MongoDB存储
1、链接MongoDB
指定数据库
指定集合
import pymongo ## 连接数据库 client = pymongo.MongoClient(host=‘localhost‘, port=27017) ## 指定数据库 kuluma db = client.kuluma ## 指定集合 collection = db.mycol
2、数据库操作
①插入数据
## 插入数据
## insert_one 插入一条数据
student = {
‘id‘:‘190720157‘,
‘name‘:‘Amy‘,
‘age‘:23,
‘gender‘:‘female‘
}
result = collection.insert_one(student)
print(result) ## 返回 InsertOneResult 对象
print(result.inserted_id) ## 获取 MonggoDB 自动添加的标识符 _id :5ea5340ef3cd203fa1577e4e
## insert_many 插入多条数据
student1 = {
‘id‘:‘190720158‘,
‘name‘:‘Lily‘,
‘age‘:18,
‘gender‘:‘female‘
}
student2 = {
‘id‘:‘190720159‘,
‘name‘:‘Mark‘,
‘age‘:20,
‘gender‘:‘male‘
}
results = collection.insert_many([student1,student2])
print(results)
print(results.inserted_ids)
②查询
※find()得到一个生成器对象,需要循环遍历
## 查询多条数据
results = collection.find({‘age‘:20})
for r in results:
print(r)
※find_one()得到单个结果,字典类型
## 查询 一条数据
result = collection.find_one({‘name‘:‘Amy‘})
print(type(result)) ## <class ‘dict‘> 返回结果时字典类型
print(result)
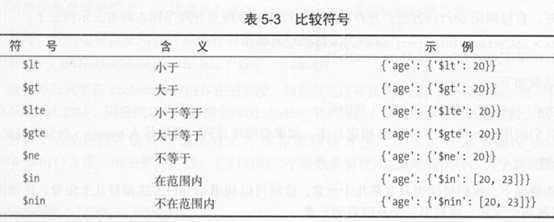
※比较查询
## 查询年龄大于等于20的数据
result1 = collection.find({‘age‘:{‘$gte‘:20}})
for r in result1:
print(r)
※正则匹配
## 正则匹配查询
##查询以 M 开头的学生
result2 = collection.find({‘name‘:{‘$regex‘:‘^M.*‘}})
for r in result2:
print(r)

③计数
## 计数 count = collection.find().count() print(count)
④排序
## 排序 s_sort = collection.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.ASCENDING) print([s for s in s_sort]) ## 升序 j_sort = collection.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.DESCENDING) print([j for j in j_sort]) ## 降序
⑤偏移
数据量过大,不建议使用偏移,可以对id_进行条件查询
## 偏移 跳过前两个查询结果,得到第三个以后的数据 skip = collection.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.ASCENDING).skip(2) print([s[‘name‘] for s in skip]) ## limit(1) 限制只返回一个结果 limit= collection.find().sort(‘age‘,pymongo.ASCENDING).skip(2).limit(1) print([l[‘name‘] for l in limit])
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/motoharu/p/12783485.html