原创转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/agilestyle/p/12690755.html
准备数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_regression from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression from sklearn.linear_model import SGDRegressor from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error X, y = make_regression(n_samples=500, n_features=1, noise=20, random_state=0) # (500, 1) X.shape # (500,) y.shape plt.scatter(X, y)
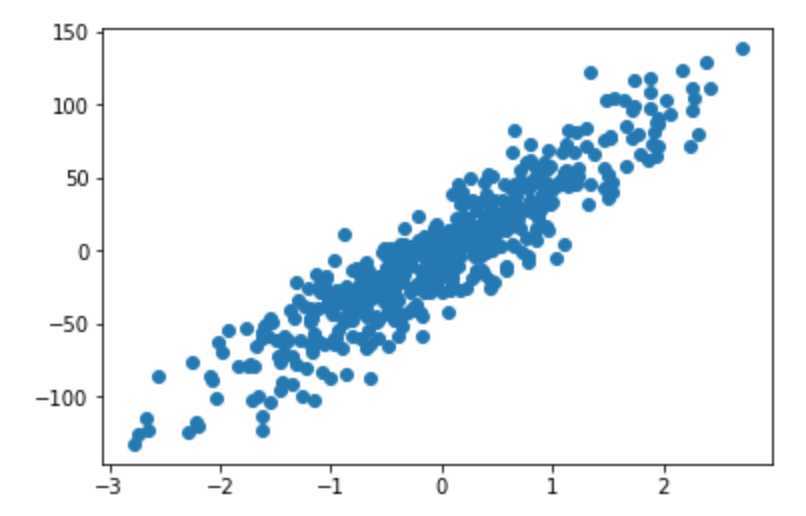
建模训练
lr = LinearRegression() y = y.reshape(-1, 1) # LinearRegression(copy_X=True, fit_intercept=True, n_jobs=None, normalize=False) lr.fit(X, y)
评价模型
# 查看模型的截距 array([-1.53821792]) lr.intercept_ # 查看模型的斜率 array([[45.2879203]]) lr.coef_ # 0.8458565184565707 lr.score(X, y) lr_mse = mean_squared_error(y, lr.predict(X)) # 均方误差 372.3837648686677 lr_mse plt.scatter(X, y) plt.plot(X, lr.predict(X), ‘r‘)
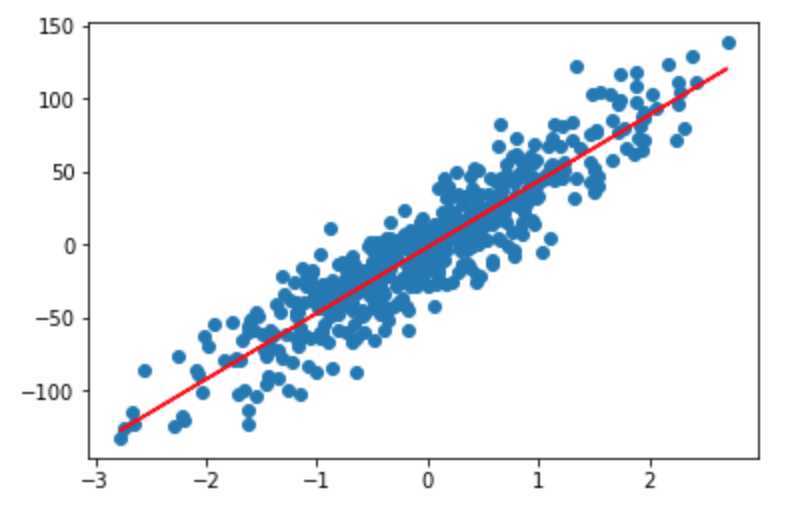
使用随机梯度下降求解参数
sgd = SGDRegressor(eta0=0.01, max_iter=100) # eta0: 初始学习率,max_iter: 最大迭代次数 sgd.fit(X, y.ravel()) sgd.score(X, y)
Note:
梯度下降的两个重要因素
scikit-learn Cookbook Second Edition
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.metrics.mean_squared_error.html
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.SGDRegressor.html
https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.ravel.html
https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/reducing-loss/gradient-descent
https://developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course/reducing-loss/learning-rate
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/agilestyle/p/12690755.html