首先我们需要先了解HTTP协议,请求头,请求行,请求体,响应头,响应行,响应体,具体请移步百度!
其次,Tomcat的底层是socket编程,没有socket基础的同学请往右拐??
https://www.cnblogs.com/fantongxue/p/12443284.html
准备好了上面两个条件,我们就可以开始写Tocmat服务器了!
客户端发送一个请求,服务端监听客户端请求,并使用IO流读取数据以及向客户端反馈数据。
首先服务端使用socket监听某一个端口,当服务端收到该端口内的请求时,同时会得到输入流(客户端发送的内容)和输出流(返回给客户端的内容)
该测试类开启socket,连接www.itcast.cn的80端口,由socket得到的输入流和输出流分别是服务器的响应内容和发送给服务器的请求内容。
public class TestClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=null;
InputStream is=null;
OutputStream ops=null;
try {
//1,创建一个socket对象,连接itcast.cn域名的80端口
socket=new Socket("www.itcast.cn",80);
//2,获取输入流对象
is = socket.getInputStream();
//3,获取输出流对象
ops=socket.getOutputStream();
//4,将HTTP协议的请求部分发送到服务端 /subject/about/index.html
ops.write("GET /subject/about/index.html HTTP/1.1\n".getBytes());
ops.write("HOST:www.itcast.cn\n".getBytes());
ops.write("\n".getBytes());
//5,读取来自服务端的数据打印到控制台
int i=is.read();
while(i!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)i);
i=is.read();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(is!=null) {
is.close();
is=null;
}
if(ops!=null) {
ops.close();
ops=null;
}
if(socket!=null) {
socket.close();
socket=null;
}
}
}
}
打印到控制台的则是itcast.cn服务器响应的页面(字符串)

下面这个测试类模拟的是服务端,服务端开启socket监听8080端口,通过socket得到输入输出流,输出流写响应内容。
public class TestServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream ops = null;
try {
//1,创建ServerSocket对象,监听本机的8080端口号
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true){
//2,等待来自客户端的请求,获取和客户端对应的Socket对象
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3,通过获取到的socket对象获取到输出流对象
ops = socket.getOutputStream();
//4,通过获取到的输出流对象将HTTP协议的响应部分发送到客户端
ops.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Server:Apache-Coyote/1.1\n".getBytes());
ops.write("\n\n".getBytes());
StringBuffer buffer=new StringBuffer();
buffer.append("<html>");
buffer.append("<head><title>Write Tomcat Service</title></head>");
buffer.append("<body>");
buffer.append("<h3>Test Page</h3>");
buffer.append("<a href=‘http://www.baidu.com‘>baidu</a>");
buffer.append("</body>");
buffer.append("</html>");
ops.write(buffer.toString().getBytes());
ops.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(ops!=null){
ops.close();
}
if(socket!=null){
socket.close();
}
if(serverSocket!=null){
serverSocket.close();
}
}
}
}
然后访问http://localhost:8080会响应下面的页面
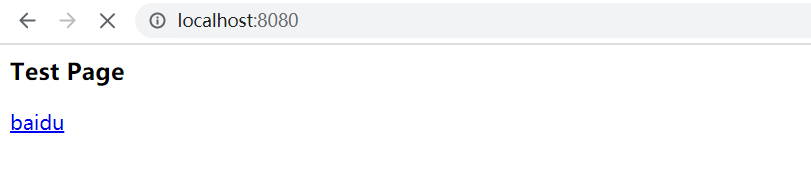
可以先看一下我的目录,这是我原来的一个springboot工程,我把启动类给删了,然后自己写一个Tomcat让项目运行起来!(TestServerOne类)

TestServerOne类(Tomcat类)
package com.example.Tomcat_one;
import com.example.controller.TestController;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.*;
public class TestServerOne {
//定义一个变量,存放服务端静态资源文件夹目录的绝对路径(本地磁盘路径)
//D:\IdeaProjects\chat-system\src\main\resources\templates
public static String property = System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\"+"src"+"\\"+"main"+"\\"+"resources"+"\\"+"templates";
//定义静态变量,用于存放本次请求的静态页面路径
private String url="";
//用于存放本次请求的静态页面名称
private String title="";
//定义一个静态类型map,存储服务端的配置文件conf.properties的配置信息(当然这里是自定义的)
static Map<String,String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
static {
//静态代码块的目的是该块中的内容需要在测试类启动时就先被加载
//Tomcat服务器启动之前将配置文件的参数加载到map中
//创建一个properties对象(加载自定义配置文件)
Properties prop=new Properties();
try {
//加载resources文件夹下的conf.properties配置文件
prop.load(new FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\"+"src"+"\\"+"main"+"\\"+"resources"+"\\"+"conf.properties"));
//将配置文件中的数据读取到map中
Set set=prop.keySet();
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
String key=(String)iterator.next();
String value=prop.getProperty(key);
map.put(key,value);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Tomcat启动入口
@Test
public void test() throws IOException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, ClassNotFoundException {
ServerSocket serverSocket=null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream ops = null;
try {
//1,创建serversocket,监听本机器的80端口,等待来自客户端的请求
serverSocket=new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true){
//2,获取到客户端对应的socket
socket = serverSocket.accept();
//3,获取到输入流对象
is = socket.getInputStream();
//4,获取到输出流对象
ops = socket.getOutputStream();
//5,获取HTTP协议的请求部分,截取客户端要访问的资源名称,将这个资源名称赋值给url
String titles = parse(is);
url=property+"\\"+titles;
title=titles;
if(titles.endsWith(".html")){
//说明客户端请求的是index.html这种静态资源
//6,发送静态资源(也就是页面)
sendStaticResource(ops);
}else{
//客户端请求的是/test这种路径映射(访问的class文件)
sendDynamicResource(is,ops);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(is!=null){
is.close();
}
if(ops!=null){
ops.close();
}
if(socket!=null){
socket.close();
}
if(serverSocket!=null){
serverSocket.close();
}
}
}
//客户端请求的是/test这种路径映射(访问的class文件)
private void sendDynamicResource(InputStream is, OutputStream ops) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
//将HTTP协议的响应行和响应头发送到客户端
ops.write("HTTP/1.1 200 ok\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Server:Apache\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Content-Type:text/html;chaset=utf-8\n".getBytes());
ops.write("\n".getBytes());
//判断map中是否存在一个key,这个key是否和本次请求的资源路径一致
if(map.containsKey(title)){
//如果包含指定的key,获取到map中的value(com.example.TestController路径)
String value = map.get(title);
//通过反射把对应的java程序(TestController类)加载到内存
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(value);
TestController testController=(TestController)aClass.newInstance();
testController.test(is,ops);
}
}
//获取HTTP协议的请求部分,截取客户端要访问的资源名称,将这个资源名称赋值给url
public String parse(InputStream is) throws IOException {
StringBuffer content=new StringBuffer(2048);
byte[] bytes=new byte[2048];
int i=-1;
i=is.read(bytes);
//遍历字节数组,将数组中的数据追加到content变量中
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
content.append((char)bytes[j]);
}
System.out.println(content);
//截取客户端要请求的资源路径demo.html,赋值给url (GET /index.html HTTP/1.1中的index.html)
if(content.toString()!=""&&content!=null){
int index1,index2;
String title="";
index1=content.indexOf("/");
index2=content.indexOf("H");
title=content.substring(index1+1,index2-1);
return title;
}
return "";
}
//发送静态资源(也就是页面)
public void sendStaticResource(OutputStream ops){
//定义一个字节数组,用于存放本次请求的静态资源文件的内容
byte[] bytes=new byte[2048];
//定义要给输入流,用户获取静态资源文件的内容
FileInputStream fis=null;
try {
//创建文件file,是本次请求的资源
File file=new File(url);
if(file.exists()){
//向客户端输出HTTP协议的响应头/响应体
ops.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Server:apache-Coyote/1.1\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8\n".getBytes());
ops.write("\n".getBytes());
//获取到文件输入流对象
fis=new FileInputStream(file);
//读取静态资源到字节数组
int len=fis.read(bytes);
while (len!=-1){
ops.write(bytes,0,len);
len=fis.read(bytes);
}
}else{
//如果文件不存在,向客户端响应文件不存在的消息
ops.write("HTTP/1.1 404 not found\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Server:apache-Coyote/1.1\n".getBytes());
ops.write("Content-Type:text/html;charset=utf-8\n".getBytes());
ops.write("\n".getBytes());
String errorMessage="file not found";
ops.write(errorMessage.getBytes());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
conf.properties配置文件内容
test是规定访问映射路径为/test,后面的是文件路径(包名)
test=com.example.controller.TestController
TestController内容
public class TestController {
public void test(InputStream is, OutputStream ops)throws IOException {
ops.write("My Is TestController‘s Message!".getBytes());
}
}
运行Tomcat,浏览器访问开效果
控制台打印的获取到的http协议的请求部分

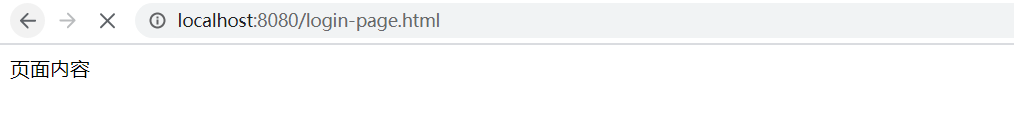
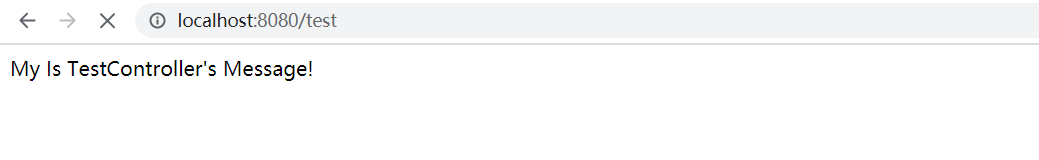
完美谢幕!
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/fantongxue/p/12739587.html