GUI技术看似成为古老的技术,但是Unity5.x之后并没有取消这种UI传统的技术。Unity4.6出现的新的UI技术称之为UGUI,我们会在之后的课程进行讲解,他的出现主要是为了重新定义UI的技术规范,统一之前UI插件繁多,混杂,标准不统一的混乱局面,大有一统江湖的目的。但是原生的GUI生命力依然旺盛。在一些早期开发的项目,小型游戏依然有其存在的价值,简单易用是它存在的硬道理。
UI是游戏组成的重要部分,游戏的很多操作直接通过UI控制。无论摄像机拍到的图像怎么变幻,GUI永远显示在屏幕上,不受变形,碰撞,光照等信息影响。
写GUI脚本,必须注意两个重要特征:
(1)GUI脚本控件必须定义在脚本文件的OnGUI事件函数中
(2)GUI每一帧都会调用
void Start () {
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
print ("update");
}
void OnGUI()
{
print ("OnGUI");
}
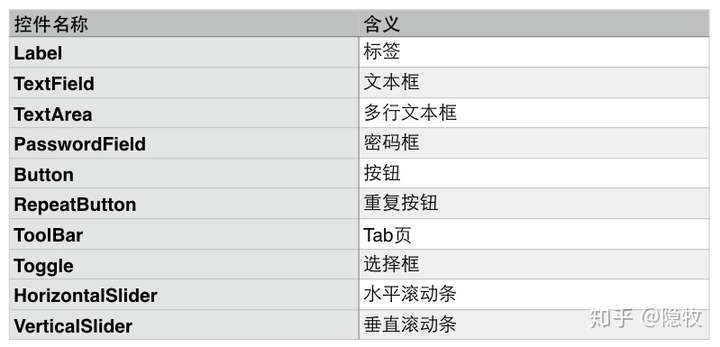
GUI基本的控件如下图所示:
public class Demo : MonoBehaviour {
private string _StrText="";
private string _StrPW="";
private int _IntSelectIndex=0;
private bool _BoolCheck1=false;
private bool _BoolCheck2=false;
private float value=0;
private int min=0;
private int max=100;
void OnGUI()
{
GUI.Label (new Rect(0,0,100,30),"I am the Label");
_StrText = GUI.TextField (new Rect(0,50,100,30),_StrText);
_StrPW = GUI.TextField (new Rect (0, 100, 100, 30), _StrPW);
GUI.Button (new Rect(0,150,50,30),”Sure");
_IntSelectIndex=GUI.Toolbar(new Rect(0,200,200,30),_IntSelectIndex,new string[]{"Duty","Equip","Peopel"} );
_BoolCheck1 = GUI.Toggle (new Rect(0,260,100,50),_BoolCheck1,"zhuangbei");
_BoolCheck2 = GUI.Toggle (new Rect(0,300,100,50),_BoolCheck2,"renyuan");
value = GUI.HorizontalSlider (new Rect (0, 350, 200, 50), value, max, min);}
}
前面我们进行布局的时候,会发现每次都需要输入new Rect(),里面包含四个坐标。为了解决这个烦人的问题,Unity公司提供了一个相对简单的布局方案。即每个控件的宽带高度按照一些字体的大小进行统一计算。位置采取靠左对齐,一个控件占据一行的原则。
void OnGUI()
{
GUILayout.BeginArea (new Rect (100, 200, 300, 400));
GUILayout.Label ("I am label");
GUILayout.Label ("hello world");
GUILayout.Label ("Hello Mornig");
GUILayout.EndArea ();
}
GUILayout.BeginArea (new Rect (100, 200, 300, 400));
//相当于布局一个盒子,盒子使用Rect进行定义,如果字体太多,超出范围则不显示。
private bool _BoolDisplay=false;
private bool _BoolDisplayWindow=false;
void OnGUI()
{
if (GUILayout.Button ("Show")) {
GUILayout.Label("I can‘t show in window");
}
if (GUILayout.Button (" xianshi")) {
_BoolDisplay=true;
}
if (_BoolDisplay) {
GUILayout.Label("I can be show");
}
if (GUILayout.Button ("Show Window")) {
_BoolDisplayWindow=true;
}
if (_BoolDisplayWindow) {
GUILayout.Window(0,new Rect(100,100,200,200),AddWindow,"MyWindow");
}
}
void AddWindow(int winId)
{
if (GUILayout.Button ("Exit")) {
_BoolDisplayWindow=false;
}
}
1:我们使用GUI.DrawTexture()方法进行贴图的绘制输出,另外,我们还可以结合Resource.Load()类静态方法进行动态提取项目视图中存在的贴图资源。
public class Demo4 : MonoBehaviour {
//public Texture2D Txt2D_bird;
private Texture2D _Txt2D_bird;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
_Txt2D_bird = (Texture2D)Resources.Load ("A");
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
}
void OnGUI()
{
GUI.DrawTexture (new Rect(Screen.width/2-_Txt2D_bird.width/2,Screen.height/2-_Txt2D_bird.height/2,_Txt2D_bird.width,
_Txt2D_bird.height),_Txt2D_bird);
}
}
之前我们设计的界面,美观程度太低了,真正的游戏项目不可能接受丑陋的界面的,那么我们该如何去做呢?Unity已经为我们提供好了一个解决方案,答案就是使用GUISkin
(1)首先项目视图中鼠标右键点击Create->GUI SKin,然后选择CustomStyle进行贴图的赋值,需要几个就进行赋值几个即可。
(2)代码中public GUISkin prijectSkin,进行连接即可。
public class Demo5 : MonoBehaviour {
public GUISkin projectSkin;
public Texture2D Text2D_Btn1;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
}
void OnGUI()
{
GUI.skin = projectSkin;
GUI.Button(new Rect(0,0,100,100),"",projectSkin.GetStyle("Button1"));
}
}
2:滚动视图的使用
滚动视图是一种非常大众化的界面,大部分游戏都存在滚动视图的影子。
//Parameters(参数):
position : Rect —— 滚动视图在屏幕上的矩形位置;
scrollPosition : Vector2 —— 用来显示滚动位置;
viewRect : Rect —— 滚动视图内使用的矩形;
alwayShowHorizontal : boolean —— 可选参数!总是显示水平滚动条,如果设置为false或者不设置时,只用当内矩形区域宽于外矩形区域时才显示;
alwayShowVertical : boolean —— 可选参数!总是显示垂直滚动条,如果设置为false或者不设置时,只用当内矩形区域高于外矩形区域时才显示;
horizontalScrollbar : GUIStyle —— 用于水平滚动条的可选设置,如果不设置,水平滚动条将使用当前的GUISkin;
verticalScrollbar : GUIStyle —— 用于垂直滚动条的可选设置,如果不设置,垂直滚动条将使用当前的GUISkin;
Returns(返回):Vector2 二维向量—— 被修改的滚动位置scrollPosition。返回值应该赋予你的变量;
Description(描述):在GUI中开始一个滚动视图,滚动视图让你在屏幕上产生一个小的区域,使用滚动条可以查看一个大的区域。
private string[] infos= new string [5];
? Vector2 scrollPosition;
void OnGUI(){
//开始滚动视图
? scrollPosition = GUI.BeginScrollView(?
new Rect(10,10,400,400),?
scrollPosition,new Rect(10,10,700,700)?
,false,false);
? //标签内容
? GUI.Label(new Rect(10,10,770,40),infos[0]);
? GUI.Label(new Rect(10,50,770,40),infos[1]);
? GUI.Label(new Rect(10,90,770,40),infos[2]);
? GUI.Label(new Rect(10,130,770,60),infos[3]);
? GUI.Label(new Rect(10,190,770,40),infos[4]);
?? //结束滚动视图
? GUI.EndScrollView();
}
3:网格布局的使用
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {?
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
? if (GUI.Button (new Rect (100 * j, 100 * i,80, 80),"", mySkin.GetStyle ("Coin1"))) {
? ButtonClicked (i * 5 + j);?
}?
}
? }
void ButtonClicked(int tag){?
print (tag);?
}
4:游戏暂停与继续
public class NewBehaviourScript : MonoBehaviour {
?? public float moveSpeed = 2.0f;
? ?void Update ()?
{?
transform.Translate (new Vector3(0,0,?moveSpeed* Time.deltaTime));?
}?
void OnGUI ()?
{?
if (GUI.Button (new Rect (140, 0, 100, 50), "暂停")) {?
Time.timeScale = 0;?
}?
if (GUI.Button (new Rect (280, 0, 100, 50), "继续")) {?
Time.timeScale = 1;?
}
? }?
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xingchong/p/11984522.html