用例1:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { //system("pause"); return 0; }
assembly:
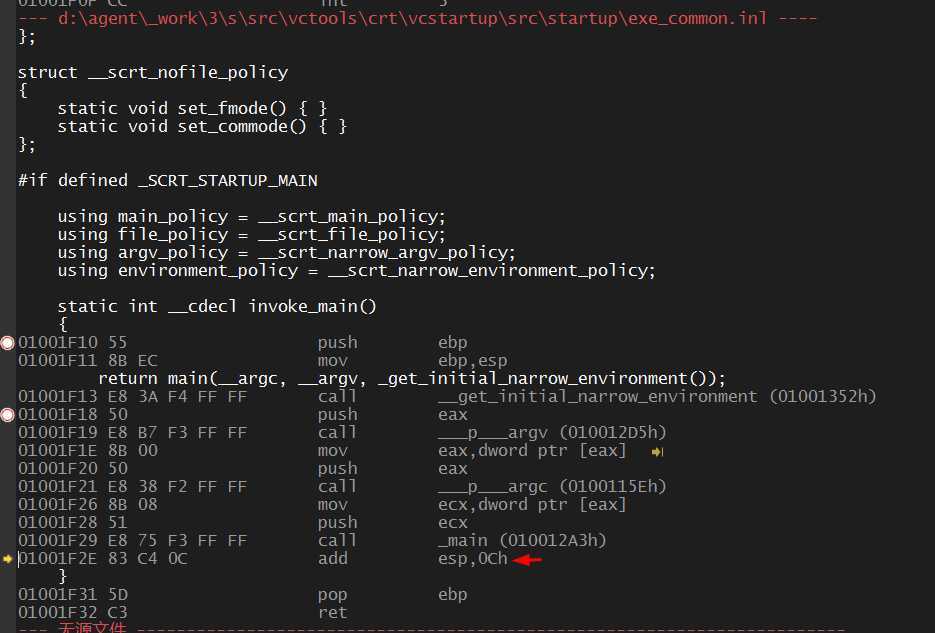
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { 010017B0 55 push ebp 010017B1 8B EC mov ebp,esp 010017B3 81 EC C0 00 00 00 sub esp,0C0h 010017B9 53 push ebx 010017BA 56 push esi 010017BB 57 push edi 010017BC 8D BD 40 FF FF FF lea edi,[ebp-0C0h] 010017C2 B9 30 00 00 00 mov ecx,30h 010017C7 B8 CC CC CC CC mov eax,0CCCCCCCCh 010017CC F3 AB rep stos dword ptr es:[edi] 010017CE B9 27 C0 00 01 mov ecx,offset _2755CF99_test@cpp (0100C027h) 010017D3 E8 3A FA FF FF call @__CheckForDebuggerJustMyCode@4 (01001212h) //system("pause"); return 0; 010017D8 33 C0 xor eax,eax } 010017DA 5F pop edi 010017DB 5E pop esi 010017DC 5B pop ebx 010017DD 81 C4 C0 00 00 00 add esp,0C0h 010017E3 3B EC cmp ebp,esp 010017E5 E8 32 FA FF FF call __RTC_CheckEsp (0100121Ch) 010017EA 8B E5 mov esp,ebp 010017EC 5D pop ebp 010017ED C3 ret
ret跳转

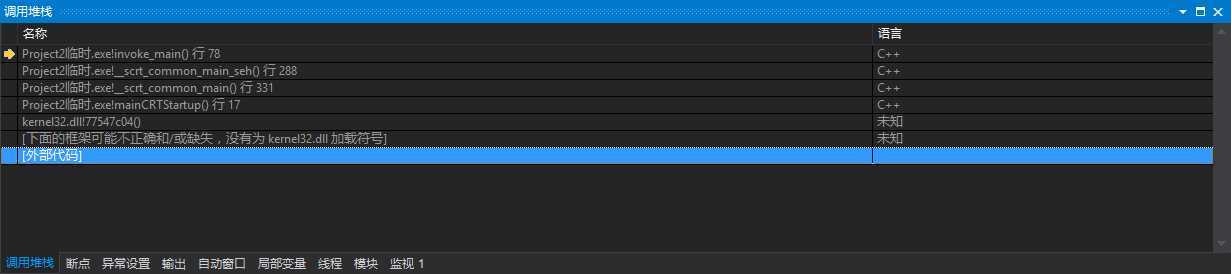
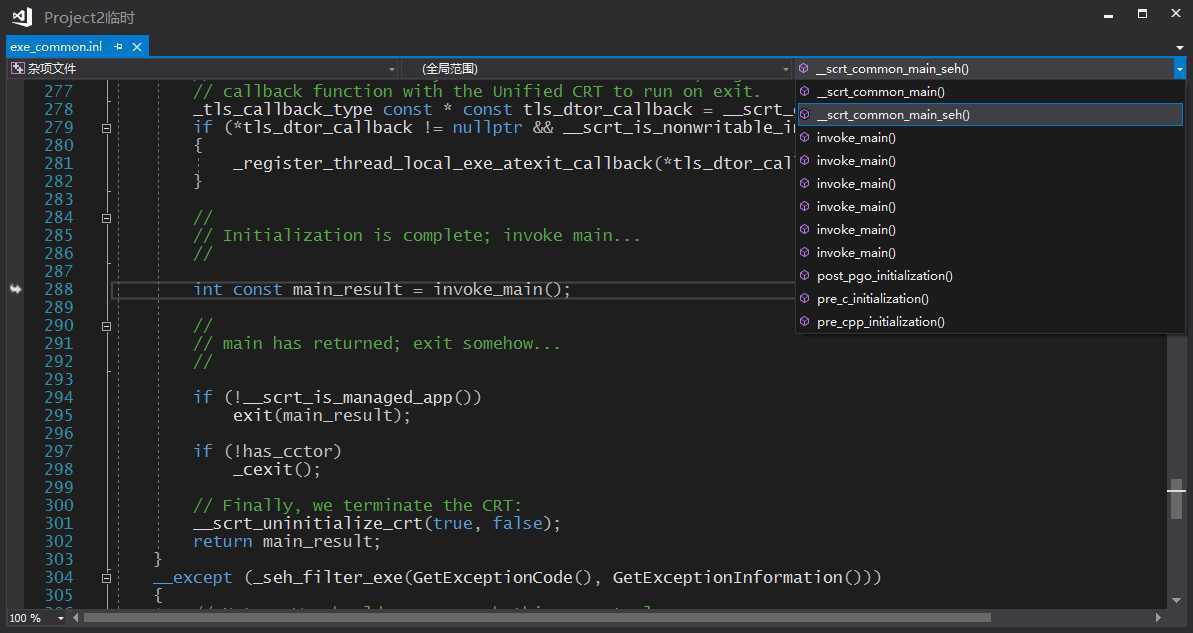
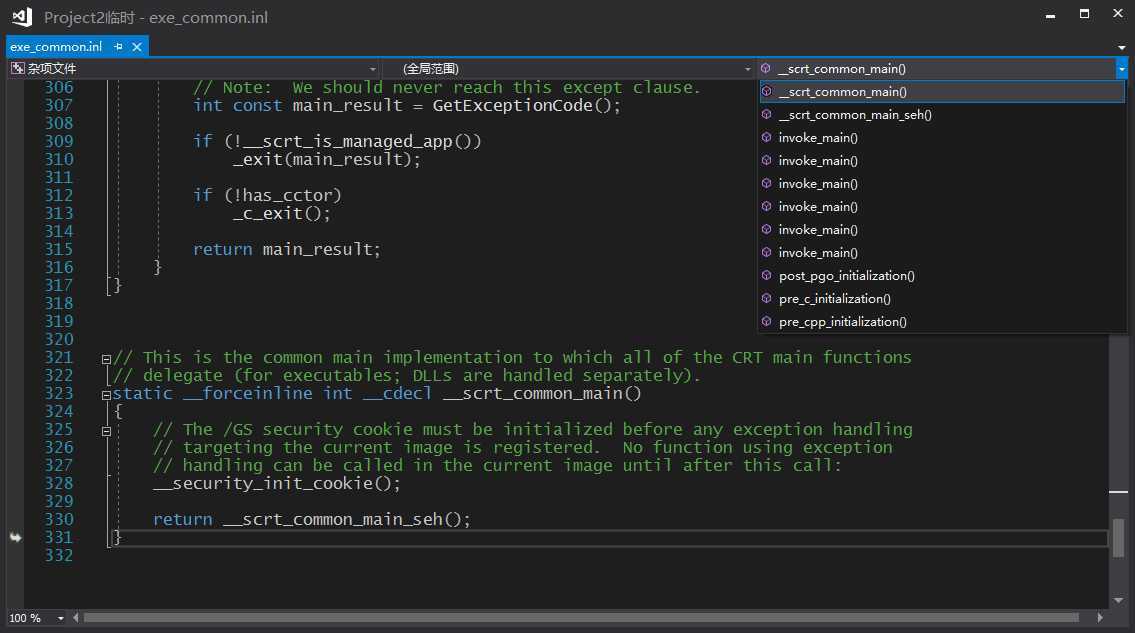
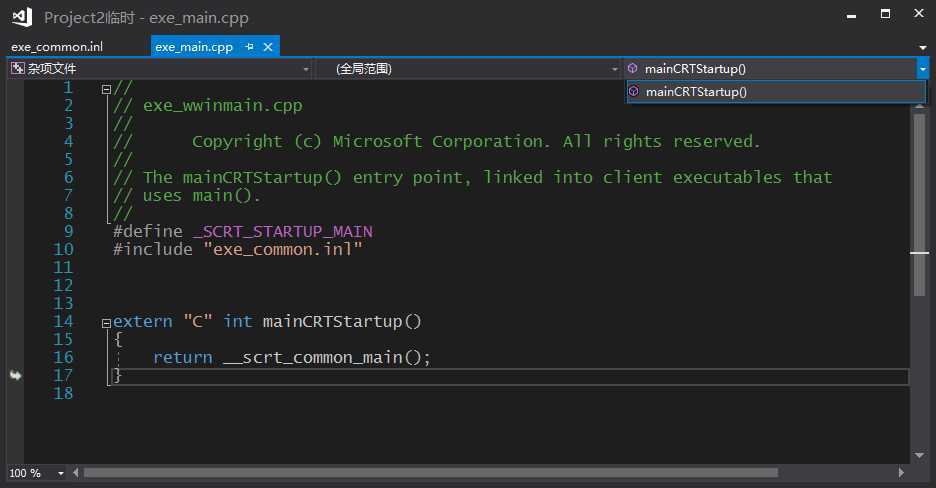
// // exe_common.inl // // Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. // // The implementation of the common executable entry point code. There are four // executable entry points defined by the CRT, one for each of the user-definable // entry points: // // * mainCRTStartup => main // * wmainCRTStartup => wmain // * WinMainCRTStartup => WinMain // * wWinMainCRTStartup => wWinMain // // These functions all behave the same, except for which user-definable main // function they call and whether they accumulate and pass narrow or wide string // arguments. This file contains the common code shared by all four of those // entry points. // // The actual entry points are defined in four .cpp files alongside this .inl // file. At most one of these .cpp files will be linked into the resulting // executable, so we can treat this .inl file as if its contents are only linked // into the executable once as well. // #include <vcstartup_internal.h> #include <vcruntime_internal.h> #include <locale.h> #include <math.h> #include <new.h> #include <process.h> #include <rtcapi.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> //-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ // // Common main()/WinMain() implementation // //-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ struct __scrt_main_policy { static void set_app_type() { _set_app_type(_crt_console_app); } }; struct __scrt_winmain_policy { static void set_app_type() { _set_app_type(_crt_gui_app); } }; struct __scrt_enclavemain_policy { static void set_app_type() { } }; struct __scrt_file_policy { static void set_fmode() { _set_fmode(_get_startup_file_mode()); } static void set_commode() { _commode = _get_startup_commit_mode(); } }; struct __scrt_nofile_policy { static void set_fmode() { } static void set_commode() { } }; #if defined _SCRT_STARTUP_MAIN using main_policy = __scrt_main_policy; using file_policy = __scrt_file_policy; using argv_policy = __scrt_narrow_argv_policy; using environment_policy = __scrt_narrow_environment_policy; static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return main(__argc, __argv, _get_initial_narrow_environment()); } #elif defined _SCRT_STARTUP_WMAIN using main_policy = __scrt_main_policy; using file_policy = __scrt_file_policy; using argv_policy = __scrt_wide_argv_policy; using environment_policy = __scrt_wide_environment_policy; static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return wmain(__argc, __wargv, _get_initial_wide_environment()); } #elif defined _SCRT_STARTUP_WINMAIN using main_policy = __scrt_winmain_policy; using file_policy = __scrt_file_policy; using argv_policy = __scrt_narrow_argv_policy; using environment_policy = __scrt_narrow_environment_policy; static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return WinMain( reinterpret_cast<HINSTANCE>(&__ImageBase), nullptr, _get_narrow_winmain_command_line(), __scrt_get_show_window_mode()); } #elif defined _SCRT_STARTUP_WWINMAIN using main_policy = __scrt_winmain_policy; using file_policy = __scrt_file_policy; using argv_policy = __scrt_wide_argv_policy; using environment_policy = __scrt_wide_environment_policy; static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return wWinMain( reinterpret_cast<HINSTANCE>(&__ImageBase), nullptr, _get_wide_winmain_command_line(), __scrt_get_show_window_mode()); } #elif defined _SCRT_STARTUP_ENCLAVE || defined _SCRT_STARTUP_WENCLAVE using main_policy = __scrt_enclavemain_policy; using file_policy = __scrt_nofile_policy; using argv_policy = __scrt_no_argv_policy; using environment_policy = __scrt_no_environment_policy; #if defined _SCRT_STARTUP_ENCLAVE static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return main(0, nullptr, nullptr); } #else static int __cdecl invoke_main() { return wmain(0, nullptr, nullptr); } #endif #endif static int __cdecl pre_c_initialization() { main_policy::set_app_type(); file_policy::set_fmode(); file_policy::set_commode(); if (!__scrt_initialize_onexit_tables(__scrt_module_type::exe)) __scrt_fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); #ifdef _M_IX86 // Clear the x87 exception flags. Any other floating point initialization // should already have taken place before this function is called. _asm { fnclex } #endif #ifdef _RTC _RTC_Initialize(); atexit(_RTC_Terminate); #endif if (argv_policy::configure_argv() != 0) __scrt_fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); __scrt_initialize_type_info(); // If the user provided a _matherr handler, register it with the Universal // CRT. Windows OS components cannot set a custom matherr handler (this is // a policy decision, to reduce complexity). #ifndef _CRT_WINDOWS if (__scrt_is_user_matherr_present()) { __setusermatherr(_matherr); } #endif _initialize_invalid_parameter_handler(); _initialize_denormal_control(); #ifdef _M_IX86 _initialize_default_precision(); #endif _configthreadlocale(_get_startup_thread_locale_mode()); if (_should_initialize_environment()) environment_policy::initialize_environment(); __scrt_initialize_winrt(); if (__scrt_initialize_mta() != 0) { __scrt_fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); } return 0; } static int __cdecl post_pgo_initialization() { // This function calls the __local_stdio_{printf,scanf}_options() functions. // These functions are defined in public headers with external linkage and // thus may be PGO-instrumented. We must not call these functions before the // PGO instrumentation library is initialized. __scrt_initialize_default_local_stdio_options(); return 0; } static void __cdecl pre_cpp_initialization() { // Before we begin C++ initialization, set the unhandled exception // filter so that unhandled C++ exceptions result in std::terminate // being called: __scrt_set_unhandled_exception_filter(); _set_new_mode(_get_startup_new_mode()); } // When both the PGO instrumentation library and the CRT are statically linked, // PGO will initialize itself in XIAB. We do most pre-C initialization before // PGO is initialized, but defer some initialization steps to after. See the // commentary in post_pgo_initialization for details. _CRTALLOC(".CRT$XIAA") static _PIFV pre_c_initializer = pre_c_initialization; _CRTALLOC(".CRT$XIAC") static _PIFV post_pgo_initializer = post_pgo_initialization; _CRTALLOC(".CRT$XCAA") static _PVFV pre_cpp_initializer = pre_cpp_initialization; static __declspec(noinline) int __cdecl __scrt_common_main_seh() { if (!__scrt_initialize_crt(__scrt_module_type::exe)) __scrt_fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); bool has_cctor = false; __try { bool const is_nested = __scrt_acquire_startup_lock(); if (__scrt_current_native_startup_state == __scrt_native_startup_state::initializing) { __scrt_fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); } else if (__scrt_current_native_startup_state == __scrt_native_startup_state::uninitialized) { __scrt_current_native_startup_state = __scrt_native_startup_state::initializing; if (_initterm_e(__xi_a, __xi_z) != 0) return 255; _initterm(__xc_a, __xc_z); __scrt_current_native_startup_state = __scrt_native_startup_state::initialized; } else { has_cctor = true; } __scrt_release_startup_lock(is_nested); // If this module has any dynamically initialized __declspec(thread) // variables, then we invoke their initialization for the primary thread // used to start the process: _tls_callback_type const* const tls_init_callback = __scrt_get_dyn_tls_init_callback(); if (*tls_init_callback != nullptr && __scrt_is_nonwritable_in_current_image(tls_init_callback)) { (*tls_init_callback)(nullptr, DLL_THREAD_ATTACH, nullptr); } // If this module has any thread-local destructors, register the // callback function with the Unified CRT to run on exit. _tls_callback_type const * const tls_dtor_callback = __scrt_get_dyn_tls_dtor_callback(); if (*tls_dtor_callback != nullptr && __scrt_is_nonwritable_in_current_image(tls_dtor_callback)) { _register_thread_local_exe_atexit_callback(*tls_dtor_callback); } // // Initialization is complete; invoke main... // int const main_result = invoke_main(); // // main has returned; exit somehow... // if (!__scrt_is_managed_app()) exit(main_result); if (!has_cctor) _cexit(); // Finally, we terminate the CRT: __scrt_uninitialize_crt(true, false); return main_result; } __except (_seh_filter_exe(GetExceptionCode(), GetExceptionInformation())) { // Note: We should never reach this except clause. int const main_result = GetExceptionCode(); if (!__scrt_is_managed_app()) _exit(main_result); if (!has_cctor) _c_exit(); return main_result; } } // This is the common main implementation to which all of the CRT main functions // delegate (for executables; DLLs are handled separately). static __forceinline int __cdecl __scrt_common_main() { // The /GS security cookie must be initialized before any exception handling // targeting the current image is registered. No function using exception // handling can be called in the current image until after this call: __security_init_cookie(); return __scrt_common_main_seh(); }
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/tongongV/p/12827794.html