二、Map集合类别
HashTable
线程安全,默认长度为11,扩容为2*length+1,及在默认长度情况下,第一次扩容长度为23,第二次扩容长度为47。
源码解读略。
HashMap
非线程安全,默认长度为16,扩容为当前数组长度的2倍。
具体扩容可以参考我另一篇文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/yanzige/p/8392142.html
ConcurrentHashMap
线程安全,默认长度为16,扩容为当前数组长度的2倍。
JDK8源码解读:https://blog.csdn.net/ddxd0406/article/details/81389583
LinkedHashMap
非线程安全,父类是HashMap,所以默认长度为16,负载引子为0.75,扩容为原来长度的2倍。
因为父类是HashMap,故很多方法都和父类一样,底层也是一个维护了一个数组,每一个位置有一个Entry链表,但是需要注意的是,每一个位置的Entry对象(因为LinkedHashMap中了的Entry继承于HashMap的Entry,但是在继承过程中新增了两个Entry对象,用来记录每个Entry对象的上一个和下一个Entry对象)会保存插入前后的其他Entry对象的位置(该位置可能不是同一个数组下标的Entry),通过这种方式,可以将不同数据的Entry链表串成一整个链表,也就是一个双向链表。
注:下面Entry的源码是使用的JDK8,故LinkedHashMap中的Entry继承HashMap中的Node对象,其实可以直接将JDK8中Node对象理解为JDK7中的Entry对象(两者结构完全一样,都是由final int hash;final K key;V value;Node<K,V> next;组成,只是名字叫法不同而已),所以文字统称Entry。
/**
* HashMap.Node subclass for normal LinkedHashMap entries.
*/
static class Entry<K,V> extends HashMap.Node<K,V> {
Entry<K,V> before, after;
Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
由上面的Entry代码可以看到,LinkedHashMap中的Entry除了和HashMap中的Entry一样的int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next 四个对象(用来记录同一个数组下标的链表信息),还多了Entry<K,V> before, after两个前后的Entry,用来记录新增数据的前后Entry(新增数据时,可能hash冲突在同一个链表上新增,也可能在其他数据位置或者数组其他位置的链表上新增)。通过该方式维护了一个双向的链表。
相对HashMap,因为LinkedHashMap将数组下标每一个位置的链表链接起来了,维护了一个双向的链表,故LinkedHashMap可以记录数据的插入顺序,而HashMap则不能记录插入顺序。
总结:
1、HashMap 和LinkedHashMap 是非线程安全的。
2、HashTable 是线程安全的,但是加锁的方式是在方法上加synchronized,及对整个需要操作的对象HashTable加锁,可以理解为全表锁,只有有任意一个线程访问HashTable对象,其他线程都需要等待。故并发效率很低。
3、HashMap 和ConcurrentHashMap 继承于AbstractMap 类,HashTable 是继承于Dictionary 类,而LinkedHashMap 是继承于HashMap 类,他们4者都实现了Map接口。
4、LinkedHashMap 继承于HashMap,底层实现原理和基本操作和HashMap 一样,只是多维护了一个双向的链表,使得LinkedHashMap 能够记录数据的插入顺序。
5、ConcurrentHashMap默认长度也为16,扩容方式也和HashMap一样。
1)ConcurrentHashMap在JDK7中使用分段锁,相比于HashTable的全表锁,多个线程访问ConcurrentHashMap对象,只要不是同一段的数据,可以多线程同时操作。
2)ConcurrentHashMap在JDK8中使用原子操作(CAS)和代码块synchronized,故加锁的粒度更细,并发效果更好。
三、List集合类别
ArrayList
非线程安全,除指定大小外默认长度为10,扩容为上次长度的1.5倍。若第一次创建对象使用无参构造器,则在put的时候将空数组(0)扩容到默认长度10。
1、ArrayList有三种构造器
0)首先看类中定义的变量
/**
* 初始容量大小
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 初始化数组
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* ArrayList对象存放数据的对象 底层为Object数组
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* ArrayList存放数据量的大小
*/
private int size;
1)无参构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
在无参构造器创建对象的时候,并没有指定容器大小,指定容器大小是在第一次add()的时候
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
在ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1)方法中,放入数据的时候,会检查该数组(ArrayList对象是否为初始化数组),如果为初始化对象的话,则将当前长度1和默认长度10比较,取最大值,然后执行ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity)
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
进入ensureExplicitCapacity()会比较当前大小和elementData.length大小,如果当前大于ArrayList中的数据长度,则进行扩容。第一次进来肯定扩容grow(minCapacity),因为当前elementData.length的值为0
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
下面为扩容的代码,默认将新数组长度扩充到原数组长度的1.5倍,下面代码使用原来的长度加上原长度右移1位(>>1),即新长度=(1+0.5)原长度,并将原数组数据copy到新的数组中。如果为第一次新增add()数据的时候,oldCapacity 为0,则newCapacity = minCapacity即newCapacity =10。
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
在上面扩容过程中,并对长度进行校验,判断扩容的长度是否操作最大数组长度和最大整型(int)正整数长度,及2的31次方-1
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
/**
* 最大整型正整数 2的31次方-1,16进制为0x7fffffff;
*/
public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
2)指定容量的构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
3)指定上限的集合构造器
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection‘s
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
总结:
1)ArrayList底层是一个Object数组,在初始化对象的时候,如果使用无参构造器,则默认大小为10,在第一次添加数据的时候设置初始大小。
2)ArrayList扩容就是将原来的数组的数据复制到新的数组中,除第一次外,每次扩容都变成之前容量的1.5倍
3)ArrayList底层是数组,所以数据存储是连续的,所以它们支持用下标来访问元素,索引数据的速度比较快。
Vector
线程安全,该类基本上所有的方法都是使用synchronized修饰(如:public synchronized boolean isEmpty() {return elementCount == 0;}),故线程安全。和ArrayList一样继承于AbstractList<E>类,无参构造器默认容量大小为10,Vector构造器有4个,一个无参构造器,一个指定容量大小的构造器,一个指定容量大小和超过存储量后按指定大小扩容的构造器,还有一个指定上限的集合构造器。
1、前三个构造器底层都是调用两个参数的构造器:一个指定容量大小和超过存储量后按指定大小扩容的构造器
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* capacity increment.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @param capacityIncrement the amount by which the capacity is
* increased when the vector overflows
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector with the specified initial capacity and
* with its capacity increment equal to zero.
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
/**
* Constructs an empty vector so that its internal data array
* has size {@code 10} and its standard capacity increment is
* zero.
*/
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
2、指定上限的集合构造器
/**
* Constructs a vector containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection‘s
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this
* vector
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
* @since 1.2
*/
public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
elementCount = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);
}
3、在扩容的时候,如果没有使用指定扩容大小,即没有使用上面构造器public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement)初始化对象,那么在扩容的时候直接扩容为原来的2倍
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
LinkedList
非线程安全,LinkedList 底层维护了一个双向链表,该链表有一个前向节点Node<E> first和一个后向节点Node<E> last。每次新增数据add()的时候,会在最后一个节点last后添加新节点,并且把刚添加的新节点赋值给last。如果为第一次新增,那么该新增的节点既是first节点,又是last节点。
注:Node<E>节点里面会存一个前节点的数据、后节点的数据以及自身的值。每次新增节点后,新增节点的上一个节点数据则为新增前的last节点,新增节点的后一个节点则为空,同时会将当前新增节点的数据存入上一个节点中的下节点信息中。这样就串为了一整个链表,链表中除了first和last节点外,每一个节点都包含上一个节点和下一个节点的信息。因为Node节点中存有前一节点和后一节点的数据,所以只要打开任意一个Node节点数据,向前可以查看该节点前的所有数据,向后可以查看该节点后的所有数据。如果该节点处于头部,那么向后可以查看链表的所有数据,如果该节点处于尾部,向前可以查看该链表的所有数据。
如下图处于链表尾部,该节点下一个节点为空,但是向前可以查看所有数据:
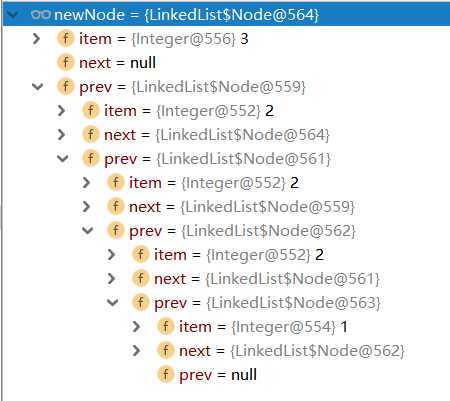
1、add()添加数据的方法
add()添加数据使用方法linkLast(),将该链表中last数据存入当前Node节点的前一个节点信息,当前Node节点的下一个节点为空,并将当前Node替换为last节点。从添加流程代码可以看出来,LinkedList 在添加的时候并没有对重复数据进行处理,所以LinkedList 中是可以存储重复数据的。添加完成后,最后将链表长度数据size大小加1,然后将操作次数modCount数据加1.
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
2、下面我们看几个remove()方法
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
remove方法通过调用unlinkFirst(f)和unlinkLast(l)进行删除,无论是删除头部还是尾部,或者是中间位置的元素,都需要把链表前后位置进行连接。
/**
* 删除头部数据first,先将该头部数据fist的下一个数据为新的first节点,然后将first节点中的prev节点设置为空,
* 再将原firt头部节点数据删除,再将原头部节点的next数据置空。最后将链表长度数据size减一,将操作次数modCount加一
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 删除尾部数据last,先将该尾部节点数据的prev取出来,并且将取出的上一个节点设置为last,在设置的同时将其中的next设置为空,
* 然后将该尾部数据以及该节点中的prev置空。最后将链表长度数据size减一和操作次数modCount加一
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 删除中间节点数据,取出该节点的next节点和prev节点数据,然后将前一个节点prev的next设置为删除数据中的next,将后一个节点的prev节点数据的next数据设置为即将删除数据的next数据,
* 然后将被删除的数据的所有数据都置空,最后将链表长度数据size减一和操作次数modCount加一
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
CopyOnWriteArrayList
线程安全,在并发包concurrent包下,使用了ReentrantLock锁来保证读写数据安全,同一时刻只能有一个线程进行写操作,但是可以有多个线程进行并发读数据,同时通过关键字volatile来保证读数据时候的可见性,及每次数据在主内存中修改后,工作内存中读取的数据会跟新为最新的数据,来保证读数据的线程安全。CopyOnWriteArrayList没有初始容量大小。
底层也是通过维护数组来存储数据,该数组使用volatile修饰的,保证数据的可见性
private transient volatile Object[] array;
CopyOnWriteArrayList 在读写的时候使用ReentrantLock来保证线程安全,为什么却说CopyOnWriteArrayList 非绝对线程安全啦?原因在于CopyOnWriteArrayList在于为保证读写效率,在写和修改的时候可以进行数据的读取,那么在数据删除的时候就会存在线程安全(报错)问题,当数据在进行删除的时候,同时在读取该数据,删除完成的瞬间,然后读数据发生,就会报错:数组下标越界。可以参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/fc0ee3aaf2df
关于更多CopyOnWriteArrayList的相关解读可以查考:https://www.cnblogs.com/myseries/p/10877420.html
总结,关于ArrayList,Vector,LinkedList和CopyOnWriteArrayList 的对比:
1、 ArrayList和Vector底层原理一样,都是使用Object数据,都是继承于AbstractList<E>类,未指定初始容量的话默认都为10,扩容的时候ArrayList为原来的1.5倍,而Vector扩容为原来的2倍。其次ArrayList为线程不安全的类,而Vector为线程安全的。因为Vector使用synchronize来保证线程安全,所以在效率上和ArrayList相比要低。
2、CopyOnWriteArrayList底层也为数组,但是没有初始容量。CopyOnWriteArrayList线程安全,和线程安全的Vector相比,因为CopyOnWriteArrayList使用ReentrantLock锁对指定代码块枷锁,能满足多线程读的需求,并且在写的过程中可以进行读数据,相比于Vector类中的synchronize对整个方法进行加锁的方式,并发效率更高。
3、LinkedList底层使用一个双向链表,和上面两个原理不一样,是线程不安全的。因为LinkedList底层是链表,所以LinkedList在新增和删除数据的时候效率很高,但是在查询的时候需要依次遍历,所以查询效率较低。相反,ArrayList和Vector底层使用数组,内存地址是连续的,所以在查询的时候效率很高,但是在新增和删除的时候设计扩容(数组的复制),所以效率相比LinkedList要低。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/kakaisgood/p/12613672.html