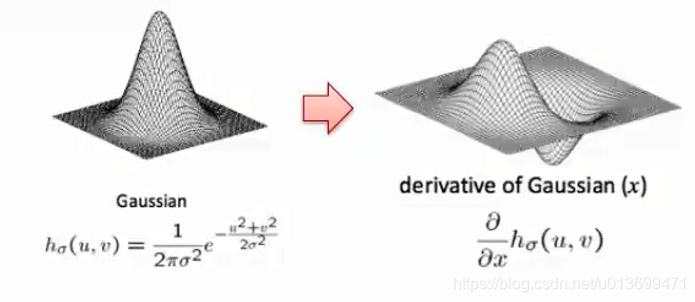
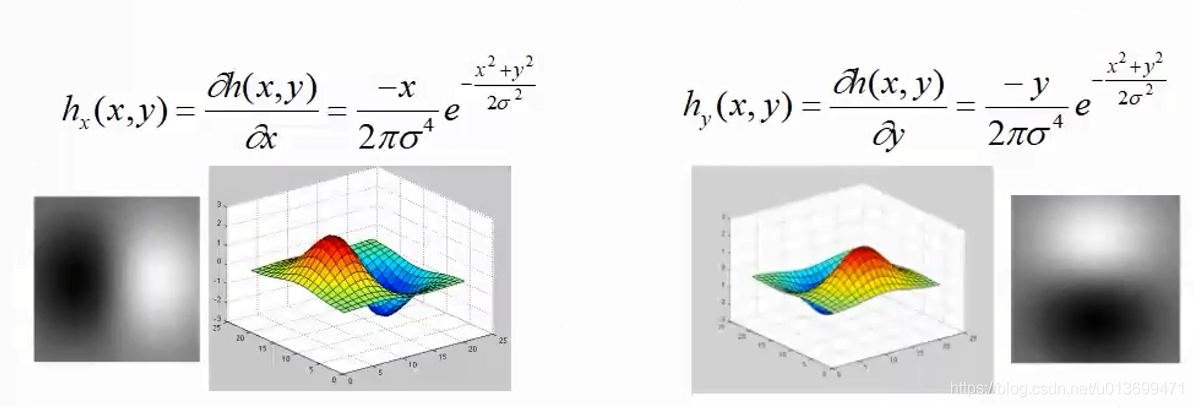
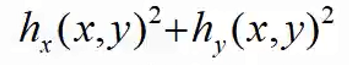
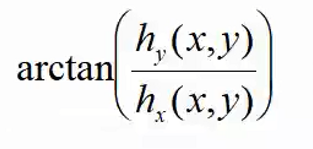
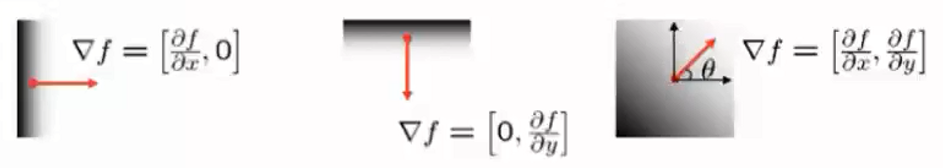
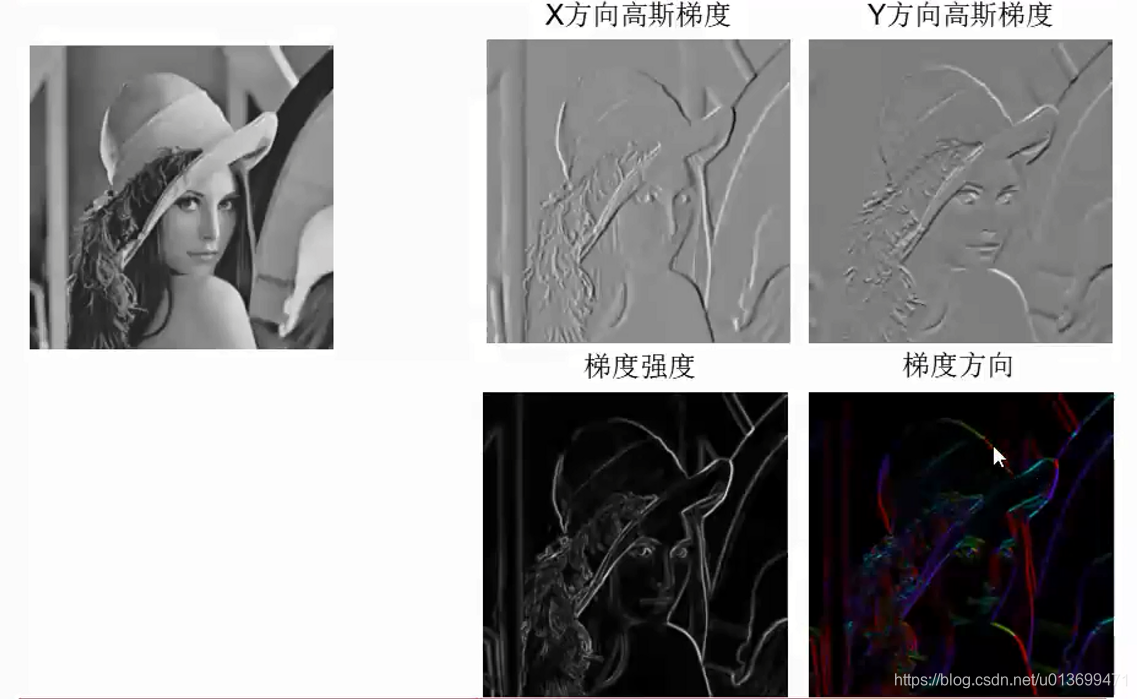
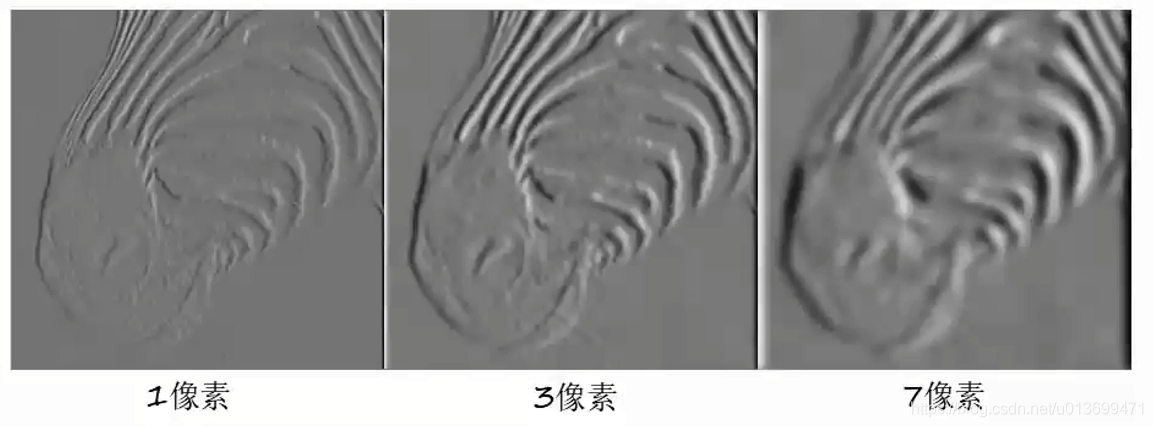
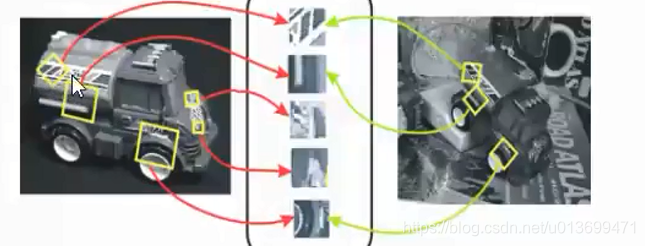

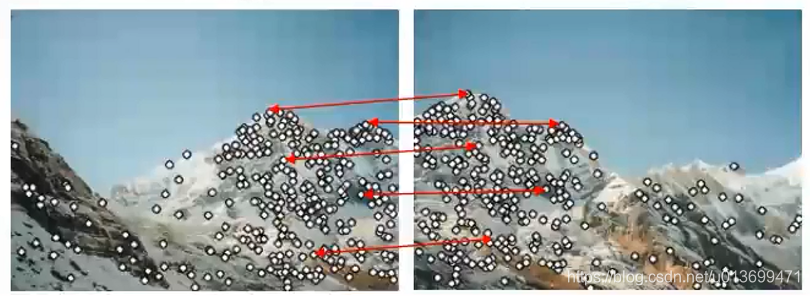

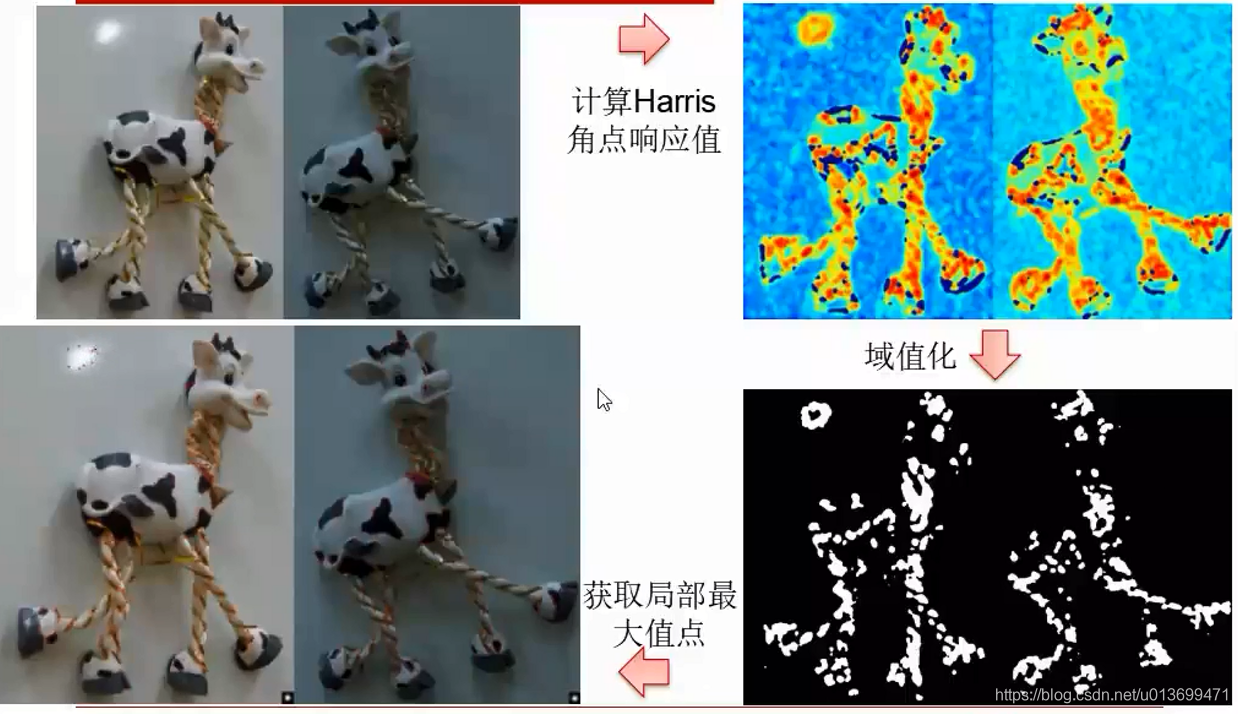
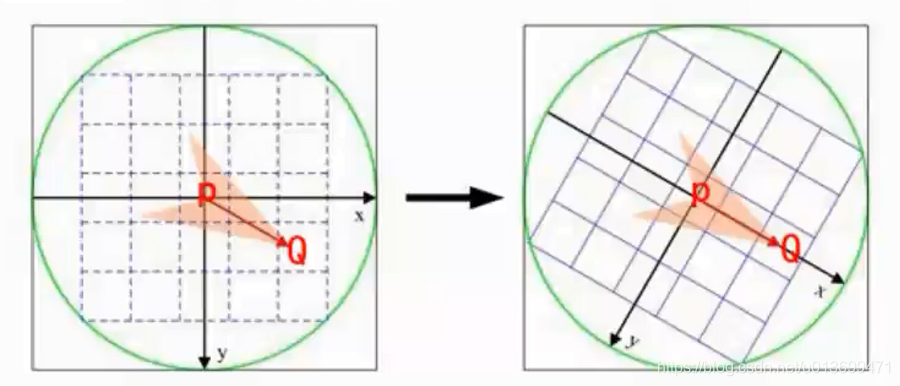
Harris角点(Corner)
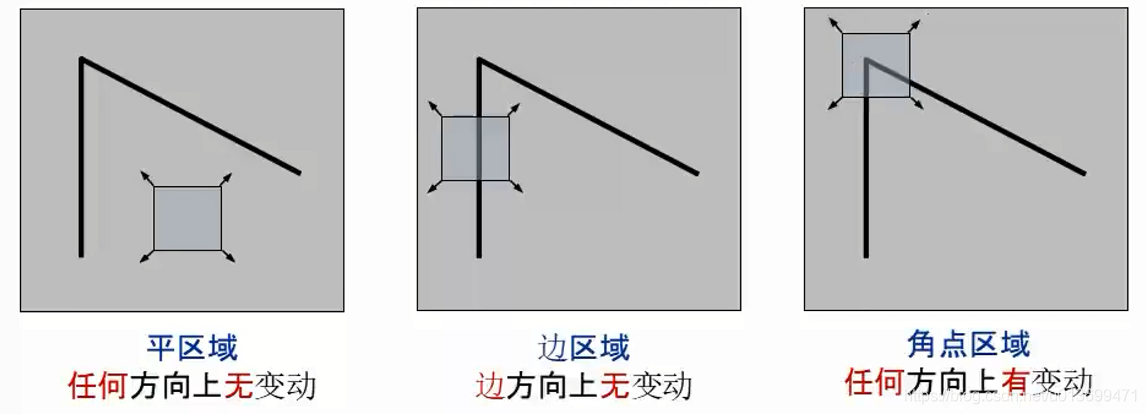

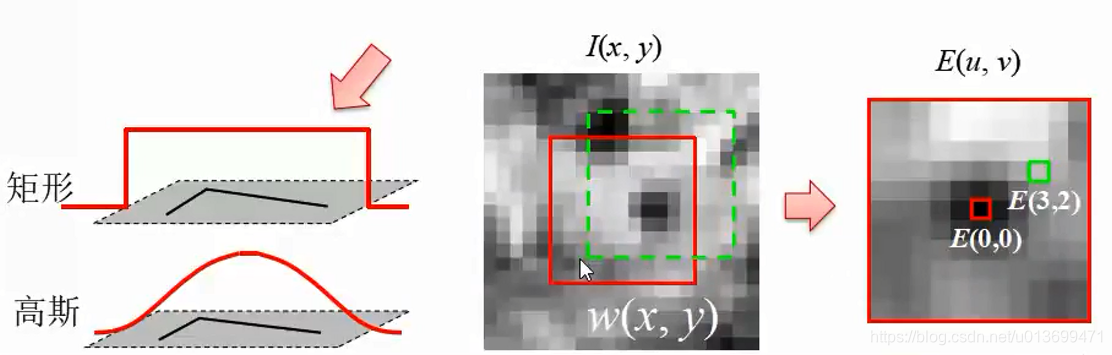
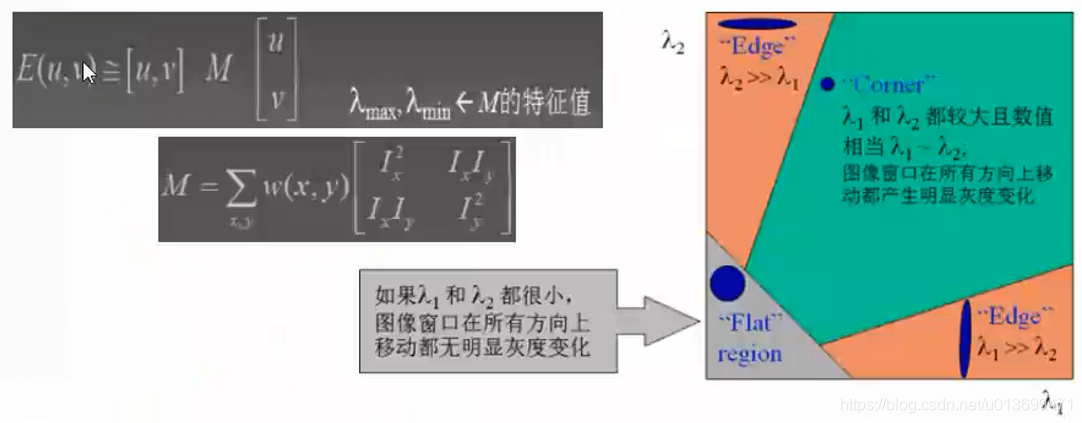
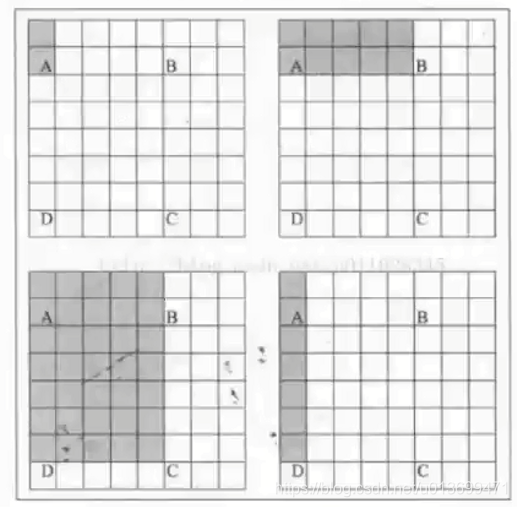
判断Harris角点:
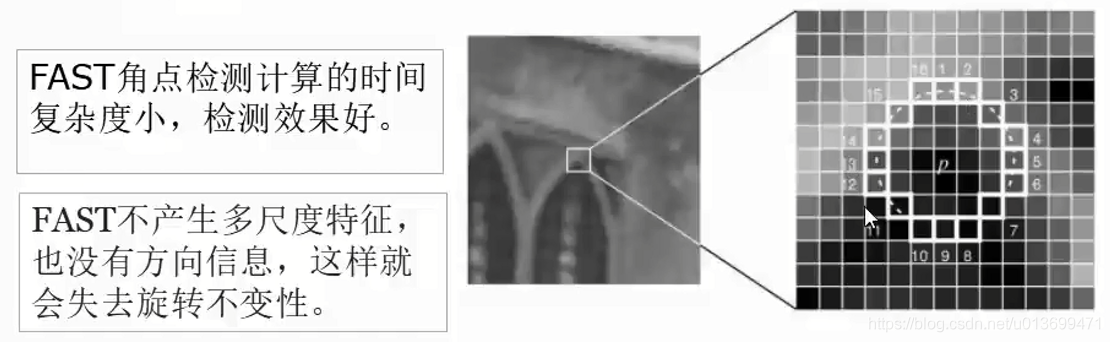
FAST角点检测是一种快速角点特征检测算法。
FAST角点定义为:若某像素点与其周围领域内足够多的像素点处于不同的区域,则该像素点可能为角点,也就是某些属性与众不同。
FAST特征点检测是对兴趣点所在圆周上的16个像素点进行判断,若判断后的当前中心像素点为暗或亮,将决定其是否为角点。
确定一个阈值t,观察某像素点为中心的一个半径等于3像素的离散化的圆,这个圆的边界上有16个像素。
如果在这个大小为16个像素的圆上有N(12)个连续的像素点,他们的像素值要么都比
I_p+tIp?+t
大,要么都比
I_p-tIp?−t
小,则p他就是一个角点。
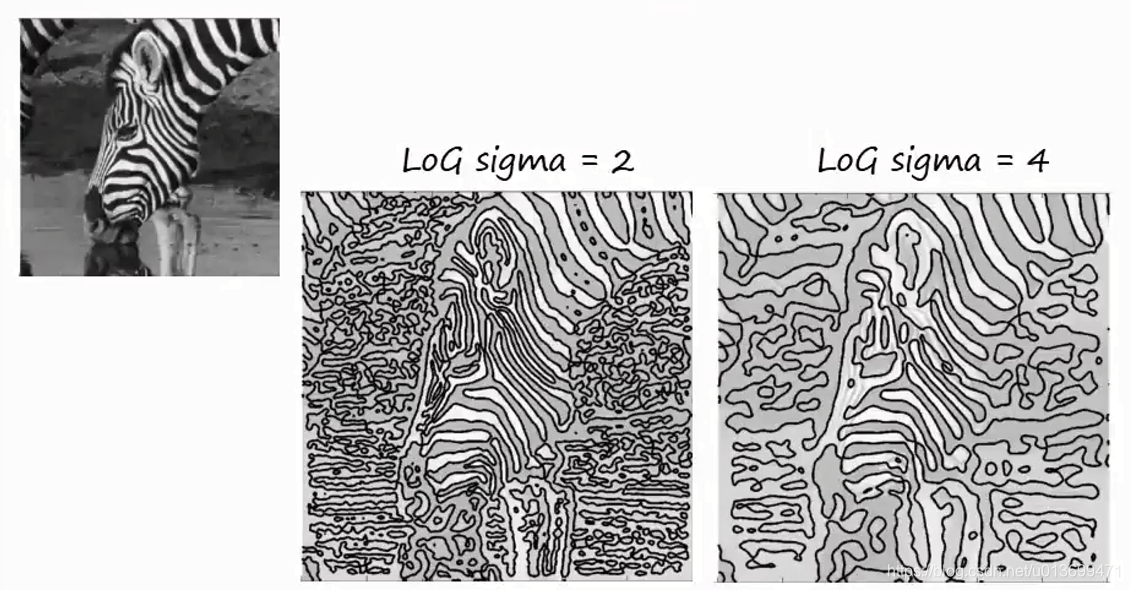
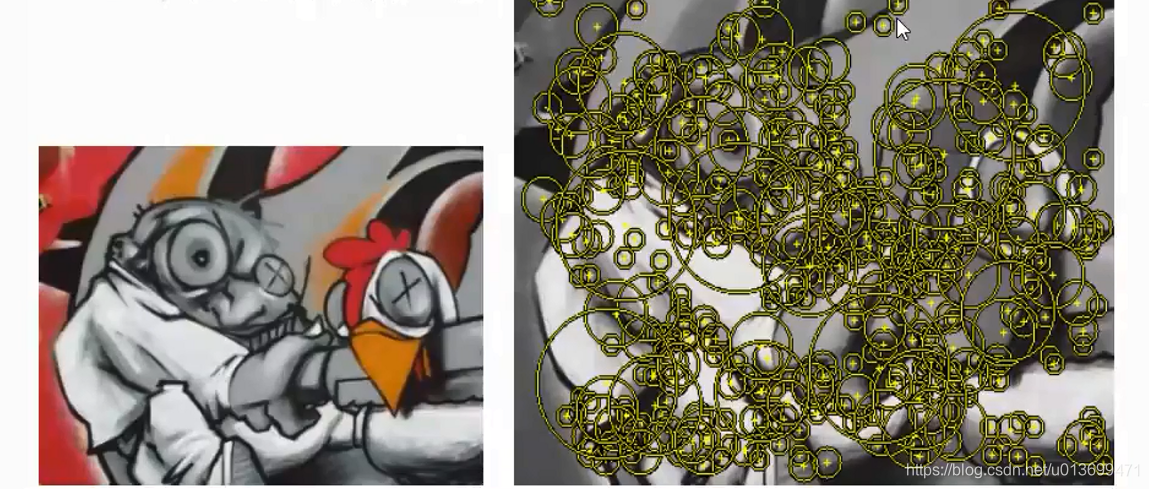
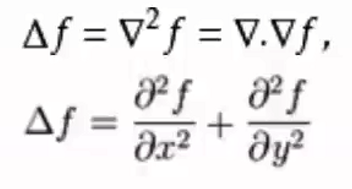
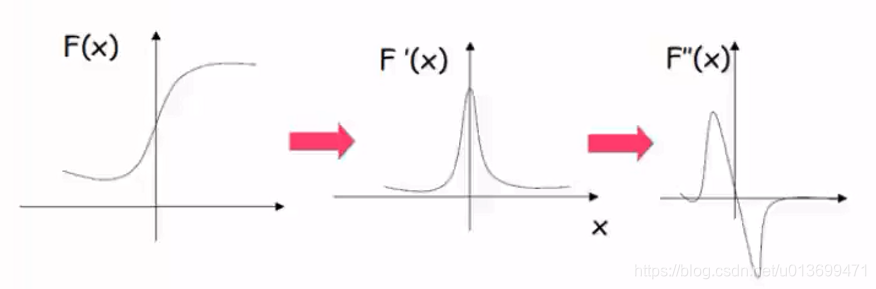
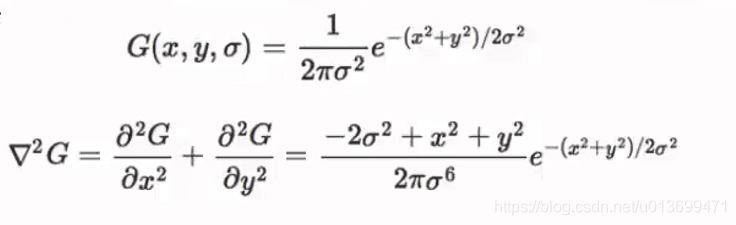
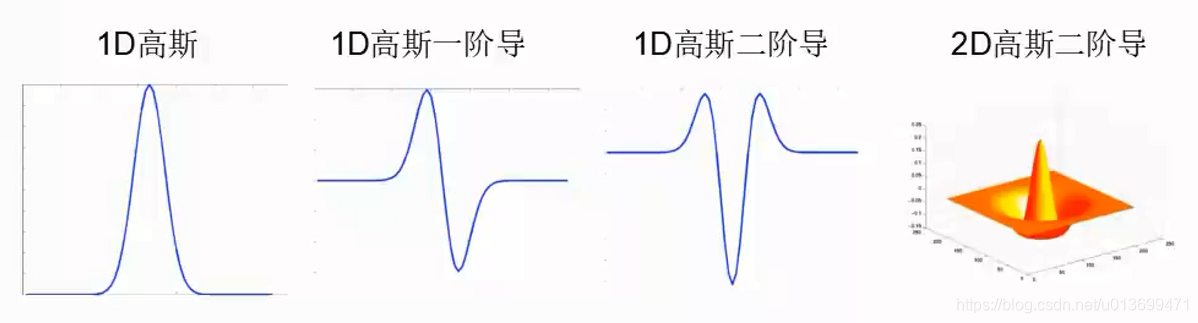


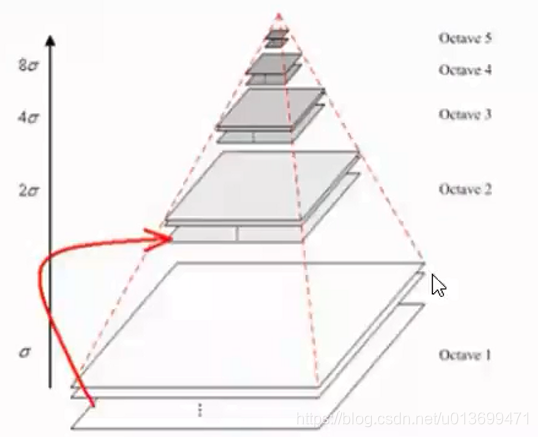

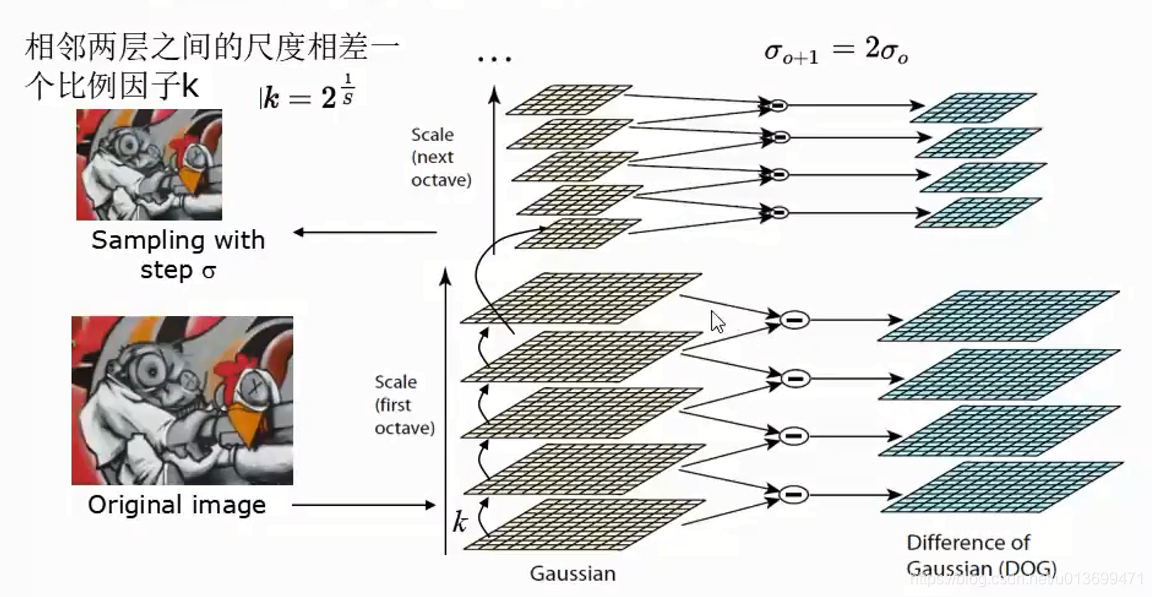
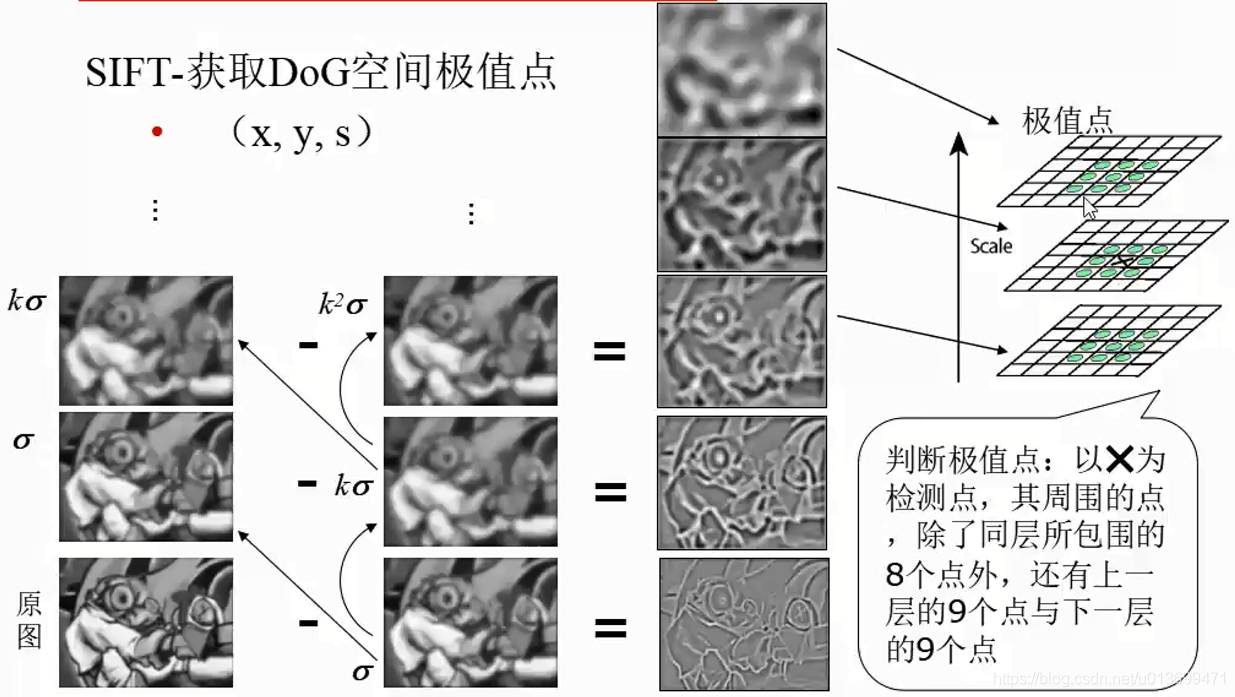

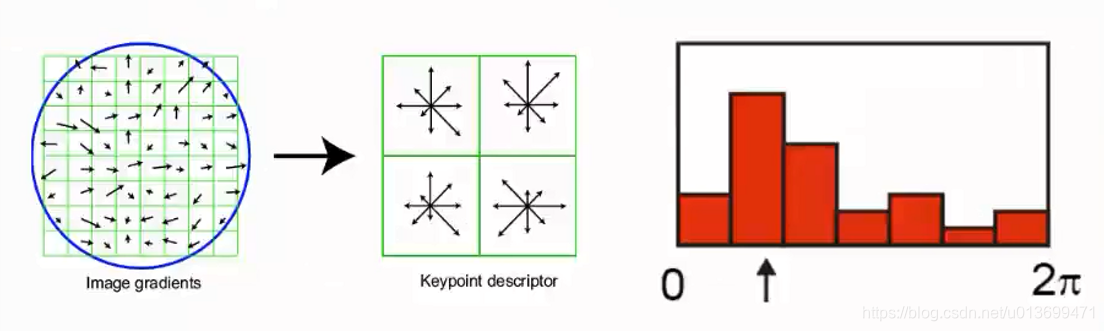
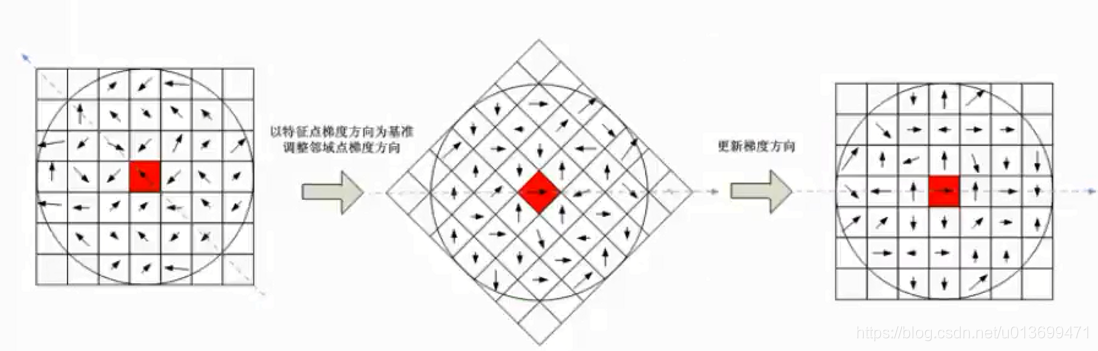
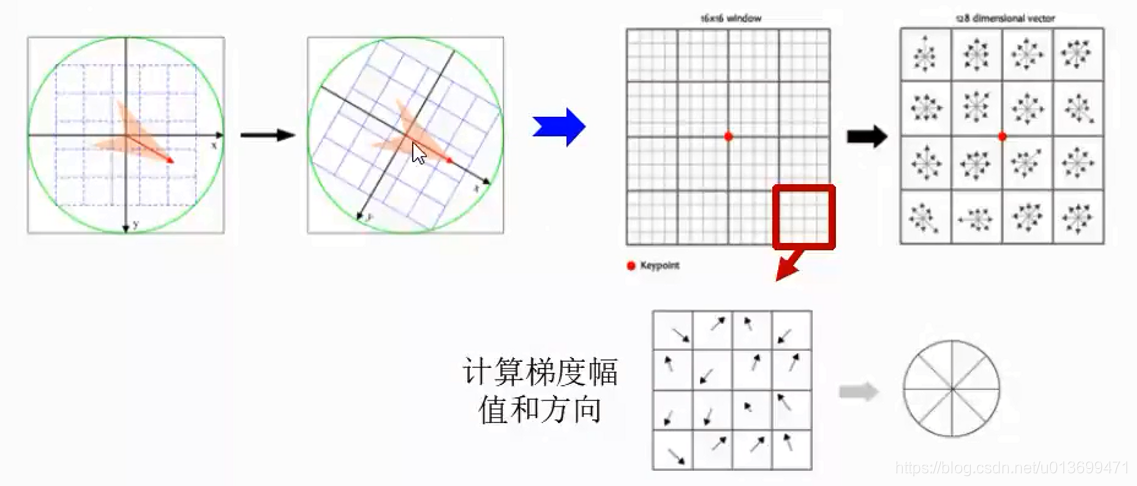
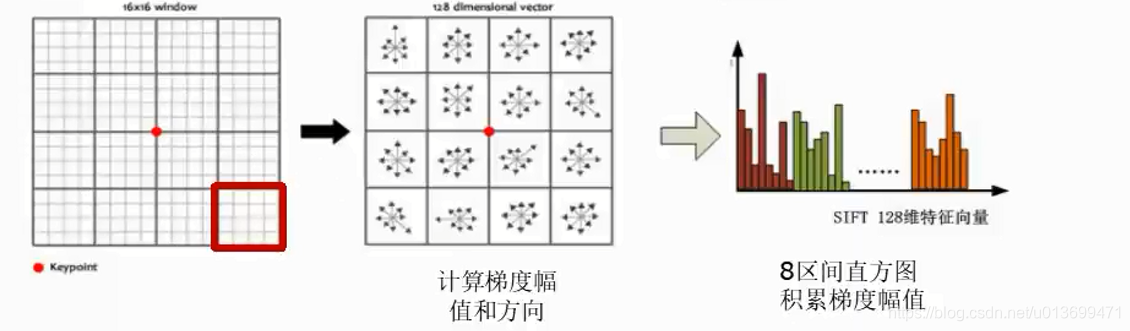

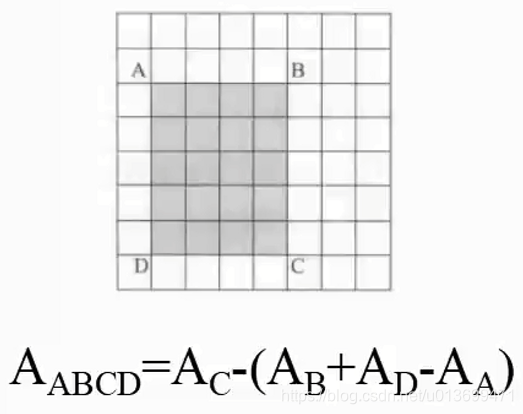
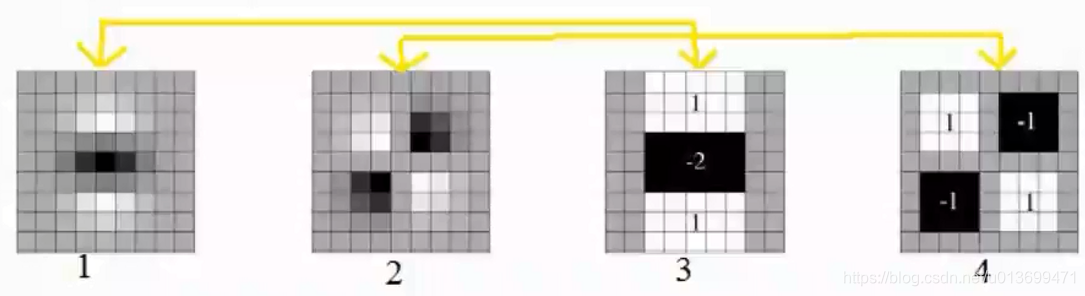
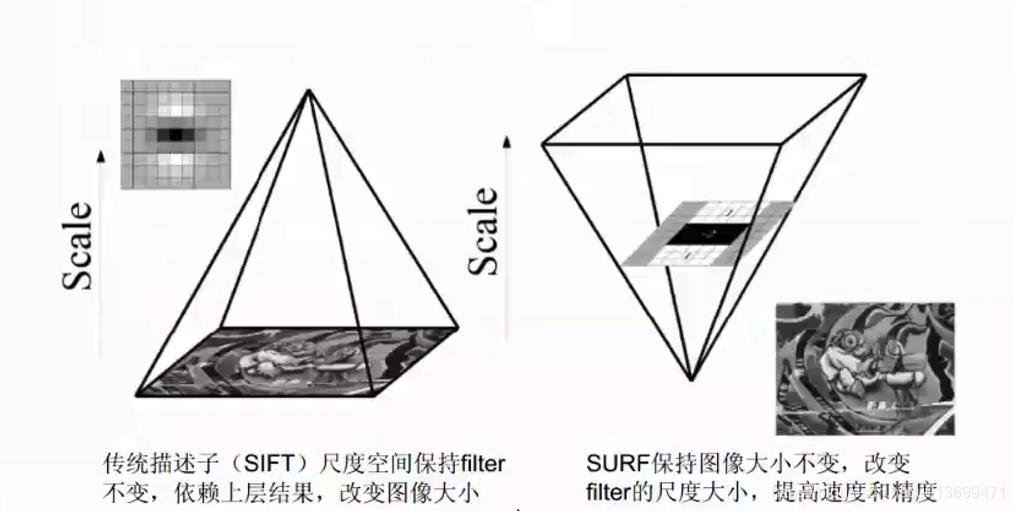
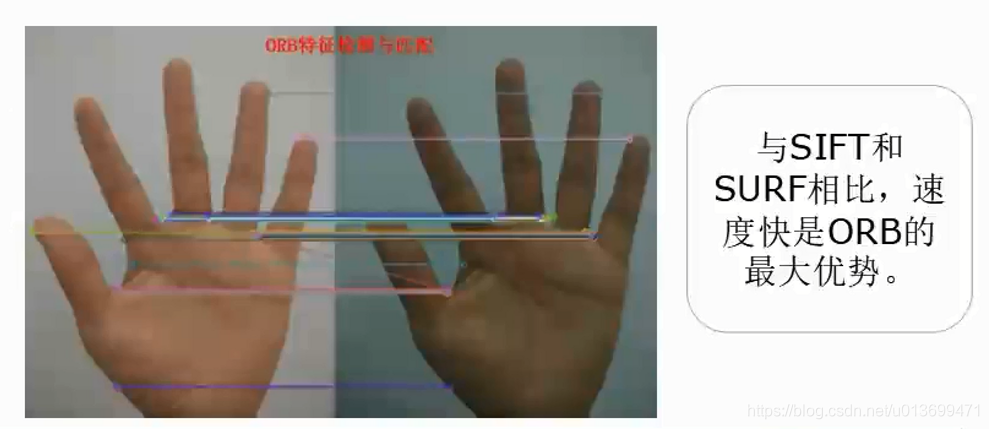
SURF(Speed-Up Robust Features)算子是Herbert Bay等人在2006年提出的,它是对SIFT的改进,可将速度提高三倍。
SURF只要是把SIFT中的某些运算做了简化。
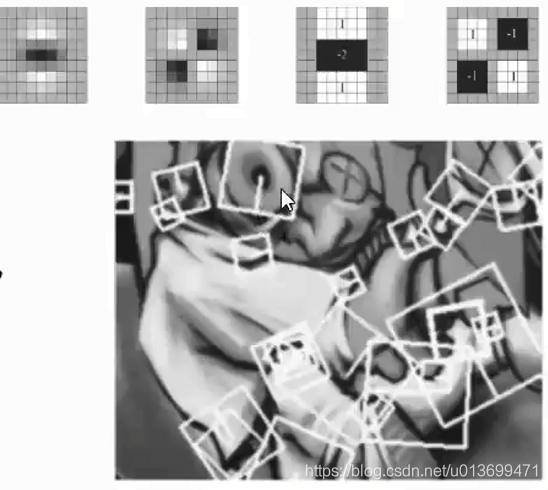
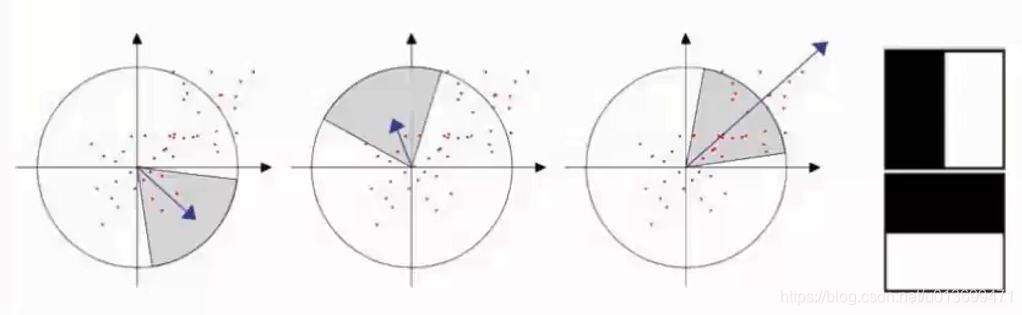
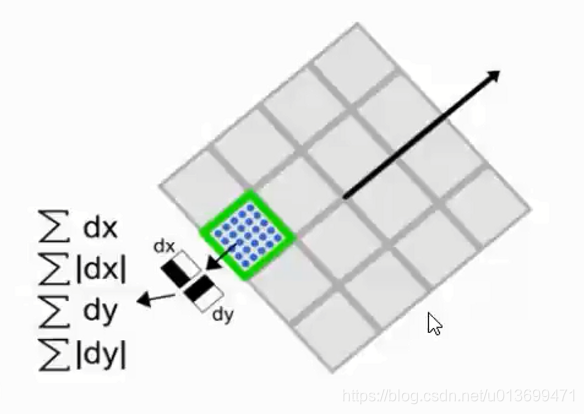

BRIEF需要先平滑图片,然后在特征点周围选择一个Patch,在这个Patch内通过一种选定的方法来挑选Nd个点对。
比较点对中两点像素的大小,进行如下赋值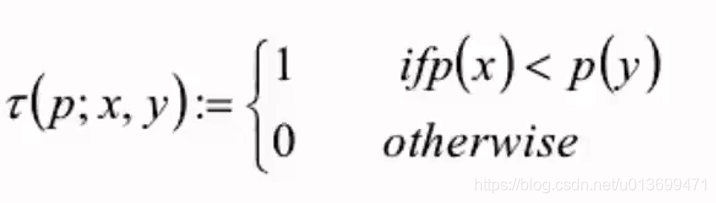
所有Nd个点对,都进行比较之间,我们就生成了一个Nd长的二进制串。
点对的生成方式(共有五种)
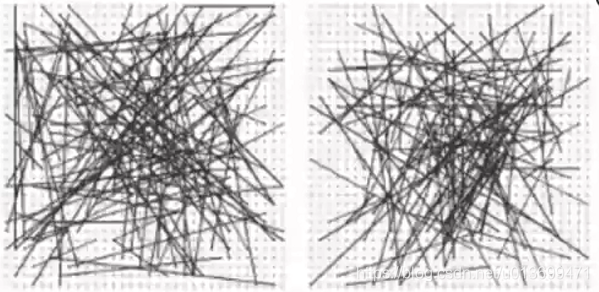
点对的位置一旦随机选定,就不能再更改
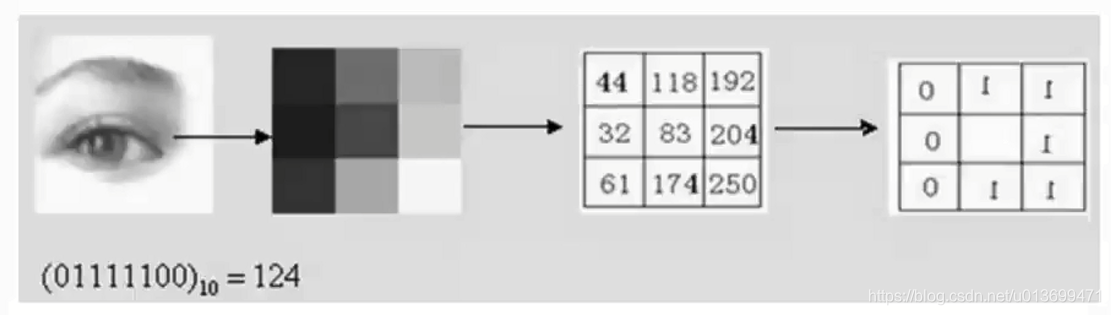
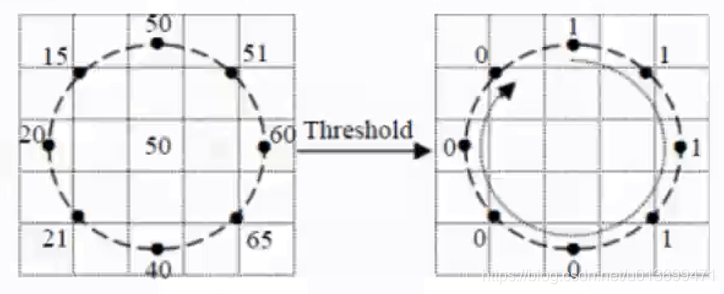
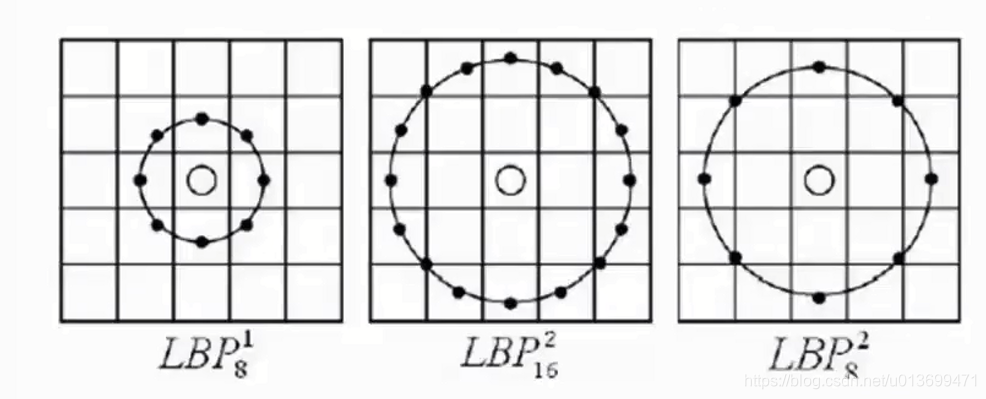
LBP(局部二值模式)
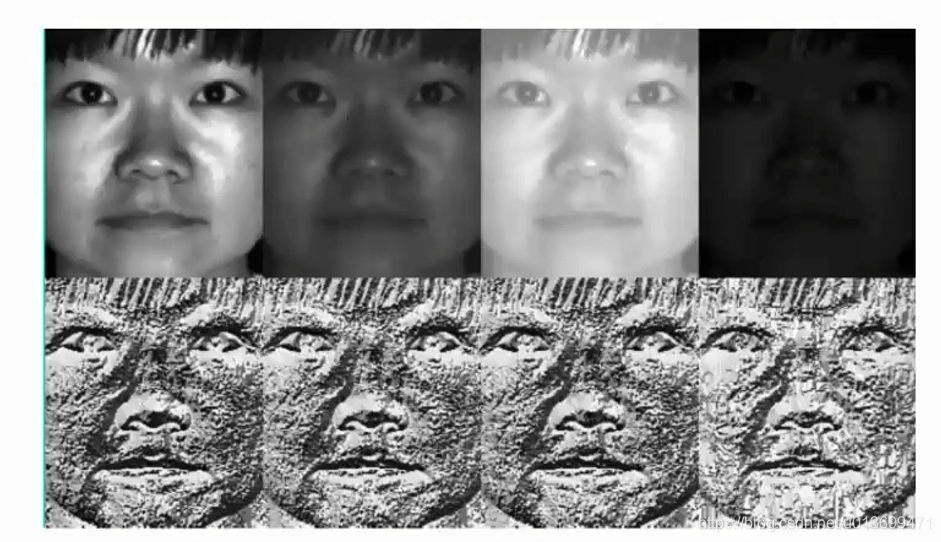

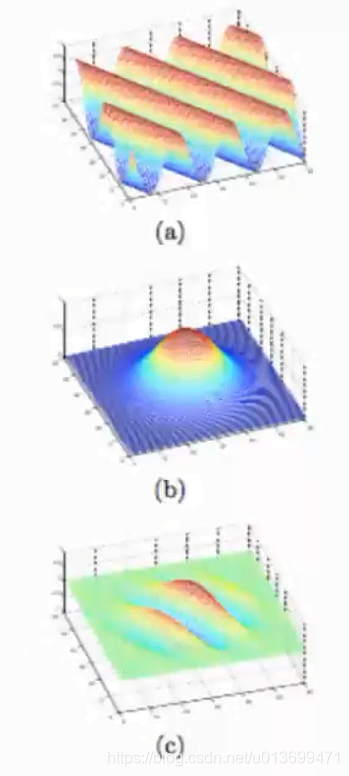
Gabor滤波器组类似于人类的视觉系统
Gabor滤波器
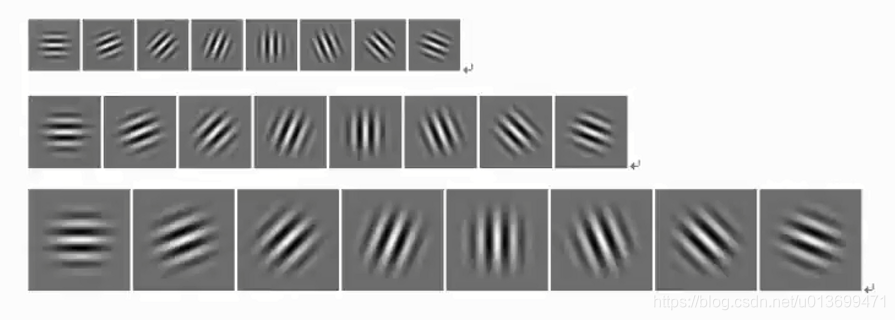
三尺度
八方向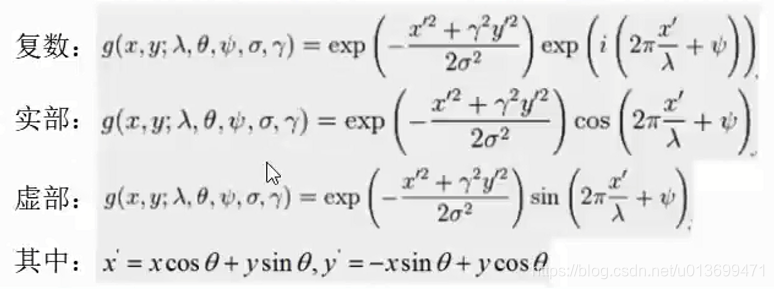
1 import numpy as np 2 import cv2 as cv 3 filename = "picture/chessboard.png" 4 img = cv.imread(filename) 5 gray = cv.cvtColor(img,cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 6 gray = np.float32(gray) 7 dst = cv.cornerHarris(gray,2,3,0.04) 8 #result is dilated for marking the corners, not important 9 dst = cv.dilate(dst,None) 10 # Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image. 11 img[dst>0.01*dst.max()]=[0,0,255] 12 cv.imshow(‘dst‘,img) 13 if cv.waitKey(0) & 0xff == 27: 14 cv.destroyAllWindows()
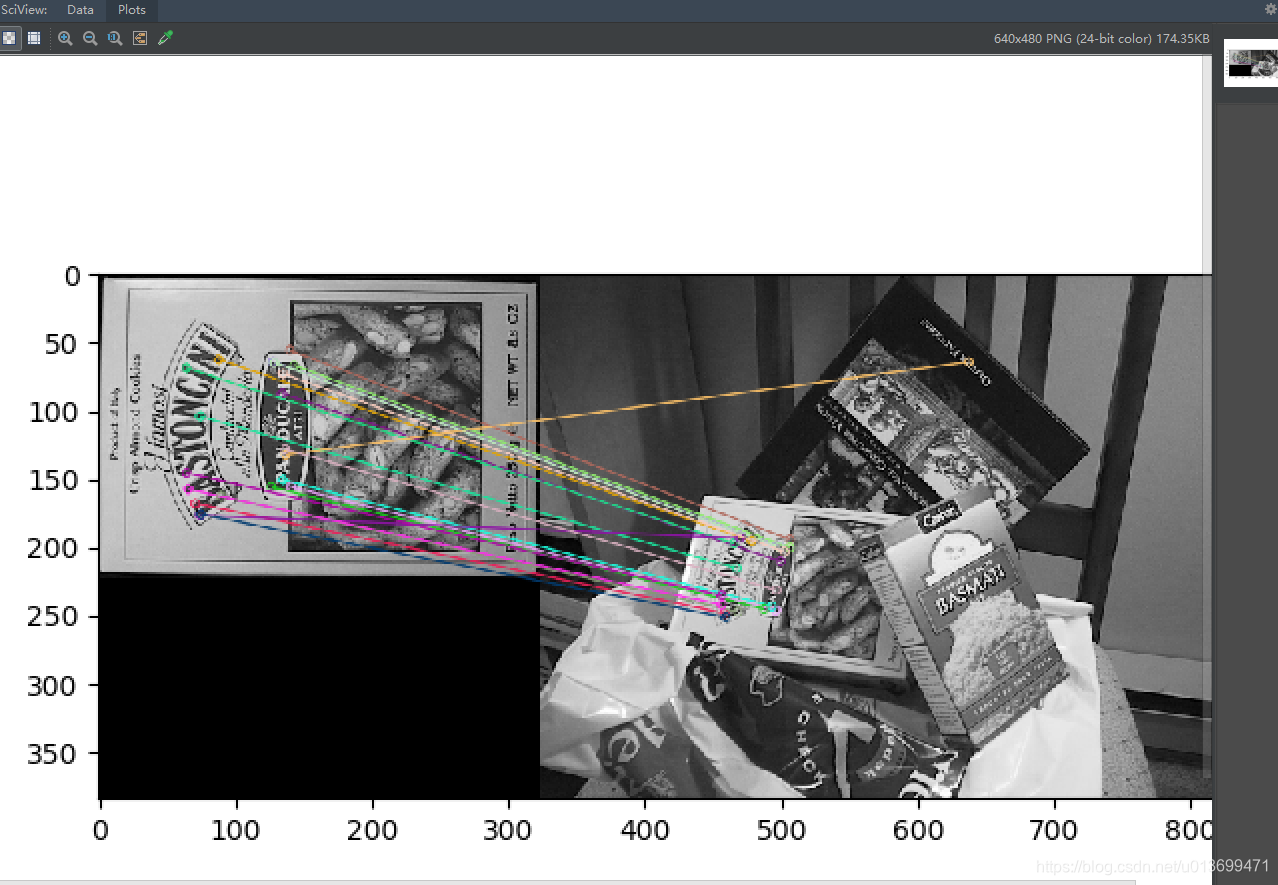
1 import numpy as np 2 import cv2 as cv 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 img1 = cv.imread(‘picture/box.png‘,0) # queryImage 5 img2 = cv.imread(‘picture/box_in_scene.png‘,0) # trainImage 6 # Initiate ORB detector 7 orb = cv.ORB_create() 8 # find the keypoints and descriptors with ORB 9 kp1, des1 = orb.detectAndCompute(img1,None) 10 kp2, des2 = orb.detectAndCompute(img2,None) 11 12 # create BFMatcher object 13 bf = cv.BFMatcher(cv.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True) 14 # Match descriptors. 15 matches = bf.match(des1,des2) 16 # Sort them in the order of their distance. 17 matches = sorted(matches, key = lambda x:x.distance) 18 # Draw first 10 matches. 19 img3 = cv.drawMatches(img1,kp1,img2,kp2,matches[:20],None, flags=2) 20 plt.imshow(img3),plt.show()
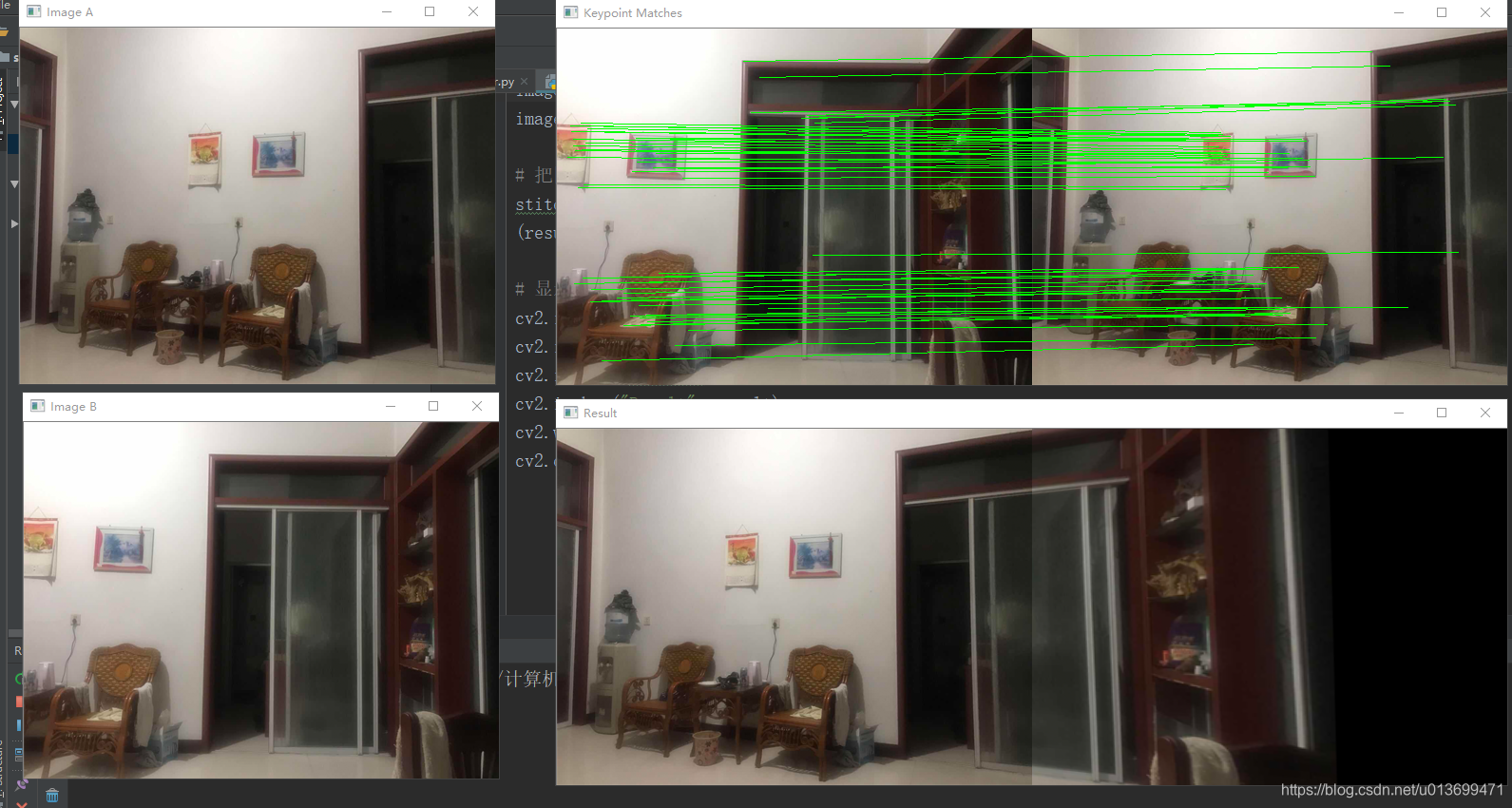
1 from Stitcher import Stitcher 2 import cv2 3 4 # 读取拼接图片 5 imageA = cv2.imread("image/3.png") 6 imageB = cv2.imread("image/4.png") 7 8 # 把图片拼接成全景图 9 stitcher = Stitcher() 10 (result, vis) = stitcher.stitch([imageA, imageB], showMatches=True) 11 12 # 显示所有图片 13 cv2.imshow("Image A", imageA) 14 cv2.imshow("Image B", imageB) 15 cv2.imshow("Keypoint Matches", vis) 16 cv2.imshow("Result", result) 17 cv2.waitKey(0) 18 cv2.destroyAllWindows()
1 import numpy as np 2 import cv2 3 4 class Stitcher: 5 6 #拼接函数 7 def stitch(self, images, ratio=0.75, reprojThresh=4.0,showMatches=False): 8 #获取输入图片 9 (imageB, imageA) = images 10 #检测A、B图片的SIFT关键特征点,并计算特征描述子 11 (kpsA, featuresA) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageA) 12 (kpsB, featuresB) = self.detectAndDescribe(imageB) 13 14 # 匹配两张图片的所有特征点,返回匹配结果 15 M = self.matchKeypoints(kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh) 16 17 # 如果返回结果为空,没有匹配成功的特征点,退出算法 18 if M is None: 19 return None 20 21 # 否则,提取匹配结果 22 # H是3x3视角变换矩阵 23 (matches, H, status) = M 24 # 将图片A进行视角变换,result是变换后图片 25 result = cv2.warpPerspective(imageA, H, (imageA.shape[1] + imageB.shape[1], imageA.shape[0])) 26 # 将图片B传入result图片最左端 27 result[0:imageB.shape[0], 0:imageB.shape[1]] = imageB 28 29 # 检测是否需要显示图片匹配 30 if showMatches: 31 # 生成匹配图片 32 vis = self.drawMatches(imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status) 33 # 返回结果 34 return (result, vis) 35 36 # 返回匹配结果 37 return result 38 39 def detectAndDescribe(self, image): 40 # 将彩色图片转换成灰度图 41 gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) 42 43 # 建立SIFT生成器 44 descriptor = cv2.xfeatures2d.SIFT_create() 45 # 检测SIFT特征点,并计算描述子 46 (kps, features) = descriptor.detectAndCompute(image, None) 47 48 # 将结果转换成NumPy数组 49 kps = np.float32([kp.pt for kp in kps]) 50 51 # 返回特征点集,及对应的描述特征 52 return (kps, features) 53 54 def matchKeypoints(self, kpsA, kpsB, featuresA, featuresB, ratio, reprojThresh): 55 # 建立暴力匹配器 56 matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create("BruteForce") 57 58 # 使用KNN检测来自A、B图的SIFT特征匹配对,K=2 59 rawMatches = matcher.knnMatch(featuresA, featuresB, 2) 60 61 matches = [] 62 for m in rawMatches: 63 # 当最近距离跟次近距离的比值小于ratio值时,保留此匹配对 64 if len(m) == 2 and m[0].distance < m[1].distance * ratio: 65 # 存储两个点在featuresA, featuresB中的索引值 66 matches.append((m[0].trainIdx, m[0].queryIdx)) 67 68 # 当筛选后的匹配对大于4时,计算视角变换矩阵 69 if len(matches) > 4: 70 # 获取匹配对的点坐标 71 ptsA = np.float32([kpsA[i] for (_, i) in matches]) 72 ptsB = np.float32([kpsB[i] for (i, _) in matches]) 73 74 # 计算视角变换矩阵 75 (H, status) = cv2.findHomography(ptsA, ptsB, cv2.RANSAC, reprojThresh) 76 77 # 返回结果 78 return (matches, H, status) 79 80 # 如果匹配对小于4时,返回None 81 return None 82 83 def drawMatches(self, imageA, imageB, kpsA, kpsB, matches, status): 84 # 初始化可视化图片,将A、B图左右连接到一起 85 (hA, wA) = imageA.shape[:2] 86 (hB, wB) = imageB.shape[:2] 87 vis = np.zeros((max(hA, hB), wA + wB, 3), dtype="uint8") 88 vis[0:hA, 0:wA] = imageA 89 vis[0:hB, wA:] = imageB 90 91 # 联合遍历,画出匹配对 92 for ((trainIdx, queryIdx), s) in zip(matches, status): 93 # 当点对匹配成功时,画到可视化图上 94 if s == 1: 95 # 画出匹配对 96 ptA = (int(kpsA[queryIdx][0]), int(kpsA[queryIdx][1])) 97 ptB = (int(kpsB[trainIdx][0]) + wA, int(kpsB[trainIdx][1])) 98 cv2.line(vis, ptA, ptB, (0, 255, 0), 1) 99 100 # 返回可视化结果 101 return vis
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/thinkinpakho/p/10880797.html