题目描述:「外观数列」是一个整数序列,从数字 1 开始,序列中的每一项都是对前一项的描述。前五项如下:

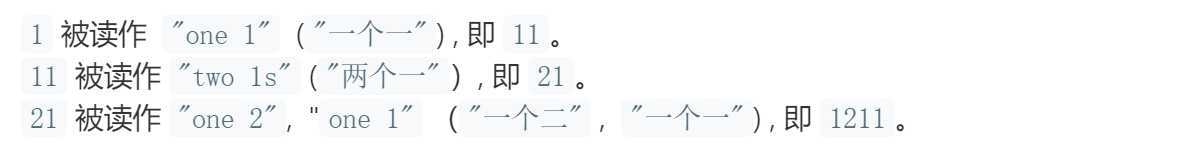
给定一个正整数 n(1 ≤ n ≤ 30),输出外观数列的第 n 项。注意:整数序列中的每一项将表示为一个字符串。
具体思路:由题意可知,第n项的值是通过遍历第n-1项所得到的,即每一项都依赖于前一项,因而自然而然地想到采用递归的方法。(自然也可以用迭代法)
1 class Solution: 2 def countAndSay(self, n: int) -> str: 3 if n == 1: 4 return ‘1‘ 5 ans = ‘‘ 6 temp = countAndSay(n-1) #递归 7 i, count = 1 8 while (i < len(temp)): 9 if temp[i] == temp[i-1]: #因为i是从1开始的,即从第2的字符开始依次与其前一个字符比较 10 count += 1 11 else: 12 ans += str(count) + temp[i-1] #temp[i-1]表示刚遍历过的那个字符 13 count = 1 14 i += 1 15 ans += str(count)+temp[i-1] #跳出while循环时,最后一个字符还未记录 16 return ans
1 class Solution: 2 def countAndSay(self, n: int) -> str: 3 if n == 1: 4 return ‘1‘ 5 pre_str = ‘1‘ 6 i = 1 7 while(i < n): 8 next_str, num, count = ‘‘, pre_str[0], 1 9 for j in range(1,len(pre_str)): 10 if pre_str[j] == pre_str[j+1]: 11 count += 1 12 else: 13 next_str = str(count)+num 14 num = pre_str[j] 15 count = 1 16 #结束内循环后 17 next_str += str(count)+num 18 pre_str = next_str 19 i += 1 20 return pre_str
1 #groupby示例 2 from itertools import groupby 3 test = ‘11233355‘ 4 for k,g in groupby(test): 5 print(k) 6 print(list(g)) 7 8 #输出 9 #1 10 #[‘1‘, ‘1‘] 11 12 #2 13 #[‘2‘] 14 15 #3 16 #[‘3‘, ‘3‘, ‘3‘] 17 18 #5 19 #[‘5‘, ‘5‘]
1 class Solution: 2 def countAndSay(self, n: int) -> str: 3 from itertools import groupby 4 result = ‘1‘ 5 for i in range(1,n): 6 result = ‘‘.join(str(len(list(g)))+k for k,g in groupby(result)) 7 return result
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/shawn-young/p/12493960.html