本场比赛的最后一题,不过好像并没有任何防AK的作用。
至于YQOI,那是没前缀名看了不顺眼。
树链剖分模板题?有点像。
给定一棵树和每个点的初始状态(标记或不标记),每次修改一个点的状态(状态取反)或询问树上所有标记点到\(u->v\)的简单路径的最短距离之和。
以下是数据范围:
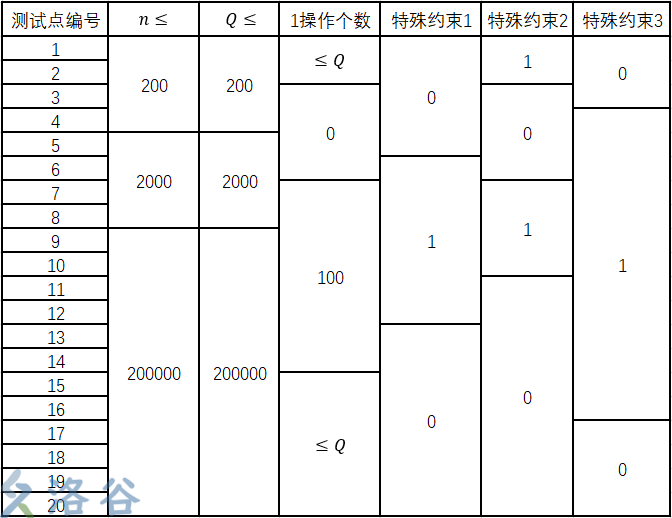
我们把矛头盯准前4个点。
\(n,m\leq 200\),这意味着什么?
直接按照题意模拟,先找出\(u->v\)简单路径上的所有点并标记,然后以每个点为根节点,找到最近的被标记的点,这个点显然最优,记录累加答案即可。
时间复杂度:\(O(n^2m)\)期望得分:\(20\).
不过由于数据比较水,放过了第\(7,8\)两个全特殊约束的点,可以拿到\(30pts.\)
解决了\(n,m\leq 200\)的点,我们可以看到接下来的数据为\(n,m\leq 2000\).
通俗易懂的讲我们要在\(O(nm)\)时间内完成答案。
在分析一下,不难发现,对于每次询问我们要做到\(O(n)\)的时间复杂度。
我们枚举链上的每个点,当枚举到点\(x\)时,考虑有哪一些标记点的最短距离是到\(x\)的。
容易发现去掉和它相邻的点所囊括的范围之后包含的点即为\(x\)点的范围。
可以这样理解:

图中红圈内的点到链上的最短距离都是到\(x\)。
设\(f[x]\)表示以\(x\)为根的所有标记点到\(x\)的距离,\(num_x\)表示以\(x\)为根的子树有多少个有标记,转移是显然的:
\[f[x]=num_y*val_{x,y}+\sum_{y\in son\{x\}}f[y].\]
累加答案即可。
时间复杂度\(O(nm)\),期望得分\(40\).
这里针对特殊约束2.
不难发现,如果询问\(u->v\)不改变的话,我们只需要针对每次修改更新答案即可。
修改点\(x\)时,我们需要快速找到\(u->v\)路径上的最近点。
如果以\(u\)为根的话,那么我们要找的点就是\(LCA(x,v)\).
时间复杂度:\(O(nlogn+mlogn)\),期望得分:\(30\).
这里针对特殊约束1.
树退化成了一条链,我们只要在这条链上寻找答案即可。
我们不妨把树链抽象成一个数列,
询问\(l->r\)时,我们只需要求出\(1->l\)中的点到\(l\)的距离和加上\(r->n\)中的点到\(r\)的距离和就行了。
这里仅考虑到\(l\)的部分(到\(r\)的部分同理)。
发现\(dis(i,l)=dis(i,n)-dis(l,n)\),
求和时,\(ans=\sum_{i=1}^ldis(i,n)-num_{1->l}*dis(l,n)\).
显然\(\sum_{i=1}^ldis(i,n)\)和\(num_{1->l}\)都是可以用某些单点修改区间求和的数据结构来维护的。
那么这几分就拿到了。
时间复杂度:\(O(nlogn+mlogn)\),期望得分:\(35\).
做到这里,应该就会有些眉目了。
发现有些点的1操作数量不会很多,只要每次修改后暴力重构,我们就只要处理询问部分。
考虑优化"高端暴力",我们发现处理这种暴力的时候每次都会重复累加好多点。
事实上,我们可以直接预处理暴力时所求的范围。
考虑倍增,设\(g[x][j]\)表示\(x\)的\(2^j\)祖先的\(f\)值去掉\(f[x]\)所剩下的值,\(G[x][j]\)表示x到祖先的同刚才那个区域到这条链上的距离。
在不考虑修改的情况下,\(f[x]\)是可以事先求出来的。
在从\(x\)跳上\(x\)的\(2^j\)祖先\(anc\)的过程中,我们只要累加上\(G[x][j]\)即可,对于外面的世界,用\(g[x][j]\)处理就行了。
时间复杂度:\(O(k(nlogn+mlogn))\)其中\(k\)是修改数,
期望得分:\(60\).(有点小卡常)。
假设所求路径\(u,v\)的\(LCA(u,v)=lca\).
我们考虑\(lca\)子树内所有的点对答案的贡献。
前面我们说到倍增是没有办法修改点的,这里我们尝试树链剖分。
首先要清楚我们所维护的值,不妨设点有没有被标记为数组\(tag[i]\).显然
\[f[x]=\sum_{tag[i],LCA(x,i)==x}dep[i]-dep[x]=\sum_{tag[i],LCA(x,i)==x}dep[i]-num_i*dep[x].\]
具体可以参考树链部分。
显然\(\sum_{tag[i],LCA(x,i)==x}dep[i]\)和\(num_i\)是可以用欧拉序加上数据结构维护的。
这意味着我们可以在\(logn\)时间内算出\(f[x]\)。
再考虑上面倍增所说到的\(g\)。
这里我们设\(g[x]\)表示\(f[x]\)减去它的重儿子的\(f\)值。
分析一下每次修改的时候我们需要更新哪些点的\(g\)值。

图中虚线代表轻链,实线代表重链。
显然那些红色圈的点才需要更新\(g\)值。
这些点都是某个点\(x\)的\(top[x]\)的父亲节点,易得这样的点有\(logn\)个,是可以做到更新的。
更新完成以后,我们尝试着求答案。
先考虑\(u->lca\)的部分。
如果\(u\)要往上跳到\(fa[top[u]]\)的话,我们的任务就是累加这一部分的和。

容易发现,当我们跳到点\(x\)时,我们若要跳到\(top[x]\),就要累加\(x->top[x]\)的这一条链上的\(g\)值。
而要从\(top[x]\)跳到\(fa[top[x]]\)时,
由于\(top[x]\)是轻儿子,我们答案应该要累加\(f[fa[top[x]]-f[top[x]]-num_{top[x]}*val_{top[x],fa[top[x]]}.\)
我们可以惊喜的发现,利用\(f\)和\(g\)可以做到以上所有操作。
这样的时间复杂度为\(O((n+m)log^2n)\).也可以过特殊约束3.
期望得分:\(65\),加上无脑暴力可以拿到\(80pts\).
接下来我们要考虑\(lca\)以外的部分,这部分的所有点到这条链上的最短距离都是到\(lca\).
不妨设\(lca\)外面的某个点为\(x\)。
显然\(dis(x,lca)=dep[x]+dep[lca]-2*dep[LCA(x,lca)].\)
那么这部分答案就为
\[\sum dep[x]+num*dep[lca]-2*\sum dep[LCA(x,lca)].\]
前一部分是很好求的,至于\(\sum dep[LCA(x,lca)]\)这部分我们依旧用类似的办法。
为了方便描述,设\(LCA(x,lca)=Lca.\)
往上跳的时候,我们把之前\(g[x]\)所维护的值换为\(num_x*dep[x]\).
我们依旧可以用同样的方法向上跳。
\(g[x]\)换掉了,同样这里的\(f[x]\)也要换掉。

搬回刚才的图,我们发现,从\(top[x]->fa[top[x]]\)的过程中,我们少掉的是\(fa[top[x]]\)的子树去除\(top[x]\)的子树这部分。
那么我们累加的答案就应是\((num_{fa[top[x]]}-num_{top[x]})*dep[fa[top[x]]\).
于是这一部分就做完了。
时间复杂度:\(O((n+m)log^2n)\),期望得分\(100\).
由于本题需要修改点的标记,我们考虑树链剖分。
以上为大概思路,具体实现应该还有一些细节。
然而值得注意的是,此题的细节极多,需要一定的代码难度。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define maxn 210000
using namespace std;
int n,m,tag[maxn],last[maxn],p,id[maxn],ID = 0;
int size[maxn],top[maxn],tail[maxn],fa[maxn],son[maxn],type;
LL Dep[maxn],dep[maxn];
LL ans = 0;
struct tree_array
{
LL d[maxn];
LL lowbit(LL x) {return x & (- x);}
LL Insert(int x,LL val) {while(x <= n) {d[x] += val; x += lowbit(x);}}
LL getsum(int x) {return x ? getsum(x - lowbit(x)) + d[x] : 0;}
LL query(int l, int r) {if(l > r) swap(l, r); return getsum(r) - getsum(l - 1);}
}A,B,C,D;
struct edge
{
int x, y, next;
LL val;
void Add_edge(int X, int Y, LL Val)
{
x = X; y = Y; val = Val;
next = last[x]; last[x] = p;
}
}e[maxn * 2];
LL getdis(int u, int v) {return abs(dep[u] - dep[v]);}
LL sumA(int x) {return A.query(id[x], id[x] + size[x] - 1);}
LL sumB(int x) {return B.query(id[x], id[x] + size[x] - 1);}
void init1(int x)
{
size[x] = 1;
for(int k = last[x]; k; k = e[k].next)
if(e[k].y != fa[x])
{
int y = e[k].y; fa[y] = x;
dep[y] = dep[x] + e[k].val;
Dep[y] = Dep[x] + 1;
init1(y);
size[x] += size[y];
if(size[y] > size[son[x]]) son[x] = y;
}
}
void init2(int x)
{
id[x] = ++ ID;
if(son[fa[x]] == x) top[x] = top[fa[x]];
else top[x] = x;
if(son[x]) init2(son[x]);
for(int k = last[x]; k; k = e[k].next)
if(e[k].y != fa[x] && e[k].y != son[x])
init2(e[k].y);
if(!son[x]) tail[x] = x;
else tail[x] = tail[son[x]];
}
int LCA(int u, int v)
{
while(u != v)
{
if(Dep[top[u]] < Dep[top[v]]) swap(u, v);
if(top[u] == top[v]) return Dep[u] < Dep[v] ? u : v;
else u = fa[top[u]];
}
return u;
}
void modify(int x)
{
tag[x] ^= 1; LL flag = tag[x] * 2 - 1;
int pos = x;
A.Insert(id[x], flag);
B.Insert(id[x], flag * dep[x]);
while(x)
{
C.Insert(id[x], flag * getdis(pos, x));
D.Insert(id[x], flag * dep[x]);
x = fa[top[x]];
}
}
LL getF(int x) {return abs(sumB(x) - dep[x] * sumA(x));}
void findsum(int x, int anc)
{
ans += getF(x);
while(x != anc)
{
if(top[x] == top[anc]) {ans += C.query(id[fa[x]], id[anc]); return;}
else
{
if(x == top[x])
ans += getF(fa[x]) - getF(x) - sumA(x) * getdis(x, fa[x]);
else
{
ans += getF(fa[top[x]]) - getF(top[x]) - sumA(top[x]) * getdis(top[x], fa[top[x]]);
ans += C.query(id[fa[x]], id[top[x]]);
}
x = fa[top[x]];
}
}
}
void Sumlink(int x)
{
while(x != 1)
{
if(top[x] == 1) {ans -= 2 * D.query(id[fa[x]], id[1]); break;}
else
{
if(x == top[x]) {ans -= 2 * ((sumA(fa[x]) - sumA(x)) * dep[fa[x]]);}
else {
ans -= 2 * D.query(id[fa[x]], id[top[fa[x]]]);
ans -= 2 * ((sumA(fa[top[x]]) - sumA(top[x])) * dep[fa[top[x]]]);
}
x = fa[top[x]];
}
}
}
LL query(int x,int y)
{
int lca = LCA(x, y); ans = 0;
findsum(x, lca);
findsum(y, lca);
ans -= getF(lca);
if(lca != 1)
{
ans += sumB(1) - sumB(lca) + (sumA(1) - sumA(lca)) * dep[lca];
Sumlink(lca);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &type);
for(int i = 1;i <= n - 1;i ++)
{
int u,v;LL w; scanf("%d%d%lld", &u, &v, &w);
e[++ p].Add_edge(u, v, w);
e[++ p].Add_edge(v, u, w);
}
init1(1); init2(1);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++)
{
int opt; scanf("%d", &opt);
if(opt) modify(i);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= m;i ++)
{
int opt, x, y;
scanf("%d%d", &opt, &x);
if(opt == 2) scanf("%d", &y);
if(opt == 1) modify(x);
else printf("%lld\n", query(x, y));
}
}记得开\(long long\)哦。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dwqhca/p/11412064.html