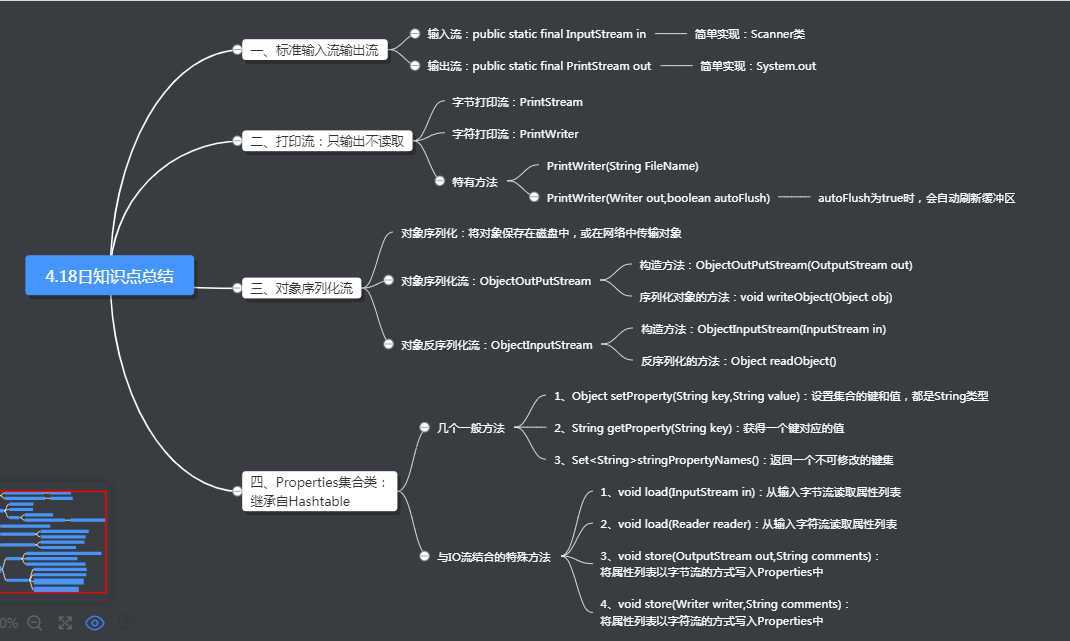
一、知识点总结
二、对象序列化流实例
package io; /* *对象序列化流 *NotSerializableException: *抛出一个实例需要一个Serializable接口,序列化运行时或实例的类可能会抛出此异常 *类的序列化由实现java.io.Serializable接口的类启用,不实现此接口的类不会使任何状态序列化或者反序列化。 */ import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; public class IODemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //构造方法:ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out): //创建一个写入指定的OutputStream的ObjectOutputStream ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\troye.txt")); //创建对象 Student s=new Student("陆婷",28); //void writeObject(Object obj):将指定的对象写入ObjectOutputStream oos.writeObject(s); //释放资源 oos.close(); } } package io; import java.io.Serializable; @SuppressWarnings("serial") public class Student implements Serializable{ private String name; private int age; public Student() { super(); } public Student(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } /** * @return the name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * @return the age */ public int getAge() { return age; } /** * @param name the name to set */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * @param age the age to set */ public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
三、对象反序列化实例(用上面的实例类)
package io; /* *对象反序列化流 */ import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; public class IODemo4 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //ObjectInputStream(InputStream in):创建从指定的InputStream读取的ObjectInputStream ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\troye.txt")); //Object readObject():从ObjectInputStream读取一个对象 Object obj=ois.readObject(); Student s=(Student)obj; System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge()); //释放资源 ois.close(); } }
三、一道综合性的编程题
来源于:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31780525/article/details/52432753
题目需求如下:
题目情景描述: 公司财务发工资时,记录了当时发工资的资料Employee.txt 1.定义公司员工类Employee,属性有:工号,姓名,性别,工资(double类型),进行属性的隐藏和封装,重写toString. 2.将D:/Employee.txt文件用程序复制到项目根目录; 3.读取项目根目录下的文件Employee.txt内容存入ArrayList<Employee> 4.以工号为键,员工姓名为值存入HashMap<String,String>中.再遍历输出Map集合中的内容; 5.当公司记录该信息的职员将信息交给经理,经理进行审查时,发现有一些信息录入错误,需要在集合中进行数据修改: ① 将陈璐璐改为:张路路且工资改为:7500.0元 ② 程曦原本是位女士 ③工号中所有的”2”都应改为”7”;输出修改后的ArrayList<Employee> 6.将修改后的职工信息按工资从高到低排序,工资相同的按工号从小到大排序. 7.判断项目根目录下是否有”result”文件夹,如果没有,则用程序新建文件夹”result”,并将 修改并排序后的信息写出到”result”文件夹的Employee-new.txt文件中,格式与Employee.txt相同
Employee.txt中的文本格式为:
J18020,周杰伦,男,8800.0 J18085,金秀贤,男,7500.0 J18504,陈璐璐,女,7340.0 J18009,岳云鹏,男,8000.0 J18775,张翠花,女,7500.0 J18325,刘静,女,10500.0 J18560,程曦,男,1000.0 J18802,AngleBaby,女,8500
我的解题思路如下:
1、新建一个实体Employee类:
package company1; //1.定义公司员工类Employee,属性有:工号,姓名,性别,工资(double类型). //进行属性的隐藏和封装,重写toString. public class Employee { private String id; private String name; private String sex; private double salary; public Employee() { } public Employee(String id, String name, String sex, double salary) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.salary = salary; } /** * @return the id */ public String getId() { return id; } /** * @return the name */ public String getName() { return name; } /** * @return the sex */ public String getSex() { return sex; } /** * @return the salary */ public double getSalary() { return salary; } /** * @param id the id to set */ public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } /** * @param name the name to set */ public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } /** * @param sex the sex to set */ public void setSex(String sex) { this.sex = sex; } /** * @param salary the salary to set */ public void setSalary(double salary) { this.salary = salary; } @Override public String toString() { return id+","+name+","+sex+","+salary; } }
2、按照要求完成代码的编写:
package company1; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.BufferedOutputStream; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeSet; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{ //2.将D:/Employee.txt文件用程序复制到项目根目录 // BufferedInputStream br=new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\Employee.txt")); // BufferedOutputStream bw=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src\\Employee.txt")); // byte[] bys=new byte[1024]; // int len; // while((len=br.read(bys))!=-1) { // bw.write(bys,0,len); // } // br.close(); // bw.close(); //3.读取项目根目录下的文件Employee.txt内容存入ArrayList<Employee> ArrayList<Employee>arr=new ArrayList<>(); BufferedReader bfr=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src\\Employee.txt")); String line; while((line=bfr.readLine())!=null) { String[] arrEmployee=line.split(","); Employee e=new Employee(); e.setId(arrEmployee[0]); e.setName(arrEmployee[1]); e.setSex(arrEmployee[2]); e.setSalary(Double.parseDouble(arrEmployee[3])); arr.add(e); } bfr.close(); //4.以工号为键,员工姓名为值存入HashMap<String,String>中.再遍历输出Map集合中的内容 // HashMap<String,String>hash=new HashMap<String,String>(); // for(Employee a:arr) { // hash.put(a.getId(), a.getName()); // } // Set<String>set=hash.keySet(); // for(String s:set) { // String value=hash.get(s); // System.out.println("id="+s+",name="+value); // } /* * 5.当公司记录该信息的职员将信息交给经理,经理进行审查时,发现有一些信息录入错误,需要在集合中进行数据修改: ① 将陈璐璐改为:张路路且工资改为:7500.0元 ② 程曦原本是位女士 ③工号中所有的”2”都应改为”7”;输出修改后的ArrayList<Employee> */ for(Employee em:arr) { if(em.getName().equals("陈璐璐")) { em.setName("张路路"); em.setSalary(7500.0); } if(em.getName().equals("程曦")) { em.setSex("女"); } if(em.getId().contains("2")) { em.setId(em.getId().replace("2", "7")); } } // for(Employee em1:arr) { // System.out.println(em1.toString()); // } //6.将修改后的职工信息按工资从高到低排序,工资相同的按工号从小到大排序. TreeSet<Employee>emSet=new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Employee>() { @Override public int compare(Employee o1, Employee o2) { int num=(int)(o2.getSalary()-o1.getSalary()); int num1=num==0?o1.getId().compareTo(o2.getId()):num; return num1; } }); for(Employee em2:arr) { emSet.add(em2); } for(Employee em3:emSet) { System.out.println(em3.toString()); } //7.判断项目根目录下是否有”result”文件夹,如果没有,则用程序新建文件夹”result”,并将 //修改并排序后的信息写出到”result”文件夹的Employee-new.txt文件中,格式与Employee.txt相同 File newfolder=new File("src\\","result"); if(!newfolder.exists()) { newfolder.mkdir(); } String fileName="Employee-new.txt"; File newFile=new File(newfolder,fileName); String line1; BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(newFile)); for(Employee em4:emSet) { line1=em4.toString(); bw.write(line1); bw.newLine(); bw.flush(); } bw.close(); } }
四、总结
学完IO流的知识以后,发现视频里老师讲的案例,或者是自己赵的练习题。都是把IO流和以前学的集合等知识结合在一起了,在此过程中,我发现了自己存在的一些问题:
1、File类对象和实际的文件/目录区分不清:File类对象只是封装了某条路径,并没有实际建立一个文件/目录。所以还需要调用其他的方法来建立文件/目录。
2、实体类有排序要求时,不太弄得清楚主要条件和次要条件。这一点经过几道习题的练习,已经好了很多。
3、字节流是判断文件的末尾是否为-1,而字符流则是判断文件的末尾是否为null。这一个区别和两者的底层实现有关。
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/yizhinailu/p/12727834.html