An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
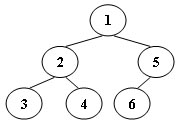
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
3 4 2 6 5 1解题思路和代码参考https://blog.csdn.net/xyt8023y/article/details/47443489
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <stack> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <sstream> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 //分别存储先序序列和中序序列 10 vector<int>preorder; 11 vector<int>inorder; 12 13 typedef struct TreeNode* Node; 14 struct TreeNode 15 { 16 int num; 17 Node left; 18 Node right; 19 }; 20 21 //根据结点值在中序序列中寻找根结点的下标位置 22 int FindRootIndex(int rootnum) { 23 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++) { 24 if (inorder[i] == rootnum) 25 return i; 26 } 27 return -1; 28 } 29 30 //通过给出中序序列中左右子树的范围建树 31 int cur;//定义遍历preorder的变量 32 Node CreateTree(int left, int right) { 33 //int cur = 0; 34 if (left > right) 35 return NULL; 36 int rootnum = preorder[cur]; 37 cur++; 38 int rootIndex = FindRootIndex(rootnum); 39 //建立该根结点 40 Node T = (Node)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode)); 41 T->num = rootnum; 42 T->left = NULL; 43 T->right = NULL; 44 if (left != right) { 45 T->left = CreateTree(left, rootIndex - 1); 46 T->right = CreateTree(rootIndex + 1, right); 47 } 48 return T; 49 } 50 51 52 //后序遍历 53 int printtag = 0; 54 void PostTraver(Node T) { 55 //int printtag = 0; 56 if (T) { 57 PostTraver(T->left); 58 PostTraver(T->right); 59 if (!printtag) { 60 cout << T->num; 61 printtag = 1; 62 } 63 else 64 cout << " " << T->num; 65 } 66 } 67 68 int main() { 69 int n; 70 stack<int>s; 71 cin >> n; 72 getchar(); 73 for (int i = 0; i < n*2; i++) { 74 string str; 75 getline(cin, str); 76 77 if (str[1] == ‘u‘) { 78 int num = stoi(str.substr(5)); 79 preorder.push_back(num); 80 s.push(num); 81 } 82 else { 83 int num = s.top(); 84 s.pop(); 85 inorder.push_back(num); 86 } 87 } 88 Node T = CreateTree(0,inorder.size()-1); 89 PostTraver(T); 90 return 0; 91 }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/PennyXia/p/12601659.html