题库链接: 1041. 困于环中的机器人.
在无限的平面上,机器人最初位于 (0, 0) 处,面朝北方。机器人可以接受下列三条指令之一:
只有在平面中存在环使得机器人永远无法离开时,返回 true。否则,返回 false。
输入:"GGLLGG" 输出:true 解释:机器人从 (0,0) 移动到 (0,2),转 180 度,然后回到 (0,0)。 重复这些指令,机器人将保持在以原点为中心,2 为半径的环中进行移动。
输入:"GG" 输出:false 解释:机器人无限向北移动。
输入:"GL" 输出:true 解释: 机器人按 (0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (-1, 1) -> (-1, 0) -> (0, 0) -> ... 进行移动。
class Solution(object): def isBoomerang(self, points): """ :type points: List[List[int]] :rtype: bool """ A,B,C=points return (A[0]-B[0])*(B[1]-C[1])-(A[1]-B[1])*(B[0]-C[0])!=0
题库链接: 237. 删除链表中的节点.
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点,你将只被给定要求被删除的节点。
现有一个链表 -- head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
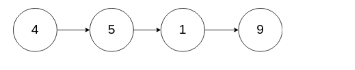
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5 输出: [4,1,9] 解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1 输出: [4,5,9] 解释: 给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9 .
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def deleteNode(self, node): """ :type node: ListNode :rtype: void Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead. """ node.val, node.next = node.next.val, node.next.next

题库链接: 1. 两数之和.
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,你不能重复利用这个数组中同样的元素。
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9 所以返回 [0, 1]
class Solution(object): def twoSum(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: List[int] """ for i in range(len(nums)): for k in range(i + 1, len(nums)): if nums[i] + nums[k] == target: return [i, k] break
运行结果

当然解法一是非常暴力的会消耗很长时间和内存空间,接下来介绍一个更好的解法。
class Solution: def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]: hashmap = {} for index, num in enumerate(nums): another_num = target - num if another_num in hashmap: return [hashmap[another_num], index] hashmap[num] = index return None
结尾

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/tiandi-fun/p/10887477.html