Map中的集合,元素是成对存在的(理解为夫妻)。每个元素由键与值两部分组成,通过键可以找对所对应的值。
Collection中的集合称为单列集合,Map中的集合称为双列集合。
需要注意的是,Map
HashMap集合的特点:
1.HashMap集合底层是哈希表:查询的速度特别的快
JDK1.8之前:数组+单向链表
JDK1.8之后:数组+单向链表|红黑树(链表的长度超过8):提高查询的速度
2.hashMap集合是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致
LinkedHashMap的特点:
1.LinkedHashMap集合底层是哈希表+链表(保证迭代的顺序)
2.LinkedHashMap集合是一个有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序是一致的
1.
public class Demo01Map { public static void main(String[] args) { show01(); } /* public V put(K key, V value): 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。 返回值:v 存储键值对的时候,key不重复,返回值V是null 存储键值对的时候,key重复,会使用新的value替换map中重复的value,返回被替换的value值 */ private static void show01() { //创建map集合对象,多态 Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<>(); String v1 = map.put("张伟","大力"); System.out.println(v1); //null String v2 = map.put("张伟","诸葛大力"); System.out.println(v2); //大力 System.out.println(map); //{张伟=诸葛大力} map.put("冷风","龙小云"); map.put("杨过","小龙女"); System.out.println(map);//杨过=小龙女, 张伟=诸葛大力, 冷风=龙小云} } }
2.
/* public V remove(Object key): 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的值。 返回值:V key存在,v返回被删除的值 key不存在,v返回null */ private static void show02() { //创建map集合对象,多态 Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("赵丽因",168); map.put("林志玲",178); map.put("杨颖",165); System.out.println(map); //{林志玲=178, 杨颖=165, 赵丽因=168} Integer r= map.remove("杨颖"); System.out.println(r); //165 System.out.println(map); //{林志玲=178, 赵丽因=168} }
3.
public class Demo01Map { public static void main(String[] args) { show03(); } /* public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。 返回值: key存在,返回对应的value值 key不存在,返回null */ private static void show03() { //创建Map集合对象 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("赵丽颖",168); map.put("杨颖",165); map.put("林志玲",178); System.out.println(map);//{林志玲=178, 赵丽颖=168, 杨颖=165} Integer v = map.get("林志玲"); System.out.println(v); //178 }
4.
/* boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合中是否包含指定的键。 包含返回true,不包含返回false */ private static void show04() { //创建Map集合对象 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("赵丽颖",168); map.put("杨颖",165); map.put("林志玲",178); boolean b = map.containsKey("杨颖"); System.out.println(b); //true boolean a = map.containsKey("一颖"); System.out.println(a); //false }
public class Demo02KeySet { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建map集合对象 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("赵丽颖",168); map.put("杨颖",165); map.put("林志玲",178); //1.使用Map集合中的方法keySet(),把Map集合所有的key取出来,存储到一个Set集合中 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); //2.遍历set集合,获取Map集合中的每一个key //使用迭代器遍历Set集合 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String key = it.next(); //3.通过Map集合中的方法get(key),通过key找到value System.out.println(key+":"+map.get(key)); } System.out.println("------------"); //使用增强for遍历set集合 for (String s : set) { System.out.println(s+":"+map.get(s)); } } }
:
思路图解:
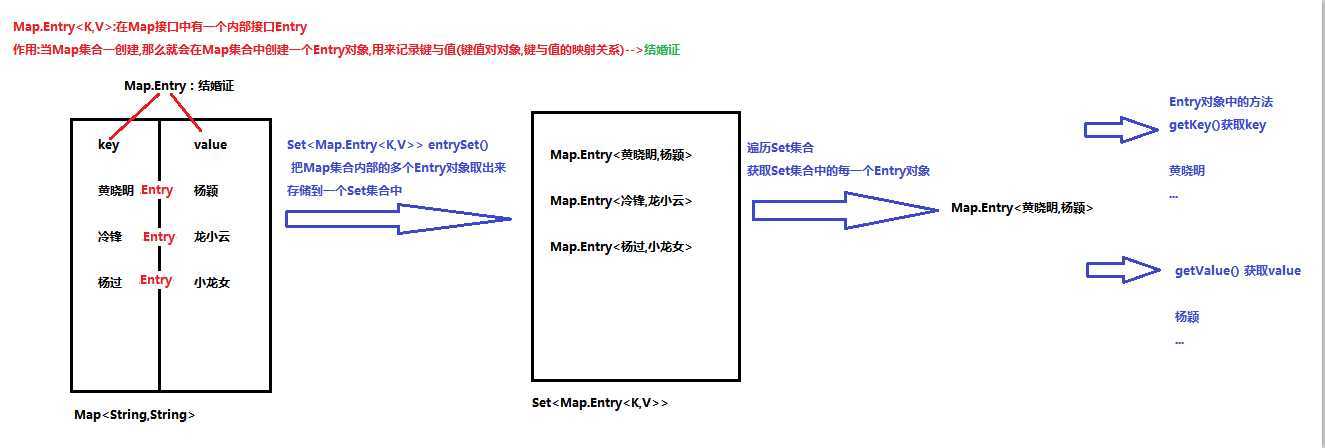
实现步骤:
1.使用Map集合中的方法entrySet(),把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来,存储到一个Set集合中
2.遍历Set集合,获取每一个Entry对象
3.使用Entry对象中的方法getKey()和getValue()获取键与值
public class Demo03EntrySet { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建Map集合对象 Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("赵丽颖",168); map.put("杨颖",165); map.put("林志玲",178); //1.使用Map集合中的方法entrySet(),把Map集合中多个Entry对象取出来,存储到一个Set集合中 Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> set = map.entrySet(); //2.遍历Set集合,获取每一个Entry对象 //使用迭代器遍历Set集合 Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = set.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry = it.next(); //3.使用Entry对象中的方法getKey()和getValue()获取键与值 String key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key+":"+value); } } }
我们知道HashMap保证成对元素唯一,并且查询速度很快,可是成对元素存放进去是没有顺序的,那么我们要保证有序,还要速度快怎么办呢?
在HashMap下面有一个子类LinkedHashMap,它是链表和哈希表组合的一个数据存储结构。
/* java.util.LinkedHashMap<K,V> entends HashMap<K,V> Map 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现,具有可预知的迭代顺序。 底层原理: 哈希表+链表(记录元素的顺序) */ public class Demo01LinkedHashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("a","a"); map.put("c","c"); map.put("b","b"); map.put("a","d"); System.out.println(map);// key不允许重复,无序 {a=d, b=b, c=c} LinkedHashMap<String,String> linked = new LinkedHashMap<>(); linked.put("a","a"); linked.put("c","c"); linked.put("b","b"); linked.put("a","d"); System.out.println(linked);// key不允许重复,有序 {a=d, c=c, b=b} } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/hps123/p/12561727.html