"Abstract:" In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child.

Strictly binary tree(more strict than the common binary tree, as called Full Binary Tree)
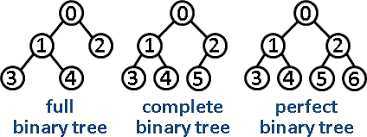
There is another definition related to the binary tree, Strictly binary tree, it‘s rooted too, but every node has 0 or 2 child nodes, and the level of nodes doesn‘t matter in the strict binary tree. In short, The full binary tree, where every node other than the leaves has two children.
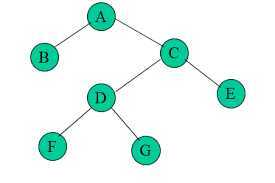
Complete binary tree
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
As for the properties of binary trees
e.g.: The number of nodes \(n\) in a full binary tree, is at least \(n=2h+1\) and at most \(n=2^{h+1}-1\), where \(h\) is the height of the tree. A tree consisting of only a root node has a height of 0. It will be easy to infer after you understand its definition.
Application in computing
- First, as a means of accessing nodes based on some value or label associated with each node. Binary trees labeled this way are used to implement binary search trees and binary heaps, and are used for efficient searching and sorting.
- Second, as a representation of data with a relevant bifurcating structure. In such cases, the particular arrangement of nodes under and/or to the left or right of other nodes is part of the information (that is, changing it would change the meaning). Common examples occur with Huffman coding and cladograms. The everyday division of documents into chapters, sections, paragraphs, and so on is an analogous example with n-ary rather than binary trees.
Copied from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_tree
Tree traversal
Huffman coding
Binary tree
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/gufana/p/12851922.html


