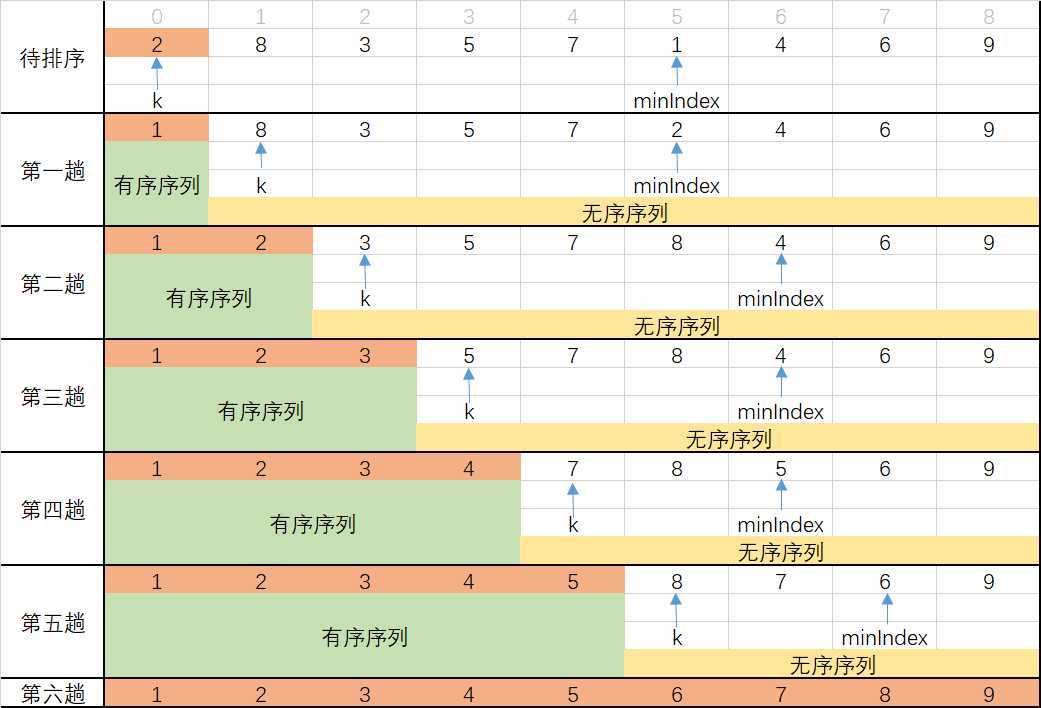
(1)从待排序序列中找到最小(大)的元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置;
(2)从剩余的待排序序列中继续寻找最小(大)元素,然后放到已排序序列的末尾;
(3)重复执行(2),直到所有排序完成。
空间复杂度O(1)
时间平均复杂度O(n^2)
(1)由于存在着不相邻元素之间的互换,故是一种不稳定的算法;
(2)使用的时候,数据的规模越小越好;
(3)不占用额外的内存空间。
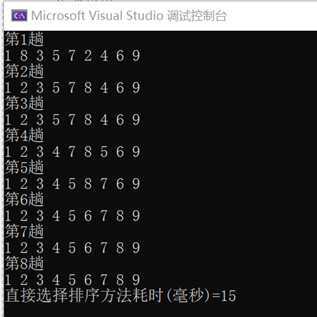
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { // 待排序数组 int[] sortArray = { 2, 8, 3, 5, 7, 1, 4, 6, 9 }; Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); SelectSort(sortArray); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("直接选择排序方法耗时(毫秒)=" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); } /// <summary> /// 直接选择排序 /// </summary> /// <param name="sortArray">待排序数组</param> private static void SelectSort(int[] sortArray) { // n个元素,需要循环n-1轮 for (int i = 0; i < sortArray.Length - 1; i++) { Console.WriteLine("第" + (i + 1) + "趟"); // 取外层计数器默认初始值 int minIndex = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < sortArray.Length; j++) { // 若最小数的索引值大于当前索引的值,则将当前索引赋值给minIndex if (sortArray[minIndex] > sortArray[j]) { minIndex = j; } } // 交换 int temp = sortArray[i]; sortArray[i] = sortArray[minIndex]; sortArray[minIndex] = temp; SortShow(sortArray); } } private static void SortShow(int[] sortArray) { for (int i = 0; i < sortArray.Length; i++) { Console.Write(sortArray[i] + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); } }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/suxiuyan/p/12704392.html