nullptr 出现的目的是为了替代 NULL(某些编译器把NULL定义为0)。
专门用来区分空指针、0
nullptr 的类型为 nullptr_t
能够隐式的转换为任何指针或成员指针的类型,也能和他们进行相等或者不等的比较。
当需要使用 NULL 时候,养成直接使用 nullptr的习惯。
类型推导,注意个别的用法(不能推导数组)
常用于迭代器的类型推导
for(vector<int>::const_iterator itr = vec.cbegin(); itr != vec.cend(); ++itr)
我们用auto就比较简单了
// 由于 cbegin() 将返回 vector<int>::const_iterator // 所以 itr 也应该是 vector<int>::const_iterator 类型 for(auto itr = vec.cbegin(); itr != vec.cend(); ++itr); 也可以用begin()
// & 启用了引用 for(auto &i : arr) { std::cout << i << std::endl; }
lambda 表达式,实际上就是提供了一个类似匿名函数的特性,而匿名函数则是在需要一个函数,但是又不想费力去命名一个函数的情况下去使用的。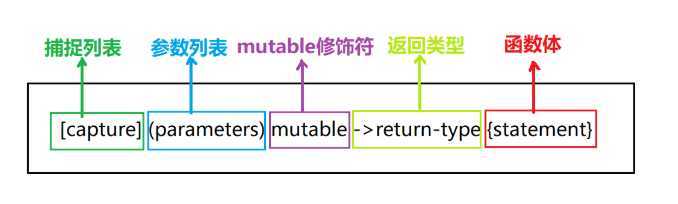
一般情况下参数修饰符和返回类型可以省略
[捕获区](参数区){代码区};
vector<int> vec = {1,3,2,34,2,11};
int m = [](int x) { return [](int y) { return y * 2; }(x)+6; }(5);
cout << m << endl;
auto func1 = [](int i) { return i + 4; }(2); // int i 这个i的值是2,
cout << func1 << endl; // 6
auto f5 = [](int a, int b) {return a + b; };
cout << f5(1,2);
// i 这个也可以从前面获取
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a, int b){return a < b;});
for(auto it : vec) // 1 2 2 3 11 34
cout << it <<" ";
cout << endl;
// for_each 遍历
for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a){cout <<a << " ";});
// 1 2 2 3 11 34
*this )一般使用场景:sort等自定义比较函数、用thread起简单的线程。
详解
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaokang01/p/12589505.html
使用{} 进行列表初始化
int a = {1};
对于 C++ 的类,如果程序员没有为其定义特殊成员函数,那么在需要用到某个特殊成员函数的时候,编译器会隐式的自动生成一个默认的特殊成员函数,
比如拷贝构造函数,或者拷贝赋值操作符。
C++11允许我们使用=default来要求编译器生成一个默认构造函数,也允许我们使用=delete来告诉编译器我们虽然定义了它,但是不能使用它
class B { B() = default; //显示声明使用默认构造函数 B(const B&) = delete; //我们虽然定义了它,但是我们不能使用它 ~B() = default; //显示声明使用默认析构函数 B& operator=(const B&) = delete; //我们虽然定义了它,但是不能使用它。 B(int a); };
https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/9038814.html
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaokang01/p/12589221.html