acwing 135.最大子序和
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/137/
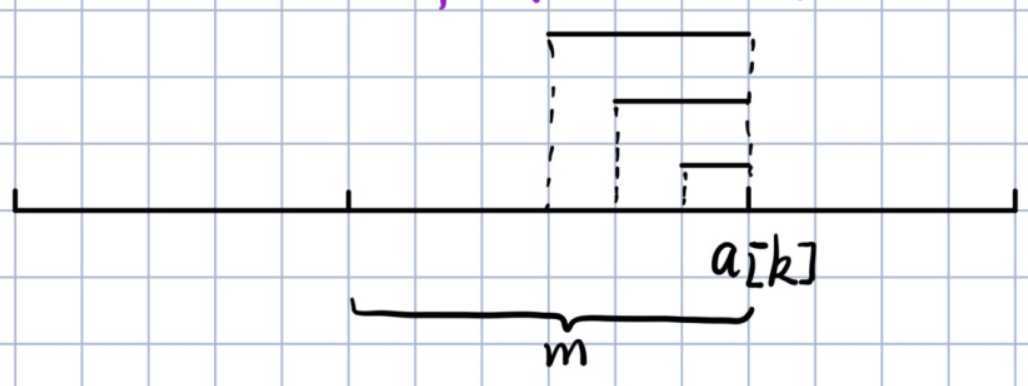
假设当前序列的最后一个数字是$a[k]$, 那么问题就变成求从$a[k-m]$到$a[k]$的长度为$m$的序列中,序列和最大的。
要求区间的和,需要预处理一个前缀和数组$s$, 所求的表达式是$s[k] - s[i], k-m <= i <= k$,因为$s[k]$是固定的,要求表达式最大,就是求$s[i]$最小。
所以问题变成了在长度为$m$的区间上,求前缀和的最小值。可以用单调队列优化。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int N = 300010, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 7 int s[N]; 8 int q[N]; 9 int n, m; 10 11 int main(){ 12 cin >> n >> m; 13 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 14 { 15 cin >> s[i]; 16 s[i] += s[i - 1]; 17 } 18 19 int hh = 0, tt = 0;//队列一开始是有一个s[0]的元素 20 int res = -INF; 21 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 22 { 23 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] < i - m)hh ++; 24 res = max(res, s[i] - s[q[hh]]); 25 while(hh <= tt && s[i] <= s[q[tt]])tt --; 26 q[ ++ tt] = i; 27 } 28 29 cout << res << endl; 30 return 0; 31 }
acwing 1089.烽火传递
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1091/
题意:每个$m$的区间内至少要有一个烽火台被点燃。
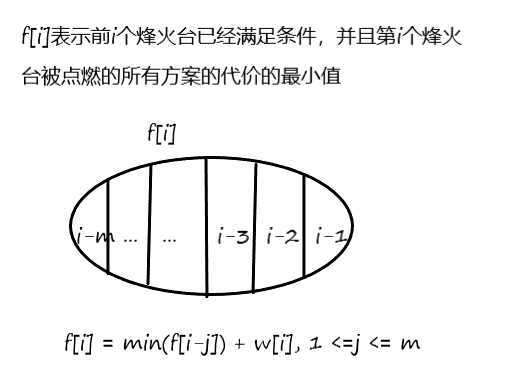
观察状态转移方程,每次都是求一个长度为$m$的区间内$f$的最小值,可以用单调队列优化。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 2e5+10; 8 9 int a[N], f[N], q[N]; 10 int n, m; 11 12 int main(){ 13 cin >> n >> m; 14 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)cin >> a[i]; 15 16 int hh = 0, tt = 0; 17 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 18 { 19 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] < i - m)hh ++; 20 f[i] = f[q[hh]] + a[i]; 21 while(hh <= tt && f[q[tt]] >= f[i])tt --;//单调队列q存储的是f的最小值 22 q[ ++ tt] = i; 23 } 24 25 int res = 1e9; 26 for(int i = n - m + 1; i <= n ; i ++)res = min(res, f[i]);//区间包括右端点长度为m,所以从n - m + 1开始 27 cout << res << endl; 28 return 0; 29 }
注意:上面烽火传递的区间是任意长度为m的区间内至少要有一个数被选。而下面的绿色通道的区间是中间可以隔最长m的空白区间。所以边界会有所区别。
acwing 1090.绿色通道
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1092/
本题的做法与烽火传递相似,不同的是多了二分答案的过程。
对答案进行二分,得到一个$mid$,分析可知,当$mid$是答案时,在其右边的数字也一定满足条件,因为小的数可以满足条件,更大的数也一定能满足条件。而对其左边,一定都不满足条件,所以是可以二分的。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 5e4+10; 8 9 int a[N], f[N], q[N]; 10 int n, m; 11 12 bool check(int bound) 13 { 14 f[0] = 0; 15 int hh = 0, tt = 0; 16 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 17 { 18 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] < i - bound - 1)hh ++;//不包括端点 19 f[i] = f[q[hh]] + a[i]; 20 while(hh <= tt && f[q[tt]] >= f[i])tt --; 21 q[ ++ tt] = i; 22 } 23 24 for(int i = n - bound ; i <= n ; i ++)//因为是要有bound长度的空白,不包括端点 25 if(f[i] <= m)return true; //而烽火传递有包括端点 26 return false; 27 } 28 29 int main(){ 30 cin >> n >> m; 31 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++)cin >> a[i]; 32 33 int l = 0, r = n; 34 while(l < r) 35 { 36 int mid = l + r >> 1; 37 if(check(mid))r = mid; 38 else l = mid + 1; 39 } 40 cout << l << endl; 41 return 0; 42 }
acwing 1087.修剪草坪
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1089/
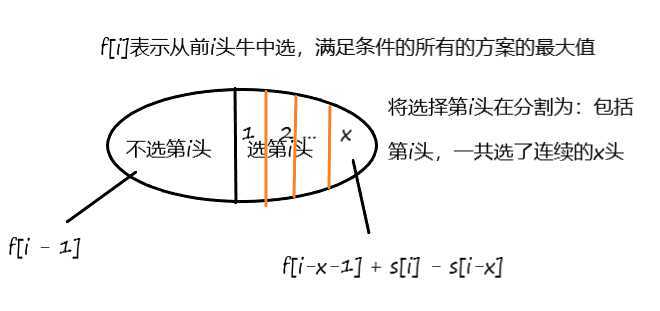
由上图得到右半部分状态转移方程为:$f[i] = f[i-x-1] + s[i] - s[i-x]$, 要使$f[i]$最大,因为$s[i]$是固定值所以状态转移方程可以表示为:$f[i] = max(f[i-x-1] - s[i-x]) + s[i], 1<=x <= k$(这里是$f[i-x-1]$是应以为已经选了连续$x$个,合法方案必须$i-x$的前一面一个开始,所以是$i-x-1$)。所以该题变成求固定区间$k$上的最大值,可以用单调队列优化。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 typedef long long LL; 7 8 const int N = 1e5+10; 9 int a[N], q[N]; 10 LL s[N], f[N]; 11 int n, m; 12 13 LL g(int x) 14 { 15 return f[x - 1] - s[x]; 16 } 17 18 int main(){ 19 cin >> n >> m; 20 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 21 { 22 cin >> a[i]; 23 s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i]; 24 } 25 26 int hh = 0, tt = 0; 27 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 28 { 29 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] < i - m)hh ++; 30 f[i] = max(f[i - 1], g(q[hh]) + s[i]); 31 while(hh <= tt && g(q[tt]) <= g(i))tt --; 32 q[++ tt] = i; 33 } 34 35 cout << f[n] << endl; 36 return 0; 37 }
acwing 1091.理想的整发型
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1093/
先对行做一遍单调队列,将维数压缩到一列,在对列对一遍单调队列即可。
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <cstring> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 1010; 8 const int INF = 1E9; 9 int row_min[N][N], row_max[N][N]; 10 int w[N][N]; 11 int q[N]; 12 int k; 13 14 void get_min(int a[], int b[], int tot) 15 { 16 int hh = 0, tt = -1; 17 for(int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++) 18 { 19 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] <= i - k)hh ++; 20 while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i])tt --; 21 q[++ tt] = i; 22 b[i] = a[q[hh]]; 23 } 24 } 25 26 void get_max(int a[], int b[], int tot) 27 { 28 int hh = 0, tt = -1; 29 for(int i = 1 ; i <= tot ; i ++) 30 { 31 if(hh <= tt && q[hh] <= i - k)hh ++; 32 while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i])tt --; 33 q[++ tt] = i; 34 b[i] = a[q[hh]]; 35 } 36 } 37 38 int main(){ 39 int n, m; 40 cin >> n >> m >> k; 41 42 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 43 for(int j = 1 ; j <= m ; j ++) 44 cin >> w[i][j]; 45 46 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++) 47 { 48 get_min(w[i], row_min[i], m); 49 get_max(w[i], row_max[i], m); 50 } 51 52 int a[N], b[N], c[N]; 53 int res = INF; 54 for(int i = k ; i <= m ; i ++) 55 { 56 for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++)a[j] = row_min[j][i]; 57 get_min(a, b, n); 58 59 for(int j = 1 ; j <= n ; j ++)a[j] = row_max[j][i]; 60 get_max(a, c, n); 61 62 for(int j = k ; j <= n; j ++)res = min(res, c[j] - b[j]); 63 } 64 65 cout << res << endl; 66 return 0; 67 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/1-0001/p/12692283.html