1.朴素贝叶斯
(1)主要内容

(2)朴素贝叶斯的假设

(3)朴素贝叶斯的推导

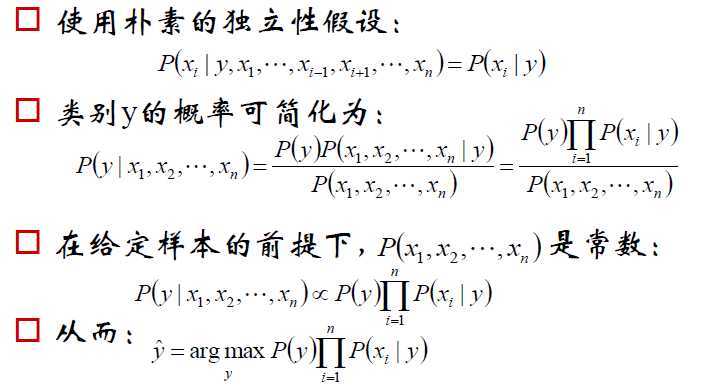

(4)朴素贝叶斯的应用举例

分析过程如下图所示:


思考:

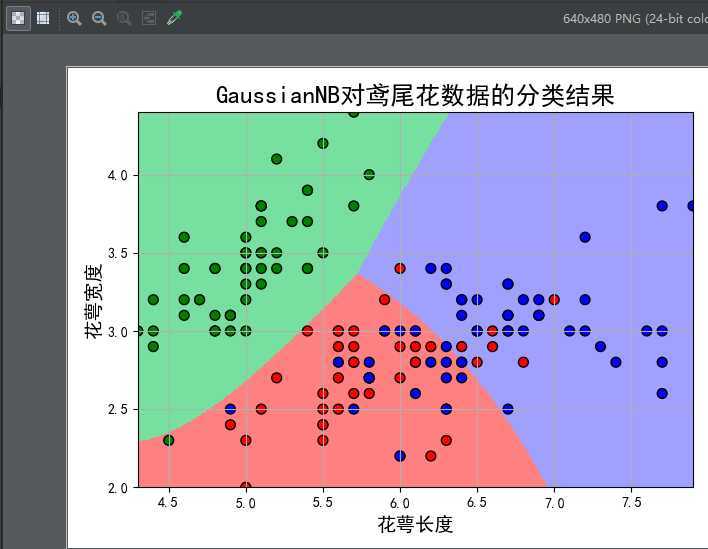
2.代码示例
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import matplotlib as mpl from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB, MultinomialNB from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier def iris_type(s): it = {b‘Iris-setosa‘: 0, b‘Iris-versicolor‘: 1, b‘Iris-virginica‘: 2} return it[s] if __name__ == "__main__": data = np.loadtxt(‘8.iris.data‘, dtype=float, delimiter=‘,‘, converters={4: iris_type}) print(data) x, y = np.split(data, (4,), axis=1) x = x[:, :2] print(x) print(y) gnb = Pipeline([ (‘sc‘, StandardScaler()), (‘clf‘, GaussianNB())]) gnb.fit(x, y.ravel()) # gnb = MultinomialNB().fit(x, y.ravel()) # gnb = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5).fit(x, y.ravel()) # 画图 N, M = 500, 500 # 横纵各采样多少个值 x1_min, x1_max = x[:, 0].min(), x[:, 0].max() # 第0列的范围 x2_min, x2_max = x[:, 1].min(), x[:, 1].max() # 第1列的范围 t1 = np.linspace(x1_min, x1_max, N) t2 = np.linspace(x2_min, x2_max, M) x1, x2 = np.meshgrid(t1, t2) # 生成网格采样点 x_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat), axis=1) # 测试点 # 无意义,只是为了凑另外两个维度 # x3 = np.ones(x1.size) * np.average(x[:, 2]) # x4 = np.ones(x1.size) * np.average(x[:, 3]) # x_test = np.stack((x1.flat, x2.flat, x3, x4), axis=1) # 测试点 mpl.rcParams[‘font.sans-serif‘] = [u‘simHei‘] mpl.rcParams[‘axes.unicode_minus‘] = False cm_light = mpl.colors.ListedColormap([‘#77E0A0‘, ‘#FF8080‘, ‘#A0A0FF‘]) cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap([‘g‘, ‘r‘, ‘b‘]) y_hat = gnb.predict(x_test) # 预测值 y_hat = y_hat.reshape(x1.shape) # 使之与输入的形状相同 plt.figure(facecolor=‘w‘) plt.pcolormesh(x1, x2, y_hat, cmap=cm_light) # 预测值的显示 plt.scatter(x[:, 0], x[:, 1], c=np.squeeze(y), edgecolors=‘k‘, s=50, cmap=cm_dark) # 样本的显示 plt.xlabel(u‘花萼长度‘, fontsize=14) plt.ylabel(u‘花萼宽度‘, fontsize=14) plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max) plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max) plt.title(u‘GaussianNB对鸢尾花数据的分类结果‘, fontsize=18) plt.grid(True) plt.show() # 训练集上的预测结果 y_hat = gnb.predict(x) y = y.reshape(-1) result = y_hat == y print(y_hat) print(result) acc = np.mean(result) print(‘准确度: %.2f%%‘ % (100 * acc))
效果图:
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/luckyplj/p/12712312.html