
package org.example.mianshi.concurrent;
/**
* 线程不安全例子,共享数据sharedState
* @author lifuchun
*/
public class ThreadSafeSample {
public int sharedState;
public void nonSafeAction() {
while (sharedState < 100000) {
int former = sharedState++;
int latter = sharedState;
if (former != latter - 1) {
System.out.printf("Observed data race, former is " +
former + ", " + "latter is " + latter);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final ThreadSafeSample sample = new ThreadSafeSample();
Thread threadA = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
sample.nonSafeAction();
}
};
Thread threadB = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
sample.nonSafeAction();
}
};
threadA.start();
threadB.start();
threadA.join();
threadB.join();
}
}
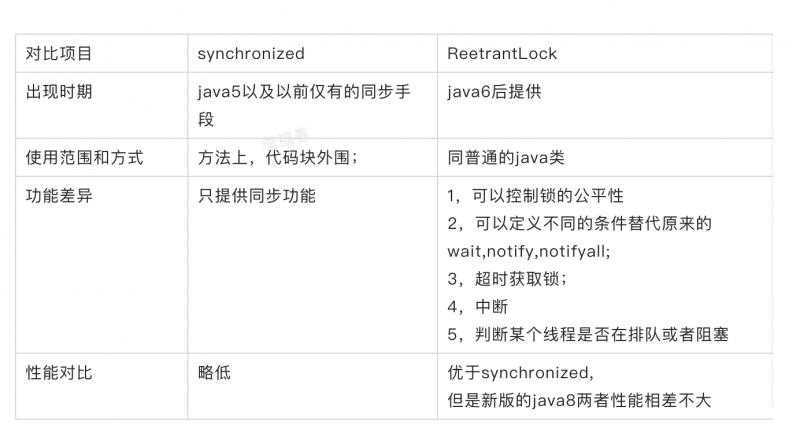
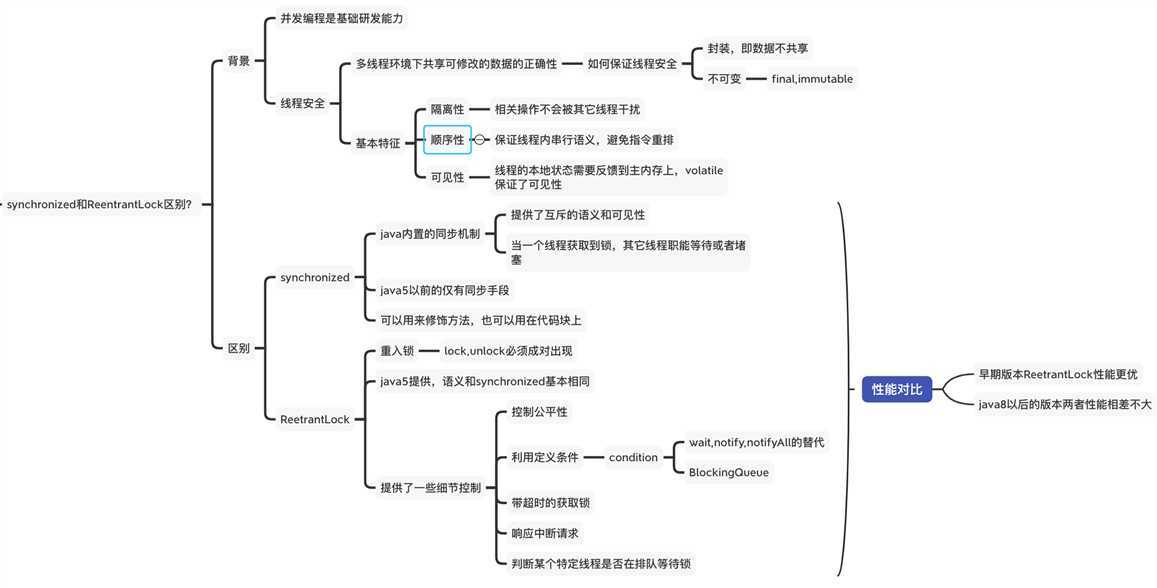
本篇对比了sychronized和ReetrantLock的区别;
然后说了线程安全的概念和保证线程手段。
原创不易,转载请注明出处。
面试刷题16:synchronized和ReentrantLock的区别?
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/snidget/p/12583808.html