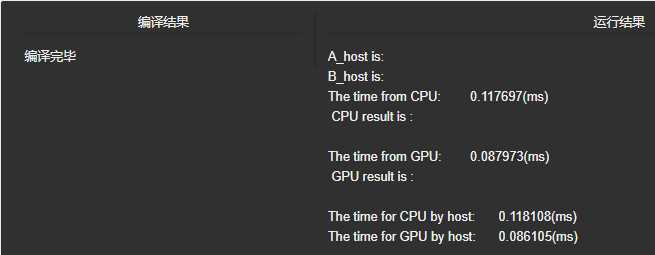
1.两个一维数组相加,求和

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 5 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 6 void initial(float *list,int size) 7 { 8 float *num = list; 9 //srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 10 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 11 { 12 num[i] = rand()%10; 13 } 14 15 } 16 void sumMatrix(float* MatA, float* MatB,float *MatC,int nx,int ny) 17 { 18 float* a=MatA; 19 float* b=MatB; 20 float* c=MatC; 21 for(int j=0; j<ny;j++) 22 { 23 for(int i=0; i<nx;i++) 24 { 25 c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; 26 } 27 c += nx; 28 b += nx; 29 a += nx; 30 } 31 } 32 33 34 //核函数 35 __global__ void GPUsumMatrix(float* MatA,float* MatB,float* MatC,int nx,int ny) 36 { 37 int ix = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x; 38 int iy = threadIdx.y + blockDim.y * blockIdx.y; 39 int idx = ix + iy * ny; 40 if(ix<nx && iy<ny) 41 { 42 MatC[idx] = MatA[idx] + MatB[idx]; 43 // printf("\n C: %f \n",MatC[idx]); 44 } 45 } 46 47 void printList(float* A,int size) 48 { 49 for (int i=0;i<size;i++) 50 { 51 printf(" %f ",A[i]); 52 } 53 } 54 int main(int argc, char** argv) 55 { 56 //CPU计时方法 57 float time_cpu, time_gpu; 58 clock_t start_cpu, stop_cpu, start_gpu, stop_gpu; 59 //GPU计时方法 60 float time_CPU, time_GPU; 61 cudaEvent_t start_GPU, stop_GPU, start_CPU, stop_CPU; 62 63 //输入二维矩阵 64 int nx = 1<<12; 65 int ny = 1<<12; 66 int nBytes = nx * ny *sizeof(float); 67 //开辟主机内存 68 float *A_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 69 float *B_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 70 float *C_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 71 float *C_from_gpu = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 72 initial(A_host,nx*ny); 73 printf("A_host is:"); 74 // printList(A_host,nx*ny); 75 initial(B_host,nx*ny); 76 printf("\nB_host is:"); 77 // printList(B_host,nx*ny); 78 79 // 创建Event 80 cudaEventCreate(&start_CPU); 81 cudaEventCreate(&stop_CPU); 82 //记录当前时间 83 cudaEventRecord(start_CPU,0); 84 start_cpu = clock(); 85 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,C_host,nx,ny); 86 stop_cpu = clock(); 87 cudaEventRecord(stop_CPU,0); 88 cudaEventSynchronize(start_CPU); 89 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_CPU); 90 //计算时间差 91 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_CPU, start_CPU,stop_CPU); 92 printf("\nThe time from CPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_CPU/1000); 93 //消除Event 94 cudaEventDestroy(start_CPU); 95 cudaEventDestroy(stop_CPU); 96 //输出结果 97 printf(" CPU result is :\n"); 98 // printList(C_host,nx*ny); 99 100 //开辟设备内存 101 float* A_dev = NULL; 102 float* B_dev = NULL; 103 float* C_dev = NULL; 104 cudaMalloc((void**)&A_dev,nBytes); 105 cudaMalloc((void**)&B_dev,nBytes); 106 cudaMalloc((void**)&C_dev,nBytes); 107 108 //输入数据,从hostTO device 109 cudaMemcpy(A_dev,A_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 110 cudaMemcpy(B_dev,B_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 111 dim3 block(2,2); 112 dim3 grid((nx-1)/block.x+1,(ny-1)/block.y+1); 113 // 创建Event 114 cudaEventCreate(&start_GPU); 115 cudaEventCreate(&stop_GPU); 116 //记录当前时间 117 cudaEventRecord(start_GPU,0); 118 start_gpu = clock(); 119 120 GPUsumMatrix<<<grid,block>>>(A_dev,B_dev,C_dev,nx,ny); 121 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,C_host,nx,ny); 122 123 stop_gpu = clock(); 124 cudaEventRecord(stop_GPU,0); 125 cudaEventSynchronize(start_GPU); 126 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_GPU); 127 //计算时间差 128 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_GPU, start_GPU,stop_GPU); 129 printf("\nThe time from GPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_GPU/1000); 130 //消除Event 131 cudaEventDestroy(start_GPU); 132 cudaEventDestroy(stop_GPU); 133 cudaMemcpy(C_from_gpu,C_dev,nBytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 134 //输出结果 135 printf(" GPU result is :\n"); 136 // printList(C_from_gpu,nx*ny); 137 138 cudaFree(A_dev); 139 cudaFree(B_dev); 140 cudaFree(C_dev); 141 free(A_host); 142 free(B_host); 143 free(C_host); 144 145 time_cpu = (float) (stop_cpu-start_cpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 146 time_gpu = (float) (stop_gpu-start_gpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 147 printf("\nThe time for CPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_cpu); 148 printf("The time for GPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_gpu); 149 150 151 cudaDeviceReset(); 152 return 0; 153 }
2.
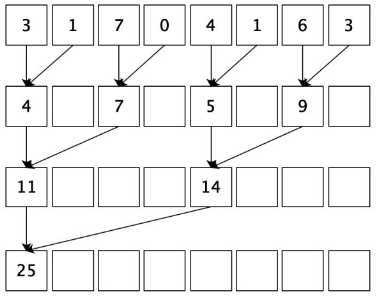
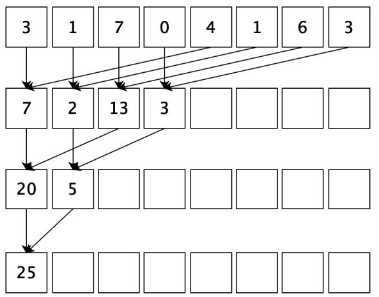
由于加法的交换律和结合律,数组可以以任意顺序求和。所以我们会自然而然产生这样的思路:首先把输入数组划分为更小的数据块,之后用一个线程计算一个数据块的部分和,最后把所有部分和再求和得出最终结果。
依照以上的思路,我们可以按下图这样计算。就上面的输入例子而言,首先需要我们开辟一个8个int的存储空间,图中一行的数据代表我们开辟的存储空间。计算时首先将相邻的两数相加(也称相邻配对),结果写入第一个数的存储空间内。第二轮迭代时我们再将第一次的结果两两相加得出下一级结果,一直重复这个过程最后直到我们得到最终的结果,空白方框里面存储的内容是我们不需要的。这个过程相当于,每一轮迭代后,选取被加数的跨度翻倍,后面我们核函数就是这样实现的。


1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 5 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 6 void initial(float *list,int size) 7 { 8 float *num = list; 9 //srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 10 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 11 { 12 num[i] = rand()%10; 13 } 14 15 } 16 void sumMatrix(float* MatA, float* MatB,int size) 17 { 18 float* a=MatA; 19 float* b=MatB; 20 int i = 0; 21 for(int j=0; j<size;j++) 22 { 23 b[i] += a[j]; 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 29 //核函数 30 __global__ void GPUreduceNeighbored(float* g_idata,float* g_odata, unsigned int n) 31 { 32 //set thread ID 33 unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x; 34 if(tid >= n) return; 35 float *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x; 36 for(int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride*=2) 37 { 38 if((tid%(2*stride))==0) 39 { 40 idata[tid] += idata[tid+stride]; 41 } 42 __syncthreads(); 43 } 44 if(tid == 0) 45 { 46 g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]; 47 } 48 49 } 50 void printList(float* A,int size) 51 { 52 for (int i=0;i<size;i++) 53 { 54 printf(" %f ",A[i]); 55 } 56 } 57 int main(int argc, char** argv) 58 { 59 //CPU计时方法 60 float time_cpu, time_gpu; 61 clock_t start_cpu, stop_cpu, start_gpu, stop_gpu; 62 //GPU计时方法 63 float time_CPU, time_GPU; 64 cudaEvent_t start_GPU, stop_GPU, start_CPU, stop_CPU; 65 66 //输入一维数组 67 int size = 1<<24; 68 69 int nBytes = size *sizeof(float); 70 //开辟主机内存 71 float *A_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 72 float *B_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 73 float *C_from_gpu = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 74 75 initial(A_host,size); 76 printf("A_host is:"); 77 // printList(A_host,size); 78 79 // 创建Event 80 cudaEventCreate(&start_CPU); 81 cudaEventCreate(&stop_CPU); 82 //记录当前时间 83 cudaEventRecord(start_CPU,0); 84 start_cpu = clock(); 85 86 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,size); 87 88 stop_cpu = clock(); 89 cudaEventRecord(stop_CPU,0); 90 cudaEventSynchronize(start_CPU); 91 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_CPU); 92 //计算时间差 93 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_CPU, start_CPU,stop_CPU); 94 printf("\nThe time from CPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_CPU/1000); 95 //消除Event 96 cudaEventDestroy(start_CPU); 97 cudaEventDestroy(stop_CPU); 98 //输出结果 99 printf(" CPU result is :\n"); 100 // printList(B_host,1); 101 102 //开辟设备内存 103 float* A_dev = NULL; 104 float* B_dev = NULL; 105 106 cudaMalloc((void**)&A_dev,nBytes); 107 cudaMalloc((void**)&B_dev,nBytes); 108 // cudaMalloc((void**)&C_dev,nBytes); 109 110 //输入数据,从hostTO device 111 cudaMemcpy(A_dev,A_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 112 //cudaMemcpy(B_dev,B_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 113 dim3 block(1024,1); 114 dim3 grid((size-1)/block.x+1,1); 115 // 创建Event 116 cudaEventCreate(&start_GPU); 117 cudaEventCreate(&stop_GPU); 118 //记录当前时间 119 cudaEventRecord(start_GPU,0); 120 start_gpu = clock(); 121 122 GPUreduceNeighbored<<<grid,block>>>(A_dev,B_dev,size); 123 124 stop_gpu = clock(); 125 cudaEventRecord(stop_GPU,0); 126 cudaEventSynchronize(start_GPU); 127 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_GPU); 128 //计算时间差 129 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_GPU, start_GPU,stop_GPU); 130 printf("\nThe time from GPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_GPU/1000); 131 //消除Event 132 cudaEventDestroy(start_GPU); 133 cudaEventDestroy(stop_GPU); 134 cudaMemcpy(C_from_gpu,B_dev,nBytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 135 //输出结果 136 printf(" GPU result is :\n"); 137 // printList(C_from_gpu,1); 138 139 cudaFree(A_dev); 140 cudaFree(B_dev); 141 142 free(A_host); 143 free(B_host); 144 145 146 time_cpu = (float) (stop_cpu-start_cpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 147 time_gpu = (float) (stop_gpu-start_gpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 148 printf("\nThe time for CPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_cpu); 149 printf("The time for GPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_gpu); 150 151 152 cudaDeviceReset(); 153 return 0; 154 }
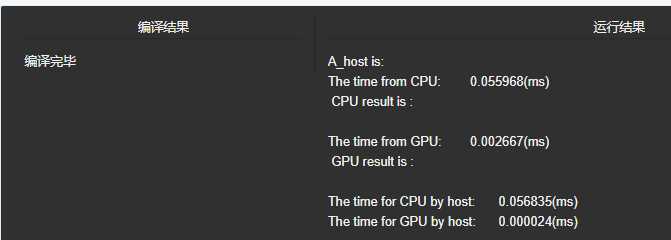
3.
首先我们来回忆一下上个程序的实现思路,我们是利用stride变量来实现每轮迭代时的被加数选择,这造成线程束的分化,也就是每个线程束中只有部分线程是活跃的,但由于硬件设计,调度会以一整个线程束为单位进行,所以影响了程序的效率。
这种情况下,我们可以通过重新组织线程索引来解决线程束分化的问题。我们把核函数的代码进行修改:
相比于之前的初版代码,我们现在使用线程ID来生成一个数组访问索引,这种方式有效地避免了线程束的分化。可能会有点迷惑,我们更具体说说,在每个线程块有1024个线程(32个线程束)时,在第一轮迭代,前16个线程束执行计算,后16个线程束什么都不做;而原来的代码中,32个线程束都执行计算,但只有偶数标号的线程活跃。第二轮迭代时,前8个线程束执行计算,后24个线程束执行计算;而原来的代码中,32个线程束都执行计算,但只有标号是4的倍数的线程活跃。这样重新组织线程ID后,线程束分化就被避免掉了。我们来实际运行一下,看看效果。
可见尽量避免线程束的分化十分重要。这给了我们一点的启发,看似不起眼的细节,在CUDA编程中却会产生不小的影响,这也是我们需要了解底层硬件运行机制的一个重要原因。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 5 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 6 void initial(float *list,int size) 7 { 8 float *num = list; 9 //srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 10 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 11 { 12 num[i] = rand()%10; 13 } 14 15 } 16 void sumMatrix(float* MatA, float* MatB,int size) 17 { 18 float* a=MatA; 19 float* b=MatB; 20 int i = 0; 21 for(int j=0; j<size;j++) 22 { 23 b[i] += a[j]; 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 29 //核函数 30 __global__ void GPUreduceNeighbored(float* g_idata,float* g_odata, unsigned int n) 31 { 32 unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x; 33 unsigned idx = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; 34 // convert global data pointer to the local point of this block 35 float *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x; 36 if (idx > n) 37 return; 38 //in-place reduction in global memory 39 for (int stride = 1; stride < blockDim.x; stride *= 2) 40 { 41 //convert tid into local array index 42 int index = 2 * stride *tid; 43 if (index < blockDim.x) 44 { 45 idata[index] += idata[index + stride]; 46 } 47 __syncthreads(); 48 } 49 //write result for this block to global men 50 if (tid == 0) 51 g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]; 52 53 } 54 void printList(float* A,int size) 55 { 56 for (int i=0;i<size;i++) 57 { 58 printf(" %f ",A[i]); 59 } 60 } 61 int main(int argc, char** argv) 62 { 63 //CPU计时方法 64 float time_cpu, time_gpu; 65 clock_t start_cpu, stop_cpu, start_gpu, stop_gpu; 66 //GPU计时方法 67 float time_CPU, time_GPU; 68 cudaEvent_t start_GPU, stop_GPU, start_CPU, stop_CPU; 69 70 //输入一维数组 71 int size = 1<<24; 72 73 int nBytes = size *sizeof(float); 74 //开辟主机内存 75 float *A_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 76 float *B_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 77 float *C_from_gpu = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 78 79 initial(A_host,size); 80 printf("A_host is:"); 81 // printList(A_host,size); 82 83 // 创建Event 84 cudaEventCreate(&start_CPU); 85 cudaEventCreate(&stop_CPU); 86 //记录当前时间 87 cudaEventRecord(start_CPU,0); 88 start_cpu = clock(); 89 90 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,size); 91 92 stop_cpu = clock(); 93 cudaEventRecord(stop_CPU,0); 94 cudaEventSynchronize(start_CPU); 95 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_CPU); 96 //计算时间差 97 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_CPU, start_CPU,stop_CPU); 98 printf("\nThe time from CPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_CPU/1000); 99 //消除Event 100 cudaEventDestroy(start_CPU); 101 cudaEventDestroy(stop_CPU); 102 //输出结果 103 printf(" CPU result is :\n"); 104 // printList(B_host,1); 105 106 //开辟设备内存 107 float* A_dev = NULL; 108 float* B_dev = NULL; 109 110 cudaMalloc((void**)&A_dev,nBytes); 111 cudaMalloc((void**)&B_dev,nBytes); 112 // cudaMalloc((void**)&C_dev,nBytes); 113 114 //输入数据,从hostTO device 115 cudaMemcpy(A_dev,A_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 116 //cudaMemcpy(B_dev,B_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 117 dim3 block(1024,1); 118 dim3 grid((size-1)/block.x+1,1); 119 // 创建Event 120 cudaEventCreate(&start_GPU); 121 cudaEventCreate(&stop_GPU); 122 //记录当前时间 123 cudaEventRecord(start_GPU,0); 124 start_gpu = clock(); 125 126 GPUreduceNeighbored<<<grid,block>>>(A_dev,B_dev,size); 127 128 stop_gpu = clock(); 129 cudaEventRecord(stop_GPU,0); 130 cudaEventSynchronize(start_GPU); 131 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_GPU); 132 //计算时间差 133 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_GPU, start_GPU,stop_GPU); 134 printf("\nThe time from GPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_GPU/1000); 135 //消除Event 136 cudaEventDestroy(start_GPU); 137 cudaEventDestroy(stop_GPU); 138 cudaMemcpy(C_from_gpu,B_dev,nBytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 139 //输出结果 140 printf(" GPU result is :\n"); 141 // printList(C_from_gpu,1); 142 143 cudaFree(A_dev); 144 cudaFree(B_dev); 145 146 free(A_host); 147 free(B_host); 148 149 150 time_cpu = (float) (stop_cpu-start_cpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 151 time_gpu = (float) (stop_gpu-start_gpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 152 printf("\nThe time for CPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_cpu); 153 printf("The time for GPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_gpu); 154 155 156 cudaDeviceReset(); 157 return 0; 158 }
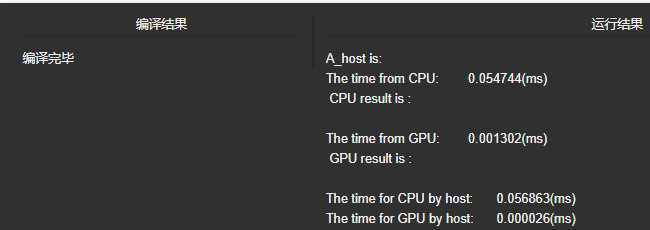
4.
在CPU编程中,我们学过空间局部性与时间局部性,这在CUDA编程中对我们也是很有启发的。之前我们采用相邻配对进行求和,这种方法最为直观,但会造成在第二轮之后内存访问的不连续(因为使用了stride变量作为跨度)。为了缓解这种现象,我们重新组织一下配对方法,让对内存的访问更加集中,如下图,这种新的配对方法我们称为交错配对。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 5 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 6 void initial(float *list,int size) 7 { 8 float *num = list; 9 //srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 10 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 11 { 12 num[i] = rand()%10; 13 } 14 15 } 16 void sumMatrix(float* MatA, float* MatB,int size) 17 { 18 float* a=MatA; 19 float* b=MatB; 20 int i = 0; 21 for(int j=0; j<size;j++) 22 { 23 b[i] += a[j]; 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 29 //核函数 30 __global__ void GPUreduceNeighbored(float* g_idata,float* g_odata, unsigned int n) 31 { 32 unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x; 33 unsigned idx = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; 34 // convert global data pointer to the local point of this block 35 float *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x; 36 if (idx >= n) 37 return; 38 //in-place reduction in global memory 39 for (int stride = blockDim.x/2; stride >0; stride >>=1) 40 { 41 42 if (tid <stride) 43 { 44 idata[tid] += idata[tid + stride]; 45 } 46 __syncthreads(); 47 } 48 //write result for this block to global men 49 if (tid == 0) 50 g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]; 51 52 } 53 void printList(float* A,int size) 54 { 55 for (int i=0;i<size;i++) 56 { 57 printf(" %f ",A[i]); 58 } 59 } 60 int main(int argc, char** argv) 61 { 62 //CPU计时方法 63 float time_cpu, time_gpu; 64 clock_t start_cpu, stop_cpu, start_gpu, stop_gpu; 65 //GPU计时方法 66 float time_CPU, time_GPU; 67 cudaEvent_t start_GPU, stop_GPU, start_CPU, stop_CPU; 68 69 //输入一维数组 70 int size = 1<<24; 71 72 int nBytes = size *sizeof(float); 73 //开辟主机内存 74 float *A_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 75 float *B_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 76 float *C_from_gpu = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 77 78 initial(A_host,size); 79 printf("A_host is:"); 80 // printList(A_host,size); 81 82 // 创建Event 83 cudaEventCreate(&start_CPU); 84 cudaEventCreate(&stop_CPU); 85 //记录当前时间 86 cudaEventRecord(start_CPU,0); 87 start_cpu = clock(); 88 89 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,size); 90 91 stop_cpu = clock(); 92 cudaEventRecord(stop_CPU,0); 93 cudaEventSynchronize(start_CPU); 94 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_CPU); 95 //计算时间差 96 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_CPU, start_CPU,stop_CPU); 97 printf("\nThe time from CPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_CPU/1000); 98 //消除Event 99 cudaEventDestroy(start_CPU); 100 cudaEventDestroy(stop_CPU); 101 //输出结果 102 printf(" CPU result is :\n"); 103 // printList(B_host,1); 104 105 //开辟设备内存 106 float* A_dev = NULL; 107 float* B_dev = NULL; 108 109 cudaMalloc((void**)&A_dev,nBytes); 110 cudaMalloc((void**)&B_dev,nBytes); 111 // cudaMalloc((void**)&C_dev,nBytes); 112 113 //输入数据,从hostTO device 114 cudaMemcpy(A_dev,A_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 115 //cudaMemcpy(B_dev,B_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 116 dim3 block(1024,1); 117 dim3 grid((size-1)/block.x+1,1); 118 // 创建Event 119 cudaEventCreate(&start_GPU); 120 cudaEventCreate(&stop_GPU); 121 //记录当前时间 122 cudaEventRecord(start_GPU,0); 123 start_gpu = clock(); 124 125 GPUreduceNeighbored<<<grid,block>>>(A_dev,B_dev,size); 126 127 stop_gpu = clock(); 128 cudaEventRecord(stop_GPU,0); 129 cudaEventSynchronize(start_GPU); 130 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_GPU); 131 //计算时间差 132 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_GPU, start_GPU,stop_GPU); 133 printf("\nThe time from GPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_GPU/1000); 134 //消除Event 135 cudaEventDestroy(start_GPU); 136 cudaEventDestroy(stop_GPU); 137 cudaMemcpy(C_from_gpu,B_dev,nBytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 138 //输出结果 139 printf(" GPU result is :\n"); 140 // printList(C_from_gpu,1); 141 142 cudaFree(A_dev); 143 cudaFree(B_dev); 144 145 free(A_host); 146 free(B_host); 147 148 149 time_cpu = (float) (stop_cpu-start_cpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 150 time_gpu = (float) (stop_gpu-start_gpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 151 printf("\nThe time for CPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_cpu); 152 printf("The time for GPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_gpu); 153 154 155 cudaDeviceReset(); 156 return 0; 157 }
这给我们的启发是,对全局内存的访问要尽量进行合并访问与存储,这样才能达到最大的带宽。
程序从2.48ms加速到1.36ms,累计获得了1.8倍的加速比。而这两点,恰恰对应了系列开篇中我们提到的CUDA编程的特点,线程组织和内存组织,这也是我们在CUDA编程中需要随时注意的。
5.
(1)现在使用高级语言编程时,我们已经不会刻意去进行循环展开了,因为这件事会由编译器帮我们完成。但在CUDA编程中,循环展开具有很重要的意义,它能给线程束调度器提供更多可用的线程束,以帮助我们有效地隐藏延时。
于是我们可以使用循环展开的方法,对并行归约的程序再来一波优化。
我们之前只是用一个线程块来处理一个小数组,我们称其为一个数据块。如果我们使用一个线程块手动展开两个数据块的处理,那会怎样呢?先给个结论,这样通过减少指令消耗和增加更多的独立调度指令,更多的并发操作被添加到流水线上,以产生了更高的指令和内存带宽。反映在宏观上就是程序执行的总体时间变少了。
(2)从概念上来讲,可以把它作为归约循环的一个迭代,此循环可在数据块间进行归约。
如果每个线程处理两个数据块,那么我们需要的线程块总量会变为原来的一半,因此主函数也要对应修改。
看上去,这样处理后线程块减少了,与我们之前要使用尽量多线程块的理论不符。但实际我们通过这种方式,让一个线程中有更多的独立内存加载/存储操作,这样可以更好地隐藏内存延时,更好地使用设备内存读取吞吐量的指标,以产生更好的性能。所以我们编程时,各个策略要针对实际情况结合使用。

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <time.h> 4 #include "cuda_runtime.h" 5 #include "device_launch_parameters.h" 6 void initial(float *list,int size) 7 { 8 float *num = list; 9 //srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); 10 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) 11 { 12 num[i] = rand()%10; 13 } 14 15 } 16 void sumMatrix(float* MatA, float* MatB,int size) 17 { 18 float* a=MatA; 19 float* b=MatB; 20 int i = 0; 21 for(int j=0; j<size;j++) 22 { 23 b[i] += a[j]; 24 } 25 26 } 27 28 29 //核函数 30 __global__ void GPUreduceNeighbored(float* g_idata,float* g_odata, unsigned int n) 31 { 32 //set thread ID 33 unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x; 34 unsigned int idx = blockDim.x*blockIdx.x*2+threadIdx.x; 35 //boundary check 36 if (tid >= n) return; 37 //convert global data pointer to the 38 float *idata = g_idata + blockIdx.x*blockDim.x*2; 39 //这一句是核心,添加来自相邻数据块的值。 40 if(idx+blockDim.x<n) 41 { 42 g_idata[idx] += g_idata[idx+blockDim.x]; 43 } 44 __syncthreads(); 45 //in-place reduction in global memory 46 for (int stride = blockDim.x/2; stride>0 ; stride >>=1) 47 { 48 if (tid <stride) 49 { 50 idata[tid] += idata[tid + stride]; 51 } 52 //synchronize within block 53 __syncthreads(); 54 } 55 //write result for this block to global mem 56 if (tid == 0) 57 g_odata[blockIdx.x] = idata[0]; 58 59 } 60 void printList(float* A,int size) 61 { 62 for (int i=0;i<size;i++) 63 { 64 printf(" %f ",A[i]); 65 } 66 } 67 int main(int argc, char** argv) 68 { 69 //CPU计时方法 70 float time_cpu, time_gpu; 71 clock_t start_cpu, stop_cpu, start_gpu, stop_gpu; 72 //GPU计时方法 73 float time_CPU, time_GPU; 74 cudaEvent_t start_GPU, stop_GPU, start_CPU, stop_CPU; 75 76 //输入一维数组 77 int size = 1<<24; 78 79 int nBytes = size *sizeof(float); 80 //开辟主机内存 81 float *A_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 82 float *B_host = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 83 float *C_from_gpu = (float*)malloc(nBytes); 84 85 initial(A_host,size); 86 printf("A_host is:"); 87 // printList(A_host,size); 88 89 // 创建Event 90 cudaEventCreate(&start_CPU); 91 cudaEventCreate(&stop_CPU); 92 //记录当前时间 93 cudaEventRecord(start_CPU,0); 94 start_cpu = clock(); 95 96 sumMatrix(A_host,B_host,size); 97 98 stop_cpu = clock(); 99 cudaEventRecord(stop_CPU,0); 100 cudaEventSynchronize(start_CPU); 101 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_CPU); 102 //计算时间差 103 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_CPU, start_CPU,stop_CPU); 104 printf("\nThe time from CPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_CPU/1000); 105 //消除Event 106 cudaEventDestroy(start_CPU); 107 cudaEventDestroy(stop_CPU); 108 //输出结果 109 printf(" CPU result is :\n"); 110 // printList(B_host,1); 111 112 //开辟设备内存 113 float* A_dev = NULL; 114 float* B_dev = NULL; 115 116 cudaMalloc((void**)&A_dev,nBytes); 117 cudaMalloc((void**)&B_dev,nBytes); 118 // cudaMalloc((void**)&C_dev,nBytes); 119 120 //输入数据,从hostTO device 121 cudaMemcpy(A_dev,A_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 122 //cudaMemcpy(B_dev,B_host,nBytes,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); 123 dim3 block(1024,1); 124 dim3 grid((size-1)/block.x+1,1); 125 // 创建Event 126 cudaEventCreate(&start_GPU); 127 cudaEventCreate(&stop_GPU); 128 //记录当前时间 129 cudaEventRecord(start_GPU,0); 130 start_gpu = clock(); 131 132 GPUreduceNeighbored<<<grid,block>>>(A_dev,B_dev,size); 133 134 stop_gpu = clock(); 135 cudaEventRecord(stop_GPU,0); 136 cudaEventSynchronize(start_GPU); 137 cudaEventSynchronize(stop_GPU); 138 //计算时间差 139 cudaEventElapsedTime(&time_GPU, start_GPU,stop_GPU); 140 printf("\nThe time from GPU:\t%f(ms)\n", time_GPU/1000); 141 //消除Event 142 cudaEventDestroy(start_GPU); 143 cudaEventDestroy(stop_GPU); 144 cudaMemcpy(C_from_gpu,B_dev,nBytes,cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); 145 //输出结果 146 printf(" GPU result is :\n"); 147 // printList(C_from_gpu,1); 148 149 cudaFree(A_dev); 150 cudaFree(B_dev); 151 152 free(A_host); 153 free(B_host); 154 155 156 time_cpu = (float) (stop_cpu-start_cpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 157 time_gpu = (float) (stop_gpu-start_gpu) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC; 158 printf("\nThe time for CPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_cpu); 159 printf("The time for GPU by host:\t%f(ms)\n", time_gpu); 160 161 162 cudaDeviceReset(); 163 return 0; 164 }
既然一个线程块处理2个数据块能获得这么高的加速比,那么处理4个,8个呢?
随着处理数据块数量的增多,处理时间不断降低。不过随着设备内存吞吐量逐渐到达极限,这个时间就不会继续降低了。
总结一下,为了隐藏延时,我们需要合理地增加一个线程块中需要处理的数据量,以便线程束调度器进行调度。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/lin1216/p/12682543.html