| 主机名称 | 操作系统版本 | 内网IP | 外网IP(模拟) | 安装软件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ansi-manager | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.180 | 10.0.0.180 | ansible |
| ansi-haproxy01 | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.181 | 10.0.0.181 | |
| ansi-haproxy02 | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.182 | 10.0.0.182 | |
| ansi-web01 | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.183 | 10.0.0.183 | |
| ansi-web02 | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.184 | 10.0.0.184 | |
| ansi-web03 | CentOS7.5 | 172.16.1.185 | 10.0.0.185 |
在实际使用中并不需要对ansible配置进行修改,或者说只有需要的时候才修改ansible配置。
说明:
1、 运维人员使用的登录账号;
2、 所有的业务都放在 /app/ 下「yun用户的家目录」,避免业务数据乱放;
3、 该用户也被 ansible 使用,因为几乎所有的生产环境都是禁止 root 远程登录的(因此该 yun 用户也进行了 sudo 提权)。
1 # 使用一个专门的用户,避免直接使用root用户 2 # 添加用户、指定家目录并指定用户密码 3 # sudo提权 4 # 让其它普通用户可以进入该目录查看信息 5 useradd -u 1050 -d /app yun && echo ‘123456‘ | /usr/bin/passwd --stdin yun 6 echo "yun ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers 7 chmod 755 /app/
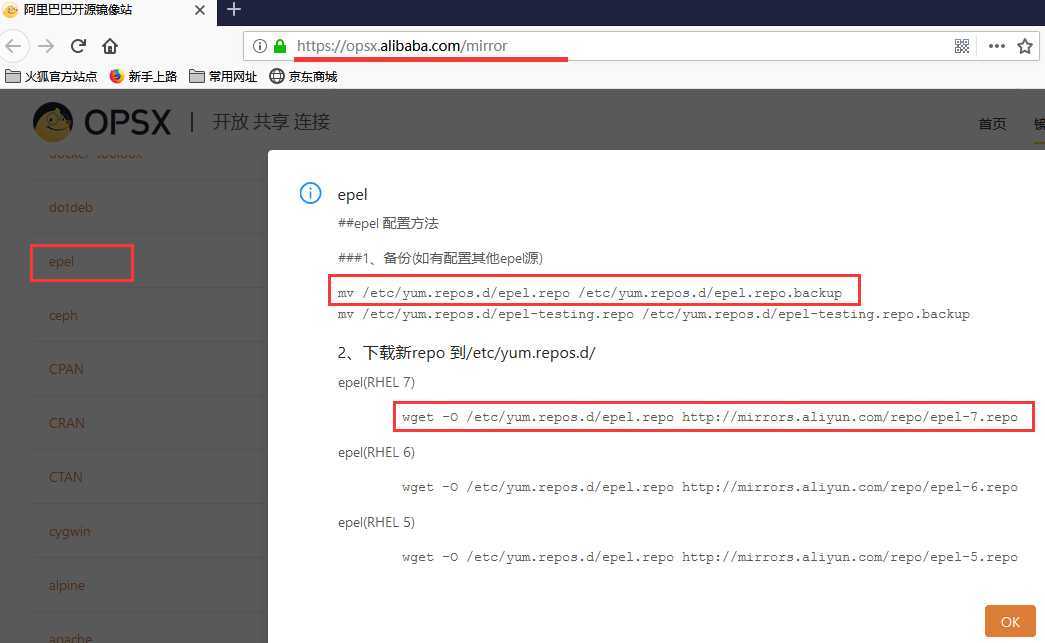
添加阿里云 epel 源
https://opsx.alibaba.com/mirror
1 [root@ansi-manager ~]# yum install -y ansible 2 [root@ansi-manager ~]# whereis ansible # ansible 位置信息 3 ansible: /usr/bin/ansible /etc/ansible /usr/share/ansible /usr/share/man/man1/ansible.1.gz 4 [root@ansi-manager ~]# ansible --version # 版本信息查看 5 ansible 2.8.1 # ansible 版本 6 config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg # 使用的配置文件 7 configured module search path = [u‘/root/.ansible/plugins/modules‘, u‘/usr/share/ansible/plugins/modules‘] # 模块查找路径 8 ansible python module location = /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/ansible # ansible Python 模块位置,使用 Python 2.7 9 executable location = /bin/ansible # ansible 执行文件的位置 10 python version = 2.7.5 (default, Apr 11 2018, 07:36:10) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-28)] # Python 版本信息 11 [yun@ansi-manager ~]$ ll /usr/bin/ansible /bin/ansible # ansible 命令位置 12 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Jun 24 14:14 /bin/ansible -> /usr/bin/ansible-2.7 13 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 20 Jun 24 14:14 /usr/bin/ansible -> /usr/bin/ansible-2.7
ansible 将从多个地方查找配置文件,顺序如下:
1、从环境变量 ANSIBLE_CONFIG 中查找,如果该环境变量有值的话;
2、当前目录的 ansible.cfg 文件;「每个项目都可以有一个该配置文件,这样可以更好的管理项目,移植时也更方便。」
3、当前用户家目录的 .ansible.cfg 文件;
4、/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 文件。
可以使用 ansible –version 命令查看使用的配置文件。
在 /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg 配置文件中有该说明
实际生产中可以无需做任何修改。
1 [yun@ansi-manager ansible]$ pwd 2 /etc/ansible 3 [yun@ansi-manager ansible]$ vim ansible.cfg 4 #inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts # 受控端主机资源清单 5 #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ # 所需依赖库路径 6 #remote_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp # 远端机器,临时文件存放位置 7 #local_tmp = ~/.ansible/tmp # 本机临时文件存放位置 8 #forks = 5 # 默认并发数 9 #poll_interval = 15 # 默认轮询时间间隔(单位秒) 10 #sudo_user = root # 默认sudo后的用户 11 #ask_sudo_pass = True # 使用sudo,是否需要输入密码 12 #ask_pass = True # 是否需要输入密码 13 #transport = smart # 传输方式 14 #remote_port = 22 # 默认远程主机的端口号 15 #module_lang = C # 模块和系统之间通信的语言 16 #module_set_locale = False 17 ……………… 18 # uncomment this to disable SSH key host checking 取消注释以禁用SSH key主机检查 【默认是注释掉的,要检查主机指纹】 19 host_key_checking = False # 解开注释,即跳过检查主机指纹 【只有 root 用户执行时才有该取消指纹检测的权限】 20 ……………… 21 # logging is off by default unless this path is defined 22 # if so defined, consider logrotate 23 #log_path = /var/log/ansible.log # 开启ansible日志 24 ……………… 25 [privilege_escalation] # 普通用户提权配置「使用地方:普通用户远程提权使用」 26 #become=True 27 #become_method=sudo 28 #become_user=root 29 #become_ask_pass=False
上述的 [privilege_escalation] 配置,可在 ansible -h 中查看如何使用。如下:
1 [yun@ansi-manager ~]$ ansible -h 2 ……………… 3 Privilege Escalation Options: # 权限提升选项 4 control how and which user you become as on target hosts 5 6 -b, --become run operations with become (does not imply password 7 prompting) 8 --become-method=BECOME_METHOD 9 privilege escalation method to use (default=sudo), use 10 `ansible-doc -t become -l` to list valid choices. 11 --become-user=BECOME_USER 12 run operations as this user (default=root) 13 -K, --ask-become-pass 14 ask for privilege escalation password 15 ………………

原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhanglianghhh/p/12445677.html