题意翻译
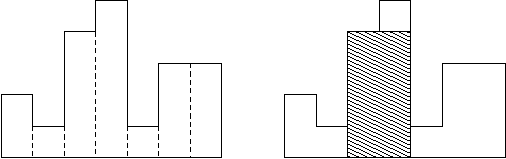
如图所示,在一条水平线上有n个宽为1的矩形,求包含于这些矩形的最大子矩形面积(图中的阴影部分的面积即所求答案)。
输入格式:
有多组测试数据,每组数据占一行。输入零时读入结束。
每行开头为一个数字n(1<=n<=100000),接下来在同一行给出n个数字h1h2...hn(0<=hi<=1000000000)表示每个矩形的高度。
输出格式:
对于每组数据,输出最大子矩阵面积,一组数据输出一行。
题目描述
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
思路:
单调栈的运用
把矩形按照高度一次递增的循序排列,当违反这一规则的时候,更新ans,用新的data替换之前的矩形。然后最后扫一遍。
#include<cmath>
#include<stack>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1000010;
long long ans;
int n,a[N],last;
struct node {
int high,id;
} now;
stack<node> st;
inline long long max(long long x,long long y) {
return x>y?x:y;
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
while(1) {
if(n==0)
break;
ans=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
a[n+1]=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n+1; i++) {
last=i;
while(!st.empty()&&st.top().high>a[i]) {
ans=max(ans,(1ll*i-st.top().id)*st.top().high);
last=st.top().id;
st.pop();
}
now.high=a[i];
now.id=last;
st.push(now);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
scanf("%d",&n);
}
return 0;
}
