There are some animals in a zoo which can be described as a grid with N rows and M columns. Your task is to place some obstacles so that no pairs of animals can reach each other.
Two animals can reach each other if and only if their cells are 4-connected. For example, in Figure 1, the central blue cell can be reached by the four red cells, and cannot be reached by the other four white cells.
Figure 1
What is more, you must put obstacles in exactly K cells, which are 4-connected and form exactly H holes. Here a hole is defined as a 4-connected part with finitely many open cells while the zoo is placed in an infinite open grid. For example, there are 2 holes (the green and the yellow areas) in Figure 2.
Figure 2
For the following grid with two animals:
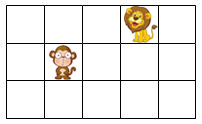
Figure 3
If K = 8 and H = 1, one way to separate them is the following:
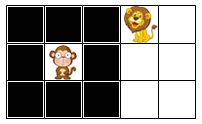
Figure 4
Figure 5 is illegal because it contains no hole.

Figure 5
Figure 6 is also illegal because the obstacles are not 4-connected.

Figure 6
Given some animals, you are supposed to count the number of different solutions.
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives four integers: N, M, K, H (2 ≤ N, M ≤ 6; 1 ≤ K ≤ 12; 0 ≤ H ≤ 2). All the numbers are separated by spaces.
Then N lines follow, each contains M characters, which are either . or O, representing an open cell or an animal, respectively. There will be at least 2 animals.
For each case, print a single line containing a single integer: the number of solutions.
3 5 8 1
...O.
.O...
.....
81 #include<map> 2 #include<set> 3 #include<ctime> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<queue> 6 #include<string> 7 #include<vector> 8 #include<cstdio> 9 #include<cstring> 10 #include<iostream> 11 #include<algorithm> 12 #include<functional> 13 using namespace std; 14 #define ms(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x)) 15 #define rep(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i<=k;i++) 16 #define per(i,j,k) for(int i=j;i>=k;i--) 17 #define loop(i,j,k) for (int i=j;i!=-1;i=k[i]) 18 #define inone(x) scanf("%d",&x) 19 #define intwo(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y) 20 #define inthr(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z) 21 #define infou(x,y,z,p) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z,&p) 22 #define lson x<<1,l,mid 23 #define rson x<<1|1,mid+1,r 24 #define mp(i,j) make_pair(i,j) 25 #define ff first 26 #define ss second 27 typedef int LL; 28 typedef pair<LL, LL> pii; 29 const int low(int x) { return x&-x; } 30 const double eps = 1e-6; 31 const int INF = 0x7FFFFFFF; 32 const int mod = 1e9 + 7; 33 const int N = 15; 34 int n, m, t, h; 35 int fa[N*N][N*N], ga[N*N][N*N], sa[N*N][N*N], a[N][N], ans, vis[N][N]; 36 int ha[N*N][N*N], hole[N], b[N*N]; 37 char s[N][N]; 38 int dir[4][2] = { 0,1,0,-1,1,0,-1,0 }; 39 40 int get(int fa[], int x) { 41 return fa[x] == x ? x : fa[x] = get(fa, fa[x]); 42 } 43 44 void dfs(int now, int cnt, int con) { 45 if (cnt > t) return; 46 if (con - 1 > t - cnt) return; 47 if (t - cnt > n*m - now + 1) return; 48 if (now > n * m) { 49 if (cnt < t || con != 1 || hole[now - 1] != h) return; 50 ans++; 51 return; 52 } 53 54 int x = (now - 1) / m + 1, y = (now - 1) % m + 1; 55 rep(i, 1, n*m) { 56 fa[now][i] = fa[now - 1][i]; 57 ga[now][i] = ga[now - 1][i]; 58 sa[now][i] = sa[now - 1][i]; 59 ha[now][i] = ha[now - 1][i]; 60 } 61 hole[now] = hole[now - 1] + 1; 62 if (con == 1 && cnt == t) { 63 64 } 65 else if (now > m) { 66 int sz = 0; 67 rep(i, 1, m) { 68 int x = (now - i - 1) / m + 1, y = (now - i - 1) % m + 1; 69 if (!a[x][y]) continue; 70 b[sz++] = get(fa[now], now - i); 71 } 72 sort(b, b + sz); 73 sz = unique(b, b + sz) - b; 74 if (sz < con) { 75 return; 76 } 77 } 78 79 if (y > 1 && !a[x][y - 1]) { 80 int fx = get(ha[now], now), fy = get(ha[now], now - 1); 81 if (fx != fy) { 82 if (!fx || !fy) ha[now][fx + fy] = 0; 83 else ha[now][fx] = fy; 84 hole[now]--; 85 } 86 } 87 if (x > 1 && !a[x - 1][y]) { 88 int fx = get(ha[now], now), fy = get(ha[now], now - m); 89 if (fx != fy) { 90 if (!fx || !fy) ha[now][fx + fy] = 0; 91 else ha[now][fx] = fy; 92 hole[now]--; 93 } 94 } 95 if (y==1 || y==m || x == 1 || x == n) { 96 int fx = get(ha[now], now); 97 if (fx) { 98 ha[now][fx] = 0; hole[now]--; 99 } 100 } 101 102 int flag = 1; 103 if (y > 1 && !a[x][y - 1]) { 104 int fx = get(ga[now], now), fy = get(ga[now], now - 1); 105 if (fx != fy) { 106 ga[now][fx] = fy; 107 if ((sa[now][fy] += sa[now][fx]) > 1) flag = 0; 108 } 109 } 110 if (x > 1 && !a[x - 1][y]) { 111 int fx = get(ga[now], now), fy = get(ga[now], now - m); 112 if (fx != fy) { 113 ga[now][fx] = fy; 114 if ((sa[now][fy] += sa[now][fx]) > 1) flag = 0; 115 } 116 } 117 if (flag) dfs(now + 1, cnt, con); 118 119 if (s[x][y] == ‘O‘) return; 120 rep(i, 1, n*m) { 121 fa[now][i] = fa[now - 1][i]; 122 ga[now][i] = ga[now - 1][i]; 123 sa[now][i] = sa[now - 1][i]; 124 ha[now][i] = ha[now - 1][i]; 125 } 126 hole[now] = hole[now - 1]; 127 a[x][y] = 1; 128 con++; 129 if (y > 1 && a[x][y-1]) { 130 int fx = get(fa[now], now), fy = get(fa[now], now - 1); 131 if (fx != fy) { fa[now][fx] = fy; con--; } 132 } 133 if (x > 1 && a[x-1][y]) { 134 int fx = get(fa[now], now), fy = get(fa[now], now - m); 135 if (fx != fy) { fa[now][fx] = fy; con--; } 136 } 137 dfs(now + 1, cnt + 1, con); 138 a[x][y] = 0; 139 } 140 141 int main() { 142 scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &t, &h); 143 rep(i, 1, n) scanf("%s", s[i] + 1); 144 rep(i, 1, n) rep(j, 1, m) { 145 fa[0][i*m - m + j] = i*m - m + j; 146 ga[0][i*m - m + j] = i*m - m + j; 147 ha[0][i*m - m + j] = i*m - m + j; 148 sa[0][i*m - m + j] = s[i][j] == ‘O‘; 149 hole[0] = 0; 150 } 151 ans = 0; 152 dfs(1, 0, 0); 153 printf("%d\n", ans); 154 return 0; 155 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/SkystarX/p/12285778.html