参考:
1. CNN 模型所需的计算力(flops)和参数(parameters)数量是怎么计算的?
理论上的计算公式如下:
\begin{equation}
\label{FLOPs}
\begin{split}
& param_{conv} = (k_w * k_h * c_{in}) * c_{out} + c_{out} \\
& macc_{conv} = (k_w * k_h * c_{in}) * c_{out} * H * W \\
& FLOPs_{conv} = [2 * (k_w * k_h * c_{in}) * c_{out} + c_{out}] * H * W \\
& param_{fc} = (n_{in} * n_{out}) + n_{out} \\
& macc_{fc} = n_{in} * n_{out} \\
& FLOPs_{fc} = 2 * (n_{in} * n_{out}) + n_{out} \\
\end{split}
\end{equation}
注:以上公式是考虑常规卷积/全连接层操作且有 bias 的情况!
卷积层的参数量和卷积核的大小、输入输出通道数相关;全连接层的参数量则只与输入输出通道数有关。
MACCs:是multiply-accumulate operations,指点积运算, 一个 macc = 2FLOPs
FLOPs 的全称是 floating points of operations,即浮点运算次数,用来衡量模型的计算复杂度。计算 FLOPs 实际上是计算模型中乘法和加法的运算次数。卷积层的浮点运算次数不仅取决于卷积核的大小和输入输出通道数,还取决于特征图的大小;而全连接层的浮点运算次数和参数量是相同的。
特别的,对于 Group Conv:
\begin{equation}
\label{GC_FLOPs}
\begin{split}
& param_{GC} = (k_w * k_h * \frac{c_{in}}{G}) * c_{out} + c_{out} \\
& macc_{GC} = (k_w * k_h * \frac{c_{in}}{G}) * c_{out} * H * W \\
& FLOPs_{GC} = [2 * (k_w * k_h * \frac{c_{in}}{G}) * c_{out} + c_{out}] * H * W \\
\end{split}
\end{equation}
简单起见,这里以 LeNet 为例:
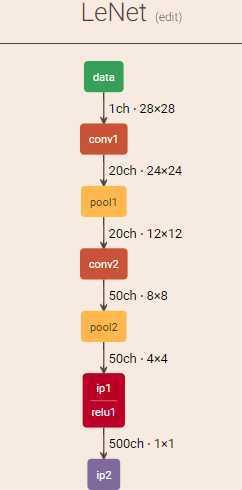
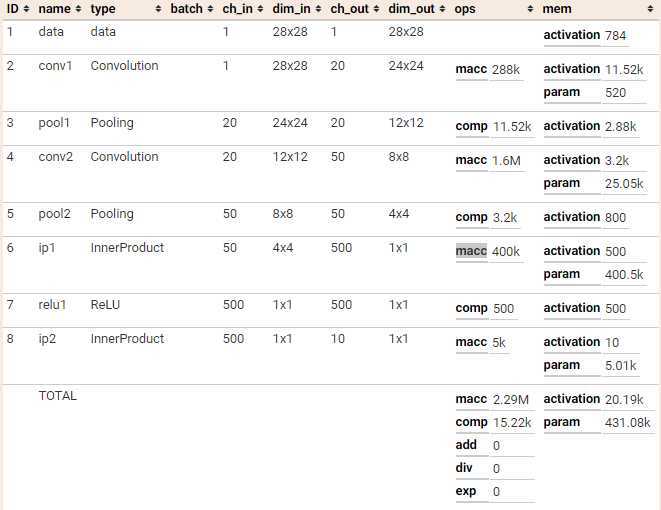
我们这里先手工计算下:
\begin{equation}
\label{Example}
\begin{split}
& param_{conv1} = (5^2 * 1) * 20 + 20 = 520 \\
& macc_{conv1} = (5^2 * 1) * 20 * 24 * 24 = 288k \\
& FLOPs_{conv1} = 2 * macc_{conv1} + 20 * 24 * 24 = 587.52k \\
& \\
& FLOPs_{pool1} = 20 * 24 * 24 = 11.52k \\
& \\
& param_{conv2} = (5^2 * 20) * 50) + 50 = 25.05k \\
& macc_{conv1} = (5^2 * 20) * 50 * 8 * 8 = 1.6M \\
& FLOPs_{conv2} = 2 * macc_{conv2} + 50 * 8 * 8 = 3203.2k \\
& \\
& FLOPs_{pool2} = 50 * 8 * 8 = 3.2k \\
& \\
& param_{ip1} = (50*4*4) * 500 + 500 = 400.5k \\
& macc_{ip1} = (50*4*4) * 500 = 400k \\
& FLOPs_{ip1} = 2* macc_{ip1} + 500 = 800.5k \\
&\\
& param_{ip2} = 500 * 10 + 10 = 5.01k \\
& macc_{ip2} = 500 * 10 = 5k \\
& FLOPs_{ip2} = 2 * macc_{ip2} + 10 = 10.01k \\
\end{split}
\end{equation}
那么,对于 Depthwise Separable Convolution = DW+PW 的

name: "LeNet" input: "data" input_shape { dim: 1 dim: 1 dim: 28 dim: 28 } layer { name: "conv1" type: "Convolution" bottom: "data" top: "conv1" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } convolution_param { num_output: 20 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "xavier" } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "pool1" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv1" top: "pool1" pooling_param { pool: MAX kernel_size: 2 stride: 2 } } layer { name: "conv2" type: "Convolution" bottom: "pool1" top: "conv2" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } convolution_param { num_output: 50 kernel_size: 5 stride: 1 weight_filler { type: "xavier" } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "pool2" type: "Pooling" bottom: "conv2" top: "pool2" pooling_param { pool: MAX kernel_size: 2 stride: 2 } } layer { name: "ip1" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "pool2" top: "ip1" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } inner_product_param { num_output: 500 weight_filler { type: "xavier" } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } } layer { name: "relu1" type: "ReLU" bottom: "ip1" top: "ip1" } layer { name: "ip2" type: "InnerProduct" bottom: "ip1" top: "ip2" param { lr_mult: 1 } param { lr_mult: 2 } inner_product_param { num_output: 10 weight_filler { type: "xavier" } bias_filler { type: "constant" } } }
我们可以把网络用 Netscope 工具打开,直接得到结果:

import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data # ================================================================ # # Train a Sample Model # # ================================================================ # # 1. create data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(‘../MNIST‘, one_hot=True) with tf.variable_scope(‘Input‘): tf_x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 28 * 28], name=‘x‘) image = tf.reshape(tf_x, [-1, 28, 28, 1], name=‘image‘) tf_y = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, 10], name=‘y‘) is_training = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool, shape=None) # 2. define Network with tf.variable_scope(‘Net‘): """ "SAME" 类型的padding: out_height = ceil(in_height / strides[1]); ceil向上取整 out_width = ceil(in_width / strides[2]) "VALID"类型的padding: out_height = ceil((in_height - filter_height + 1) / striders[1]) out_width = ceil((in_width - filter_width + 1) / striders[2] """ conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=image, filters=20, kernel_size=5, strides=1, padding=‘valid‘, activation=None, name=‘conv1‘) # 20x24x24 pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=2, strides=2, name=‘pool1‘) # 20x12x12 conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(pool1, 50, 5, 1, ‘valid‘, activation=None, name=‘conv2‘) # 50x8x8 pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, 2, 2, name=‘pool2‘) # 50x4x4 pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 4 * 4 * 50]) fc1 = tf.layers.dense(pool2_flat, 500, tf.nn.relu, name=‘ip1‘) # 500 predict = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 10, name=‘ip2‘) # 10 # 3. define loss & accuracy with tf.name_scope(‘loss‘): loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(onehot_labels=tf_y, logits=predict, label_smoothing=0.01) with tf.name_scope(‘accuracy‘): # tf.metrics.accuracy() 返回 累计[上次的平均accuracy, 这次的平均accuracy] accuracy = tf.metrics.accuracy(labels=tf.argmax(tf_y, axis=1), predictions=tf.argmax(predict, axis=1))[1] # 4. define optimizer with tf.name_scope(‘train‘): optimizer_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(loss) # 5. initialize init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer()) # 6.train saver = tf.train.Saver() save_path = ‘./leNet_mnist.ckpt‘ with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) for step in range(11000): """ mnist.train.num_examples=55000 11000*100/mnist.train.num_examples=20epochs """ batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(100) _, ls = sess.run([optimizer_op, loss], feed_dict={tf_x: batch_x, tf_y: batch_y, is_training: True}) if step % 100 == 0: acc_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={tf_x: mnist.test.images, tf_y: mnist.test.labels, is_training: False}) print(‘Step: ‘, step, ‘ | train loss: {:.4f} | test accuracy: {:.3f}‘.format(ls, acc_test)) sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # 不加上这句的话 accuracy 就是个累积平均值了 saver.save(sess, save_path) # 7.test with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init_op) saver.restore(sess, save_path) acc_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={tf_x: mnist.test.images, tf_y: mnist.test.labels, is_training: False}) print(‘test accuracy: {}‘.format(acc_test)) # test accuracy: 0.991100013256073
训练得到示例模型 LeNet_mnist.ckpt, 随后为了确定输出节点(Net/ip2/BiasAdd),我们需要到 tensorboard 里去瞅瞅

from tensorflow.summary import FileWriter sess = tf.Session() tf.train.import_meta_graph("leNet_mnist.ckpt.meta") FileWriter("__tb", sess.graph)
知道了输出节点我们就可以将模型转换成 pb 文件了并计算 FLOPs 了:

# ================================================================ # # Convert ckpt to pb & Compute FLOPs # # ================================================================ # from tensorflow.python.framework import graph_util def stats_graph(graph): flops = tf.profiler.profile(graph, options=tf.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder.float_operation()) params = tf.profiler.profile(graph, options=tf.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder.trainable_variables_parameter()) print(‘FLOPs: {}; Trainable params: {}‘.format(flops.total_float_ops, params.total_parameters)) with tf.Graph().as_default() as graph: # 1. Create Graph image = tf.Variable(initial_value=tf.random_normal([1, 28, 28, 1])) conv1 = tf.layers.conv2d(inputs=image, filters=20, kernel_size=5, strides=1, padding=‘valid‘, activation=None, name=‘conv1‘) # 20x24x24 pool1 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(inputs=conv1, pool_size=2, strides=2, name=‘pool1‘) # 20x12x12 conv2 = tf.layers.conv2d(pool1, 50, 5, 1, ‘valid‘, activation=None, name=‘conv2‘) # 50x8x8 pool2 = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(conv2, 2, 2, name=‘pool2‘) # 50x4x4 pool2_flat = tf.reshape(pool2, [-1, 4 * 4 * 50]) fc1 = tf.layers.dense(pool2_flat, 500, tf.nn.relu, name=‘ip1‘) # 500 predict = tf.layers.dense(fc1, 10, name=‘ip2‘) # 10 print(‘stats before freezing‘) stats_graph(graph) # 2. Freeze Graph with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) output_graph = graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(sess, graph.as_graph_def(), [‘ip2/BiasAdd‘]) with tf.gfile.GFile(‘LeNet_mnist.pb‘, "wb") as f: f.write(output_graph.SerializeToString()) def load_pb(pb): with tf.gfile.GFile(pb, "rb") as f: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read()) with tf.Graph().as_default() as graph: tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name=‘‘) return graph # 3. Load Frozen Graph graph = load_pb(‘LeNet_mnist.pb‘) print(‘stats after freezing‘) stats_graph(graph)
stats before freezing
FLOPs: 5478522; Trainable params: 431864
stats after freezing
FLOPs: 4615950; Trainable params: 0
具体的:
node name | # parameters _TFProfRoot (--/431.86k params) Variable (1x28x28x1, 784/784 params) conv1 (--/520 params) conv1/bias (20, 20/20 params) conv1/kernel (5x5x1x20, 500/500 params) conv2 (--/25.05k params) conv2/bias (50, 50/50 params) conv2/kernel (5x5x20x50, 25.00k/25.00k params) ip1 (--/400.50k params) ip1/bias (500, 500/500 params) ip1/kernel (800x500, 400.00k/400.00k params) ip2 (--/5.01k params) ip2/bias (10, 10/10 params) ip2/kernel (500x10, 5.00k/5.00k params) node name | # float_ops _TFProfRoot (--/4.62m flops) conv2/Conv2D (3.20m/3.20m flops) ip1/MatMul (800.00k/800.00k flops) conv1/Conv2D (576.00k/576.00k flops) conv1/BiasAdd (11.52k/11.52k flops) pool1/MaxPool (11.52k/11.52k flops) ip2/MatMul (10.00k/10.00k flops) conv2/BiasAdd (3.20k/3.20k flops) pool2/MaxPool (3.20k/3.20k flops) ip1/BiasAdd (500/500 flops) ip2/BiasAdd (10/10 flops)

import torch import torchvision import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torchvision.transforms as transforms from torchsummary import summary # Device configuration device = torch.device(‘cpu‘) #torch.device(‘cuda: 0‘ if torch.cuda.is_available() else ‘cup‘) print(device, torch.__version__) # Hyper parameters num_epochs = 5 num_classes = 10 batch_size = 100 learning_rate = 0.01 # MINST DATASET train_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root=‘H:/Other_Datasets/‘, train=True, transform=transforms.ToTensor(), download=True) test_dataset = torchvision.datasets.MNIST(root=‘H:/Other_Datasets/‘, train=False, transform=transforms.ToTensor()) # Data loader train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True) test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=test_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) class LeNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes): super(LeNet, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 20, kernel_size=5, stride=1) # 20x24x24 self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 20x12x12 self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 50, kernel_size=5, stride=1) # 50x8x8 self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2) # 50x4x4 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(50 * 4 * 4, 500) # 500 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(500, num_classes) # 10 def forward(self, input): out = self.conv1(input) out = self.pool1(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.pool2(out) out = out.reshape(out.size(0), -1) # pytorch folow NCHW convention out = F.relu(self.fc1(out)) out = self.fc2(out) return out model = LeNet(1, num_classes).to(device)
可直接使用 torchsummary 模块统计参数量
summary(model, (1, 28, 28), device=device.type) """ ---------------------------------------------------------------- Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================ Conv2d-1 [-1, 20, 24, 24] 520 MaxPool2d-2 [-1, 20, 12, 12] 0 Conv2d-3 [-1, 50, 8, 8] 25,050 MaxPool2d-4 [-1, 50, 4, 4] 0 Linear-5 [-1, 500] 400,500 Linear-6 [-1, 10] 5,010 ================================================================ Total params: 431,080 Trainable params: 431,080 Non-trainable params: 0 ---------------------------------------------------------------- Input size (MB): 0.00 Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.14 Params size (MB): 1.64 Estimated Total Size (MB): 1.79 ---------------------------------------------------------------- """
from thop import profile input = torch.randn(1, 1, 28, 28) macs, params = profile(model, inputs=(input, )) print(‘Total macc:{}, Total params: {}‘.format(macs, params)) """ Total macc:2307720.0, Total params: 431080.0 """
from torchstat import stat stat(model, (1, 28, 28)) """ module name input shape output shape params memory(MB) MAdd Flops MemRead(B) MemWrite(B) duration[%] MemR+W(B) 0 conv1 1 28 28 20 24 24 520.0 0.04 576,000.0 299,520.0 5216.0 46080.0 99.99% 51296.0 1 pool1 20 24 24 20 12 12 0.0 0.01 8,640.0 11,520.0 46080.0 11520.0 0.00% 57600.0 2 conv2 20 12 12 50 8 8 25050.0 0.01 3,200,000.0 1,603,200.0 111720.0 12800.0 0.00% 124520.0 3 pool2 50 8 8 50 4 4 0.0 0.00 2,400.0 3,200.0 12800.0 3200.0 0.00% 16000.0 4 fc1 800 500 400500.0 0.00 799,500.0 400,000.0 1605200.0 2000.0 0.00% 1607200.0 5 fc2 500 10 5010.0 0.00 9,990.0 5,000.0 22040.0 40.0 0.00% 22080.0 total 431080.0 0.07 4,596,530.0 2,322,440.0 22040.0 40.0 99.99% 1878696.0 ========================================================================================================================================== Total params: 431,080 ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Total memory: 0.07MB Total MAdd: 4.6MMAdd Total Flops: 2.32MFlops Total MemR+W: 1.79MB """
不过,貌似这里和论文中的计算方式不一样,感觉上 conv = macc/2 + bias_op, fc = macc, pool 对于 caffe 的 comp
ps: 网上有评论说 MAdd 和 Flops 应该对调!
深度学习笔记(二十)网络的参数量(param) 和浮点计算量(FLOPs)
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuanyuyt/p/12653041.html