什么是API?
Object类中的toString()方法
Object类中的equals()方法
String类中重写了toString()方法和equals()方法
equals()方法深层次剖析
Object类中的finalize()方法
Object类中的hashCode()方法
应用程序編程接口。(Application Program Interface)
整个JDK的类库就是一个javase的API,每一个API都会配置一套API帮助文档。
public string tostring(){
return this.getclass().getName () + "@" + Integer.toHexstring (hashcode ());
}
源代码上toString()方法的默认实现是:类名@对象的内存地址转换为十六进制的形式。
2、toString()方法的设计目的是:
通过调用这个方法可以将一个"Java对象"转换成‘‘字符串”。
3、其实SUN公司开发Java语言的时候,建议所有的子类都去重写toString()方法应该是一个简洁的、详实的、易阅读的。
package com.zyh.ToString;
public class MyTime {
int year;
int month;
int day;
public MyTime(){
}
public MyTime(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
/*重写toString()方法*/
public String toString(){
return this.year + "年" + this.month + "月" + this.day + "日";
}
}
package com.zyh.ToString;
public class MyTimeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTime t1 = new MyTime(1999,3, 10);
System.out.println(t1);
/*直接输出结果为:
com.zyh.ToString.MyTime@74a14482*/
String s1 = t1.toString();
System.out.println(s1);
/*重写toString()方法后,输出结果为:
1999年3月10日*/
System.out.println(t1);
/*可以省略后面的.toString()方法,默认调用。
输出结果同上*/
}
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}
以上这个方法是object类的默认实现。在object类中的equals方法当中,默认采用的是"=="判断两个java对象是否相等。
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class Eqs {
int year;
int month;
int day;
public Eqs(){
}
public Eqs(int year, int month, int day){
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
/*默认的equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (this == obj);
}*
}
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class EqsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
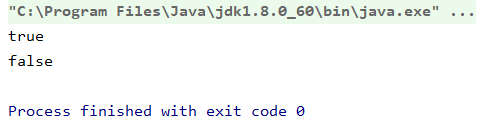
System.out.println(a == b);
Eqs e1 = new Eqs(2020, 3, 25);
Eqs e2 = new Eqs(2020, 3, 25);
System.out.println(e1 == e2);
}
}
由于e1、e2中保存的对象内存地址不同,所以输出:
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class Eqs {
int year;
int month;
int day;
public Eqs() {
}
public Eqs(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
//重写equals方法
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
int year1 = this.year;
int month1 = this.month;
int day1 = this.day;
if (obj instanceof Eqs){
Eqs m1 = (Eqs) obj;
int year2 = m1.year;
int month2 = m1.month;
int day2 = m1.day;
if (year1==year2&&month1==month2&&day1==day2){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class EqsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
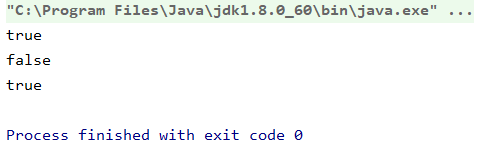
int b = 10;
System.out.println(a == b);
Eqs e1 = new Eqs(2020, 3, 25);
Eqs e2 = new Eqs(2020, 3, 25);
System.out.println(e1 == e2);
//重写equals方法后
boolean flag = e1.equals(e2);
System.out.println(flag);
}
}
输出:
public boolean equals(Object obj){
//如果obj是空,直接返回false
if (obj==null){
return false;
}
//如果oj不是一个Eqs。没必要比较了,直接返回false
if (!(obj instanceof Eqs)){
return false;
}
/*如果this和obj保存的内存地址相同,
没必要比较了,直接返回true。
内存地址相同的时候指向的堆内存
的对象肯定是同一个。*/
if (this == obj){
return true;
}
/*程序能够执行到此处说明:
obj不是null, obj是Eqs类型*/
Eqs m1 = (Eqs) obj;
if (this.year==m1.year && this.month==m1.month && this.day==m1.day){
return true;
}
//程序能到这里返回false
return false;
/*再改良
Eqs m1 = (Eqs) obj;
return this.year==m1.year && this.month==m1.month && this.day==m1.day;
*/
}
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "zyh";
String s2 = "zyh";
System.out.println(s1 == s2);/*这里是true,
原因是因为String是sun亲生的,所以双引是常量,
常量和常量用等就是true,方法区有个常量池。*/
String s3 = new String("yu");
String s4 = new String("yu");
System.out.println(s3 == s4);//false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));//true;
}
}
package com.zyh.ToStAndEquals;
public class Str {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String x = new String("zhang");
System.out.println(x.toString());//输出:zhang
System.out.println(x);//输出:zhang
}
}
package com.zyh.EqsPro;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Address {
String city;
String street;
String zipcode;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String city, String street, String zipcode) {
this.city = city;
this.street = street;
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
/*这里也要进行对equals的重写,
否则比较的就是u1、u2中的Address的
内存地址,而不是内容
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Address address = (Address) o;
return city.equals(address.city) &&
street.equals(address.street) &&
zipcode.equals(address.zipcode);
}
/*重写toString方法,保证输出的Address
是指定内容,而不是哈希值。
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"city=‘" + city + ‘\‘‘ +
", street=‘" + street + ‘\‘‘ +
", zipcode=‘" + zipcode + ‘\‘‘ +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.zyh.EqsPro;
import java.util.Objects;
public class User {
String name;
Address addr;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, Address addr) {
this.name = name;
this.addr = addr;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
/*u2传进来的时候发生了类型自动转换,
转换成了Object类型。
*/
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
User user = (User) o;
return this.name.equals(user.name) &&
this.addr.equals(user.addr);
/*这里的equals是this.name字符串里的equals方法,
不是equals方法里面又用equals方法*/
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name=‘" + name + ‘\‘‘ +
", addr=" + addr +
‘}‘;
}
}
package com.zyh.EqsPro;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User("zhang", new Address("CD", "px","111"));
User u2 = new User("zhang", new Address("CD", "px","111"));
System.out.println(u1.equals(u2));
System.out.println(u1);
}
}
protected void finalize() throws Throwable { }
package com.zyh.FinalizeDemo;
public class Person {
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
/*重写finalize()方法。
Person类型的对象被垃圾回收器回收的时候,
垃圾回收器负责调用:p.finalize()*/
System.out.println(this + "垃圾被回收!");
/*项目开发中有这样的业务需求:
所有对象在JVM中被释放的时候,记录释放时间*/
}
}
package com.zyh.FinalizeDemo;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person();
p = null;
/*提示:ava中的垃圾回收器不是轻易启动的,
垃圾太少,或者时间没到。
种种条件下,有可能启动,也有可能不启动。
例如:家里的垃圾桶不会有垃圾就去倒*/
//制造大量垃圾,使其启动
for (int i = 1; i < 1000000; i++) {
Person q = new Person();
q = null;
}
System.gc();
/*建议启动垃圾回收器,提高启动的概率
(只是建议,可能不启动,也可能启动)*/
}
}
public native int hashCode();
这个方法不是抽象方法,带有native关键字,底层调用C+程序。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o = new Object();
System.out.println(o.hashCode());
//输出:1956725890
Object o1 = new Object();
System.out.println(o1.hashCode());
//输出:356573597
/*对象内存地址经过哈希算法转换的一个数字,
可以等同看做内存地址。*/
}
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yu011/p/12632727.html