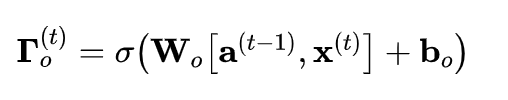
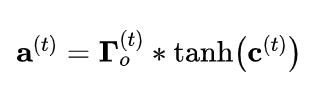
def lstm_cell_forward(xt, a_prev, c_prev, parameters):
"""
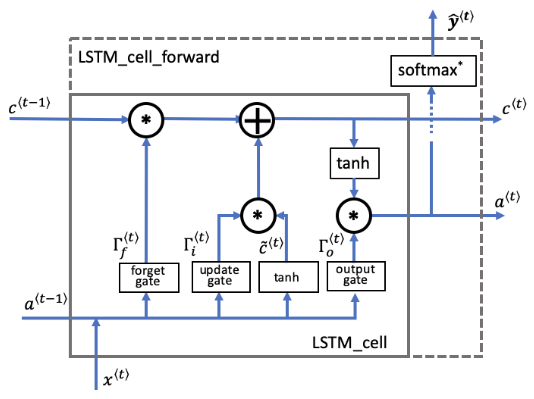
Implement a single forward step of the LSTM-cell as described in Figure (4)
?
Arguments:
xt -- your input data at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_x, m).
a_prev -- Hidden state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m)
c_prev -- Memory state at timestep "t-1", numpy array of shape (n_a, m)
parameters -- python dictionary containing:
Wf -- Weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bf -- Bias of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wi -- Weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
? bi -- Bias of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wc -- Weight matrix of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bc -- Bias of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wo -- Weight matrix of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bo -- Bias of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wy -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a)
by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1)
?
Returns:
a_next -- next hidden state, of shape (n_a, m)
c_next -- next memory state, of shape (n_a, m)
yt_pred -- prediction at timestep "t", numpy array of shape (n_y, m)
cache -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, xt, parameters)
?
Note: ft/it/ot stand for the forget/update/output gates, cct stands for the candidate value (c tilde),
c stands for the cell state (memory)
"""
# 从 "parameters" 中取出参数。
Wf = parameters["Wf"] # 遗忘门权重
bf = parameters["bf"]
Wi = parameters["Wi"] # 更新门权重 (注意变量名下标是i不是u哦)
bi = parameters["bi"] # (notice the variable name)
Wc = parameters["Wc"] # 候选值权重
bc = parameters["bc"]
Wo = parameters["Wo"] # 输出门权重
bo = parameters["bo"]
Wy = parameters["Wy"] # 预测值权重
by = parameters["by"]
# 连接 a_prev 和 xt
concat = np.concatenate((a_prev, xt), axis=0)
# 等价于下面代码
# 从 xt 和 Wy 中取出维度
# n_x, m = xt.shape
# n_y, n_a = Wy.shape
# concat = np.zeros((n_a + n_x, m))
# concat[: n_a, :] = a_prev
# concat[n_a :, :] = xt
# 计算 ft (遗忘门), it (更新门)的值
# cct (候选值), c_next (单元状态),
# ot (输出门), a_next (隐藏单元)
ft = sigmoid(np.dot(Wf, concat) + bf) # 遗忘门
it = sigmoid(np.dot(Wi, concat) + bi) # 更新门
cct = np.tanh(np.dot(Wc, concat) + bc) # 候选值
c_next = ft * c_prev + it * cct # 单元状态
ot = sigmoid(np.dot(Wo, concat) + bo) # 输出门
a_next = ot * np.tanh(c_next) # 隐藏状态
# 计算LSTM的预测值
yt_pred = softmax(np.dot(Wy, a_next) + by)
# 用于反向传播的缓存
cache = (a_next, c_next, a_prev, c_prev, ft, it, cct, ot, xt, parameters)
?
return a_next, c_next, yt_pred, cache
def lstm_forward(x, a0, parameters):
"""
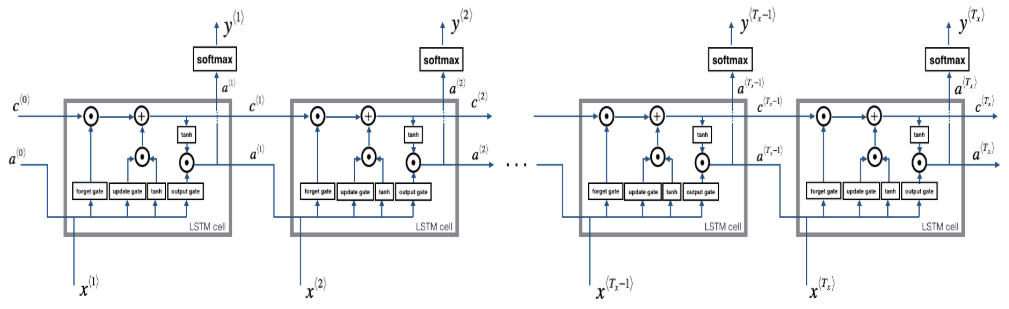
Implement the forward propagation of the recurrent neural network using an LSTM-cell described in Figure (4).
?
Arguments:
x -- Input data for every time-step, of shape (n_x, m, T_x).
a0 -- Initial hidden state, of shape (n_a, m)
parameters -- python dictionary containing:
Wf -- Weight matrix of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bf -- Bias of the forget gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wi -- Weight matrix of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bi -- Bias of the update gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wc -- Weight matrix of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bc -- Bias of the first "tanh", numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wo -- Weight matrix of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, n_a + n_x)
bo -- Bias of the output gate, numpy array of shape (n_a, 1)
Wy -- Weight matrix relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, n_a)
by -- Bias relating the hidden-state to the output, numpy array of shape (n_y, 1)
?
Returns:
a -- Hidden states for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_a, m, T_x)
y -- Predictions for every time-step, numpy array of shape (n_y, m, T_x)
c -- The value of the cell state, numpy array of shape (n_a, m, T_x)
caches -- tuple of values needed for the backward pass, contains (list of all the caches, x)
"""
?
# 初始化 "caches", 用来存储每个时间步长的cache值的
caches = []
Wy = parameters[‘Wy‘]
# 从 x 和 parameters[‘Wy‘] 的shape中获取纬度值
n_x, m, T_x = x.shape
n_y, n_a = Wy.shape
?
# 初始化 "a", "c" and "y"
a = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
c = np.zeros((n_a, m, T_x))
y = np.zeros((n_y, m, T_x))
?
# 初始化 a_next and c_next
a_next = a0
c_next = np.zeros(a_next.shape)
?
# loop over all time-steps
for t in range(T_x):
# 从3维张量x中获取t时间步长的2维张量xt
xt = x[:, :, t]
# 更新下一个时间步长的隐藏状态, 下一个单元状态, 计算预测值
a_next, c_next, yt, cache = lstm_cell_forward(xt, a_next, c_next, parameters)
# 把下一个时间步长长的隐藏状态保存起来
a[:,:,t] = a_next
# 把下一个时间步长长的单元状态保存起来
c[:,:,t] = c_next
# 把预测值保存起来
y[:,:,t] = yt
# 保存缓存值
caches.append(cache)
# 用于向后传播
caches = (caches, x)
?
return a, y, c, caches
手把手构建LSTM的向前传播(Building a LSTM step by step)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/siguamatrix/p/12543113.html