Kuriyama Mirai has killed many monsters and got many (namely n) stones. She numbers the stones from 1 to n. The cost of the i-th stone is vi. Kuriyama Mirai wants to know something about these stones so she will ask you two kinds of questions:
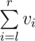 .
.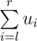 .
.For every question you should give the correct answer, or Kuriyama Mirai will say "fuyukai desu" and then become unhappy.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers: v1, v2, ..., vn (1 ≤ vi ≤ 109) — costs of the stones.
The third line contains an integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 105) — the number of Kuriyama Mirai‘s questions. Then follow m lines, each line contains three integers type, l and r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ type ≤ 2), describing a question. If type equal to 1, then you should output the answer for the first question, else you should output the answer for the second one.
Print m lines. Each line must contain an integer — the answer to Kuriyama Mirai‘s question. Print the answers to the questions in the order of input.
6
6 4 2 7 2 7
3
2 3 6
1 3 4
1 1 6
24
9
28
4
5 5 2 3
10
1 2 4
2 1 4
1 1 1
2 1 4
2 1 2
1 1 1
1 3 3
1 1 3
1 4 4
1 2 2
10
15
5
15
5
5
2
12
3
5
Please note that the answers to the questions may overflow 32-bit integer type.
刚开始没有注意下面的Note,用int类型的数组WA了。后来改用long long型。我之前也没去算过OJ可以接受多大的数组,就这道AC的代码来看4W的long long是没有问题的。
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <string> #include <set> #include <queue> #include <map> #include <sstream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <numeric> #include <cmath> #include<unordered_set> #define ll long long using namespace std; int dir[4][2] = { {1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} }; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<ll> v(n),a(n); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int t; cin >> t; v[i] = t; a[i] = t; } sort(a.begin(), a.end()); for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { v[i] += v[i - 1]; a[i] += a[i - 1]; } int m; cin >> m; while (m--) { int q, l, r; cin >> q >> l >> r; if (q == 1) { if (l == 1) cout << v[r - 1] << endl; else cout << v[r - 1] - v[l - 2] << endl; } else { if (l == 1) cout << a[r - 1] << endl; else cout << a[r - 1] - a[l - 2] << endl; } } //system("pause"); return 0; }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/dealer/p/12295876.html