Windows内核分析索引目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/onetrainee/p/11675224.html
TLB
1. CPU寻址模式
2. TLB
3. 缓存
4. shadowwalk技术
5.TLB感知实验
6.全局页
1. CPU寻址模式
之前在分页时介绍过这张图,里面分析过其对应的寻址模式:
1)CPU先尝试从TLB找到物理地址;
2)如果TLB中不存在对应的物理地址,则手动计算出物理地址;
3)之后再从缓存中尝试获取物理地址对应的数据;
4)如果缓存中没有,则去物理内存中找到相应地址来读取对应的数据。
2. TLB
TLB与缓存要区分清楚,TLB是通过线性地址找物理地址的,缓存是通过物理地址找数据的。
TLB中以页为单位来存储的,缓存直接按照字节来进行存储的,要区分他俩之间的关系,不要混为一谈。
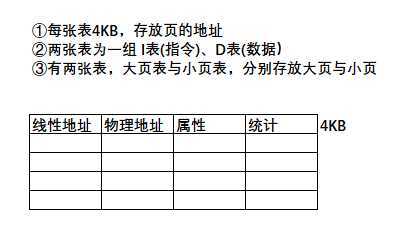
3. 缓存
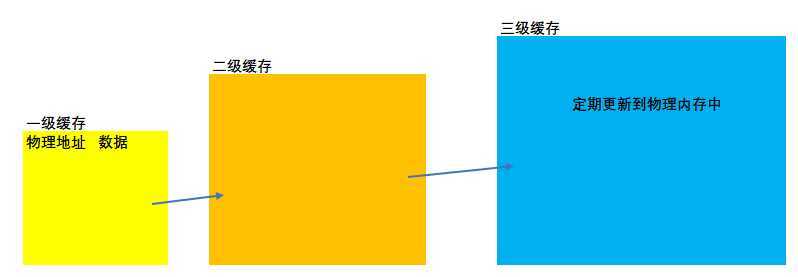
以三级缓存为例,当一级缓存满了之后会往二级缓存中存储,二级满了会往三级缓存中存储,三级缓存定期备份到物理内存中。
4. shadowwalk技术
有很多游戏等会存在CRC校验,其读取的是数据TLB,但执行的是指令TLB,因此我们保留数据TLB,修改指令TLB,这样就实现了过CRC校验。
shadowwalk等工具就是利用TLB的两张表分离实现过CRC校验的。
5.TLB感知实验
1)实验大体步骤
① 准备两个地址,在不同的页上;
② 向零地址挂上TLB,
③ 读取数据,加载到TLB中;
④ 再向0地址挂另一个物理页的PTE;
⑤ 我再读零地址,如果读出来的还是原来的数据,则证明存在TLB。
2)实验代码:
如下,我们利用windbg创建调用门:eq 8003f048 0040ec00`00081005
// 123.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <windows.h> #include <stdlib.h> char* p = NULL; char* p1 = NULL; int temp = 0; int temp1 = 0; // eq 8003f048 0040ec00`00081005 void __declspec(naked)test(){ _asm{ pushfd; pushad; push fs; mov ax,0x30; mov fs,ax; // 挂p位的 mov eax,dword ptr ds:[p]; // 取出p的地址 shr eax,9; // 由移9位 and eax,0x7FFFF8; // add eax,0xc0000000; // 取出pte mov ebx,dword ptr [eax]; mov ecx,[eax+4]; // 往0地址挂 mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000000],ebx; mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000004],ecx; // 加载到tlb中 mov eax, dword ptr ds:[0]; //int 3; //取出值 mov temp,eax; /*---------------*/ // 挂p1的 mov eax,dword ptr[p1]; // 取出p1的地址 shr eax,9; // 由移9位 and eax,0x7FFFF8; // add eax,0xc0000000; // 取出pte mov ebx,dword ptr [eax]; mov ecx,[eax+4]; // 往0地址挂 mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000000],ebx; mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000004],ecx; // 加载到tlb中 mov eax, dword ptr ds:[0]; // 取出值 mov temp1,eax; //int 3; pop fs; popad; popfd; retf; } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // 分配内存 p = (char*)VirtualAlloc(NULL,0x1000,MEM_COMMIT,PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE); p1 = (char*)VirtualAlloc(NULL,0x1000,MEM_COMMIT,PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE); char buf[]={0,0,0,0,0x48,0}; printf("%x,p1=%x,p=%x\r\n",test,p1,p); system("pause"); temp = 100; temp1 = 200; *(int*)p = 0x1000; *(int*)p1 = 0x2000; _asm{ call fword ptr buf; } printf("%x,%x\t\n",temp,temp1); printf("hello world!\r\n"); system("pause"); return 0; }
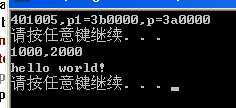
3)实验结果:
实验结果如下,可以发现第二次虽然我们在0地址处手工挂靠了物理页,但其因为第一次保存在TLB缓存当中,当第二次再开始读取的时候,通过TLB获取第一个PTE的线性地址,因此读到的是第一个。
因此通过这个实验你就可以感知到TLB缓存的存在,下面我们学习如何刷新TLB缓存。
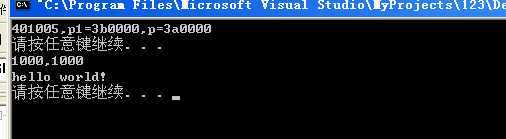
4)TLB刷新
如何刷新TLB呢?其如果刷新cr3,则就刷新TLB,因此我们如果想刷新,写上 mov eax,cr3; mov cr3,eax即可。
6.全局页
1)将其修改为全局页
如果将页置为全局页,则需要修改PTE的第8位,G位,表示全局页。

因此我们在写入PTE前,使用 or ebx,0x100将该位置1,哪怕再刷新CR3也没有效果。
2)通过cr4来禁止修改全局页
cr4存在一个PGE位,当该位为1,则允许使用全局页,现在我们将该位关掉。

因为在vc6.0环境下不支持cr4的修改,因此我们借助IDA来直接硬编码:
// cr4 PGE位关闭全局页 __emit 0x0f; // mov eax,cr4; __emit 0x20; __emit 0xE0; mov ecx,0x80; not ecx; and eax,ecx; __emit 0x0f; // mov cr4,eax; __emit 0x22; __emit 0xe0;
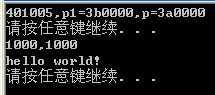
之后我们发现及时设置全局页,其也是无效的,会被置换出来

其实CPU中存在一个强制刷新地址的指令,哪怕是全局页表也会被刷新
invlpg dword ptr ds:[0],使用该条指令则会强制刷新缓存
全部试验代码如下:
// 123.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <windows.h> #include <stdlib.h> char* p = NULL; char* p1 = NULL; int temp = 0; int temp1 = 0; // eq 8003f048 0040ec00`00081005 void __declspec(naked)test(){ _asm{ pushfd; pushad; push fs; mov ax,0x30; mov fs,ax; // 挂p位的 mov eax,dword ptr ds:[p]; // 取出p的地址 shr eax,9; // 由移9位 and eax,0x7FFFF8; // add eax,0xc0000000; // 取出pte mov ebx,dword ptr [eax]; mov ecx,[eax+4]; // 往0地址挂 xor ebx,0x100; mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000000],ebx; mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000004],ecx; // 加载到tlb中 mov eax, dword ptr ds:[0]; //int 3; //取出值 mov temp,eax; mov eax,cr3; mov cr3,eax; /*---------------*/ // cr4 PGE位关闭全局页 /* __emit 0x0f; // mov eax,cr4; __emit 0x20; __emit 0xE0; mov ecx,0x80; not ecx; and eax,ecx; __emit 0x0f; // mov cr4,eax; __emit 0x22; __emit 0xe0; */ // 挂p1的 mov eax,dword ptr[p1]; // 取出p1的地址 shr eax,9; // 由移9位 and eax,0x7FFFF8; // add eax,0xc0000000; // 取出pte mov ebx,dword ptr [eax]; mov ecx,[eax+4]; // 往0地址挂 mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000000],ebx; mov dword ptr ds:[0xc0000004],ecx; // 加载到tlb中 invlpg dword ptr ds:[0]; mov eax, dword ptr ds:[0]; // 取出值 mov temp1,eax; //int 3; pop fs; popad; popfd; retf; } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { // 分配内存 p = (char*)VirtualAlloc(NULL,0x1000,MEM_COMMIT,PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE); p1 = (char*)VirtualAlloc(NULL,0x1000,MEM_COMMIT,PAGE_EXECUTE_READWRITE); char buf[]={0,0,0,0,0x48,0}; printf("%x,p1=%x,p=%x\r\n",test,p1,p); system("pause"); temp = 100; temp1 = 200; *(int*)p = 0x1000; *(int*)p1 = 0x2000; _asm{ call fword ptr buf; } printf("%x,%x\t\n",temp,temp1); printf("hello world!\r\n"); system("pause"); return 0; }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/onetrainee/p/12738275.html