案例源码链接 http://studyai.com/pytorch-1.2/beginner/fanshionmnist_tutorial.html
1、打开PyCharm,创建项目,新建python文件,hello.py
从上到下依次粘贴链接的代码,注意修改如下:
① 添加代码,其后的所有代码必须缩进 if __name__ == "__main__":
② transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
改为
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])
因为处理的是单通道的灰度图,而不是三通道。为什么是这两个数,点击参考?
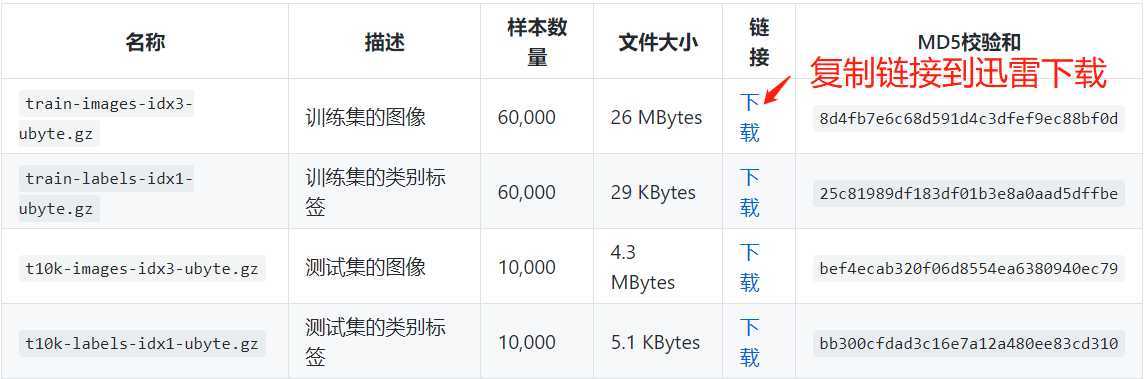
2、下载FASHION-MNIST数据,放到项目目录..\PycharmProjects\untitled4\data\fashiomnist\FashionMNIST\raw,运行程序会自动解压的。
3、运行程序
【全部程序如下】
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import torch import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms print("PyTorch Version: ", torch.__version__) print("Torchvision Version: ", torchvision.__version__) # 忽略 warnings import warnings warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") if __name__ == "__main__": ############################### 1 使用 torchvision 加载和规范训练和测试数据集 batch_size = 16 #transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))]) trainset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=‘./data/fashiomnist‘, train=True, download=True, transform=transform) trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2) testset = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=‘./data/fashiomnist‘, train=False, download=True, transform=transform) testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2) classes = (‘T-shirt/top‘, ‘Trouser‘, ‘Pullover‘, ‘Dress‘, ‘Coat‘, ‘Sandal‘, ‘Shirt‘, ‘Sneaker‘, ‘Bag‘, ‘Ankle boot‘) print("训练集大小:", len(trainloader) * batch_size) print("测试集大小:", len(testloader) * batch_size) ########################################## 展示训练集中的图片 # 用于显示一张图像的函数 def imshow(img): img = img / 2 + 0.5 # 去归一化 npimg = img.numpy() plt.imshow(np.transpose(npimg, (1, 2, 0))) # 获取一个批次的图像,一次迭代取出batch_size张图片 dataiter = iter(trainloader) images, labels = dataiter.next() # 显示一个批次的图像 imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)) # 输出 对应批次图像的标签 print(‘ ‘.join(‘%5s‘ % classes[labels[j]] for j in range(batch_size))) ######################################## 定义网络模型 import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F class Net1(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net1, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5) self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10) self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(20) def forward(self, x): x = F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2) x = F.relu(x) + F.relu(-x) x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2)) x = self.bn(x) x = x.view(-1, 320) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training) x = self.fc2(x) x = F.softmax(x, dim=1) return x class Net2(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(Net2, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5) self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d() self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10) def forward(self, x): x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2)) x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2)) x = x.view(-1, 320) x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training) x = self.fc2(x) x = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1) return x class Net3(nn.Module): """ Simple network""" def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.features = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, padding=1), # 28 nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # 14 nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 7 ) self.classifier = nn.Sequential( nn.Dropout(), nn.Linear(64 * 7 * 7, 128), nn.ReLU(inplace=True), nn.Linear(128, 10) ) def forward(self, x): x = self.features(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), 64 * 7 * 7) x = self.classifier(x) return x ################################### 将模型写入文件并用TensorBoard查看 from tensorboardX import SummaryWriter # 无意义输入,与MNIST的一个batch数据的shape相同 dummy_input = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.rand(batch_size, 1, 28, 28)) model1 = Net1() print(model1) with SummaryWriter(comment=‘_fashionmnist_net1‘) as w: w.add_graph(model1, (dummy_input,)) model2 = Net2() print(model2) with SummaryWriter(comment=‘_fashionmnist_net2‘) as w: w.add_graph(model2, (dummy_input,)) model3 = Net3() print(model3) with SummaryWriter(comment=‘_fashionmnist_net3‘) as w: w.add_graph(model3, (dummy_input,)) ################################## 定义损失函数和优化器 import torch.optim as optim device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") print(device) # 选择上面定义的任意一个模型 model1,model2,model3,... net = model3.to(device) # or = model2 loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9) writer = SummaryWriter(comment=‘_fashionmnist_logs‘) ########################################################### 计算初始网络的准确率 correct = 0 total = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for data in testloader: images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device) outputs = net(images) _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) total += labels.size(0) correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item() print(‘Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%‘ % (100 * correct / total)) ##开始训练 num_epochs = 10 num_batches = len(trainloader) for epoch in range(num_epochs): running_loss = 0.0 for step, data in enumerate(trainloader): n_iter = epoch * num_batches + step images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device) # 将梯度清零 optimizer.zero_grad() # 向前传递 out = net(images) # 计算损失 loss_value = loss(out, labels) # 向后传递 loss_value.backward() # 优化 optimizer.step() # 记录日志 writer.add_scalar(‘loss‘, loss_value.item(), n_iter) running_loss += loss_value.item() if step % 500 == 499: # 每 500 个 mini-batches 就输出一次训练信息 print(‘[%d, %5d] loss: %.3f‘ % (epoch + 1, step + 1, running_loss / 500)) running_loss = 0.0 writer.close() print(‘Finished Training‘) ############################################################ 开始测试 correct = 0 total = 0 with torch.no_grad(): for data in testloader: images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device) outputs = net(images) _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) total += labels.size(0) correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item() print(‘Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %d %%‘ % (100 * correct / total)) ############################################################ 展示每个样本上的准确率 num_classes = len(classes) class_correct = list(0. for i in range(num_classes)) class_total = list(0. for i in range(num_classes)) with torch.no_grad(): for data in testloader: images, labels = data[0].to(device), data[1].to(device) outputs = net(images) _, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1) c = (predicted == labels).squeeze() for i in range(batch_size): label = labels[i] class_correct[label] += c[i].item() class_total[label] += 1 for i in range(num_classes): print(‘Accuracy of %5s : %2d %%‘ % (classes[i], 100 * class_correct[i] / class_total[i])) ############################################ 展示测试样本、真实标签和测试标签 dataiter = iter(testloader) images, labels = dataiter.next() # print images imshow(torchvision.utils.make_grid(images)) print(‘GroundTruth: ‘, ‘ ‘.join(‘%5s‘ % classes[labels[j]] for j in range(batch_size))) outputs = net(images.to(device)) _, predicted = torch.max(outputs, 1) print(‘Predicted: ‘, ‘ ‘.join(‘%5s‘ % classes[predicted[j]] for j in range(batch_size)))
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xixixing/p/12622256.html