templates简介:
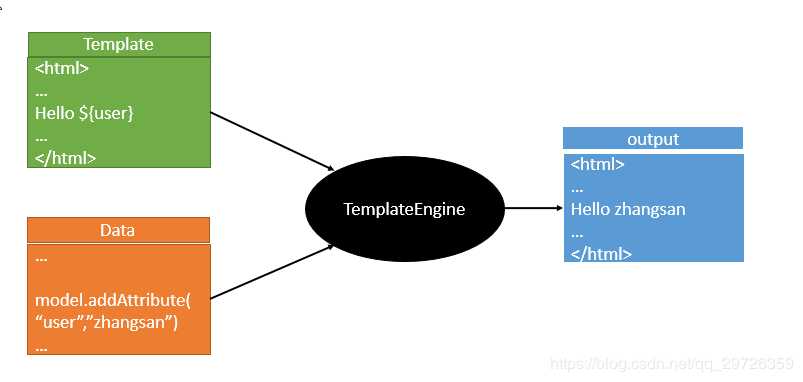
市面上的模板引擎有:JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf;
之前开发用jsp当摸吧引擎,但是springboot的特殊机制,使得springboot不支持jsp页面,但这样会有很多开发上的不方便,所以他支持了Thymelead模板引擎。
我这里就不详细介绍templates的原理,百度上面一大堆,这主要讲讲templates的用法。
首先是maven的依赖:
<!-- 模板引擎 thymeleaf的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
然后在application.properties的配置项里面配置:
#配置项, #这里主要配置模板引擎的数据 #thymeleaf配置 #模板的模式,支持如:HTML、XML、TEXT、JAVASCRIPT等 spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5 #编码,可不用配置 spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8 #内容类别,可不用配置 spring.thymeleaf.servlet.content-type=text/html #开发配置为false,避免修改模板还要重启服务器 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false #配置模板路径,默认就是templates,可不用配置 spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
配置项好之后,那么就剩下实现了。
而模板文件时要放到tempates里面的,所以要先在类路径下面创建这个文件夹,然后在说其他的。如下:

接下来写写怎么呈现集成成功。
这个是home.html,放在webapp下面,因为都可以通过项目来跳级访问资源,所以放在templates下面的那些模板文件可以和这互相访问。
以下是home.html的实现:
<html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> <title></title> </head> <body> <p>在webapp下面的资源可以访问到templates下面的资源,原因是webapp在加载的时候会放到classpath下面去</p> <p>所以可以进行交互,互相访问</p> <a href="templates/index">index</a> <a href="templates/back">more</a> </body> </html>
controller的代码:
package start.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * 控制类 * @author 徐金仁 * */ @Controller @RequestMapping("templates") public class Controller_ { @RequestMapping("index") public String showIndex(ModelMap map){ map.addAttribute("username", "蘑菇头"); map.addAttribute("password", "123456789"); map.put("tes", "你好"); return "index"; } /** * 关于模板引擎的注解,如果要返回一个视图层的话就不能使用@ResponseBody注解, * 使用@ResponseBody注解的话,会将返回的视图当做字符串来处理返回,就起不到模板引擎的效果 * 还有,上面控制类的注解:@Controller和@RestController这两个注解要区分开来 * @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody * @param map * @return */ /*@ResponseBody*/ @RequestMapping("back") public String showback(ModelMap map){ map.put("key1", "/templates/back/more.html,在controller返回" + "视图层的时候,可以省略后面的html后缀,添加上页没有什么关系"); map.put("arr", new String[]{"张三","李四","王五","赵六"}); map.put("name", "<font color = ‘red‘>赵婷</font>"); //ModelMap中的put和addAttribute同样是添加数据,那么有什么区别? //map.put(null, "null_put"); //map.addAttribute(null,"null_addAttribute"); //结果证明:put方法是能添加空值的,而addAttribute是不能添加空值的 //当put和addAllAttribute方法添加了相同的key值,会出什么问题。 map.put("key_common", "key_common_put"); map.addAttribute("key_common","key_common_addAttribute"); //结果显示,会存在相同key会覆盖的问题,后面添加的数据会将前面一个key值的数据覆盖掉 return "/back/more.html"; } }
index.html如下:
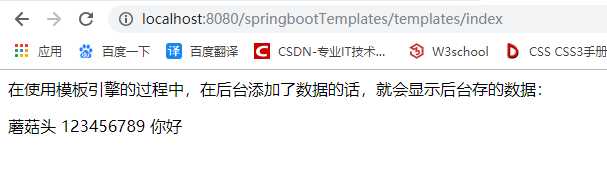
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> <title></title> </head> <body> <p>在使用模板引擎的过程中,在后台添加了数据的话,就会显示后台存的数据:</p> <span th:text = "${username}"></span> <span th:text = "${password}"></span> <span th:text="${tes}"></span> </body> </html>
more.html如下:
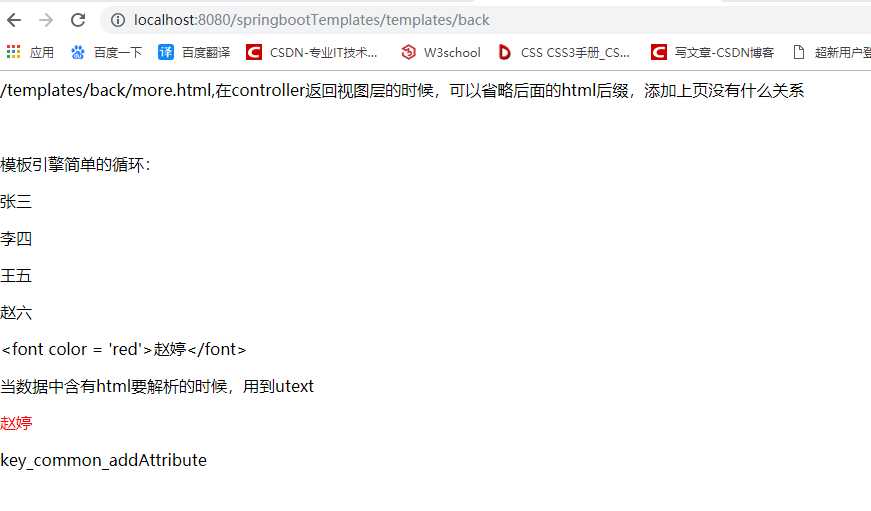
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"/> <title></title> </head> <body> <p th:text="${key1}"></p> <br/> <p>模板引擎简单的循环:</p> <p th:each = "item : ${arr}" th:text="${item}"></p> <p th:text="${name}"></p> <p>当数据中含有html要解析的时候,用到utext</p> <p th:utext="${name}"></p> <p th:text="${null}">1</p> <p th:text="${null}">2</p> <p th:text="${key_common}"></p> </body> </html>
结果如下:
思路来源:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29726359/article/details/88043652
https://blog.csdn.net/ignorewho/article/details/80692094
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/1998xujinren/p/12352855.html