
滑动窗口法
思路:
将要匹配的子串逐一和模式串比较。
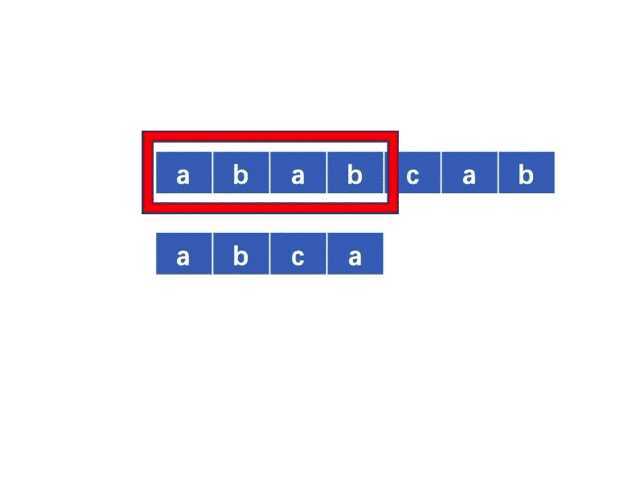
ababcab
abca
代码(利用Python自带字符串比对):
class Solution: def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int: L, n = len(needle), len(haystack) for start in range(n - L + 1): if haystack[start: start + L] == needle: return start return -1
代码(手动实现字符串的比对):
class Solution: def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int: i,j = 0,0 while i < len(haystack) and j < len(needle): if haystack[i] == needle[j]: i+=1 j+=1 else: i=i-j+1 j=0 if j == len(needle): return i-len(needle) else: return -1
KMP
思路:
在上面滑动窗口比对字符串时,有些子串的比对是没有必要可以优化省略的。
例如:
abababcab
ababc
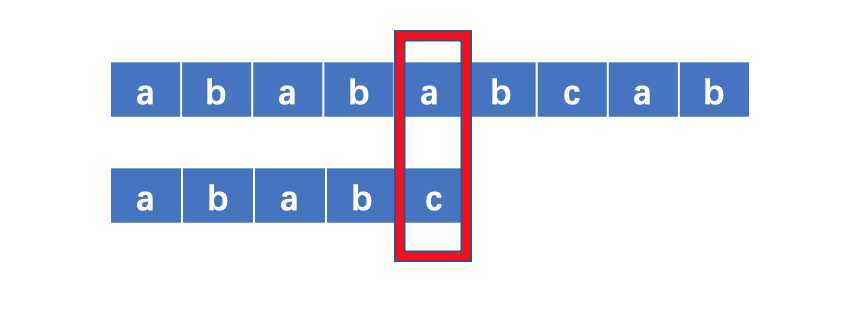
当我们比对到字符 a 和字符 c 不匹配时,我们可以发现c之前匹配成功的子串中前缀和后缀存在相同的部分,即ab。那么下一步我们直接拿匹配串不匹配的字符a和模式串相同前缀的后一个字符a进行匹配即可。
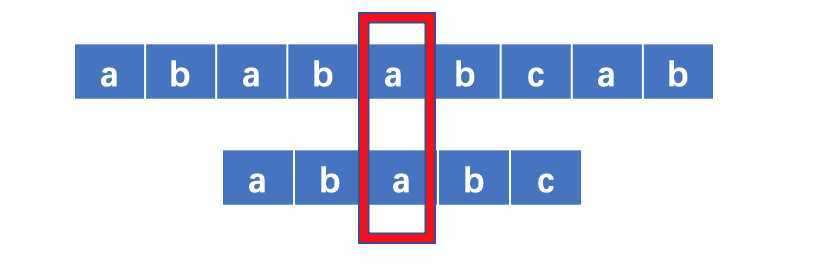
接下来我们需要确定的是如何确定在不匹配的情况下,找到下一步要匹配模式串的位置。这里我们需要对模式串进行分析。
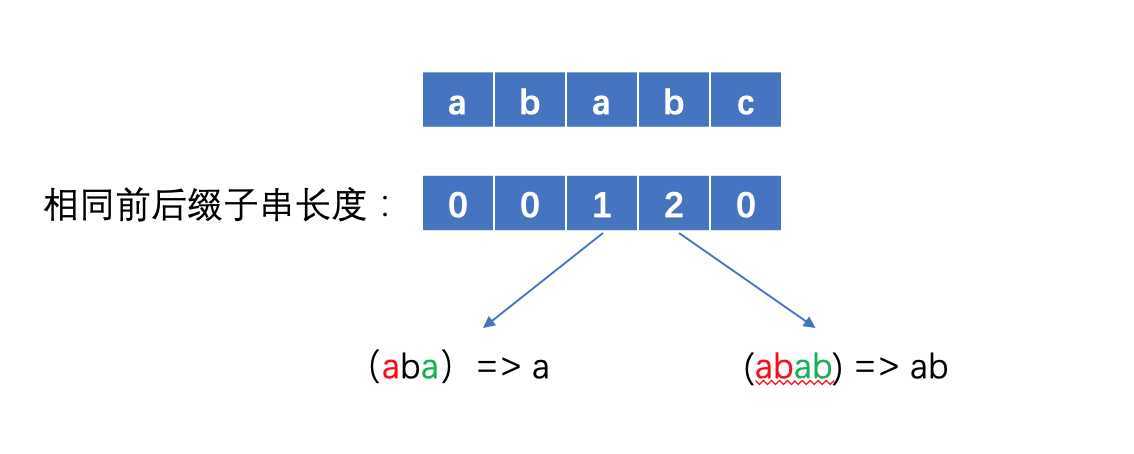
我们要研究的是如何找到相同前后缀子串长度。
这里我们以数组Result来记录每个位置对应相同前后缀长度:
首先Result[0] = 0 , 我们令i = 1,j = 0
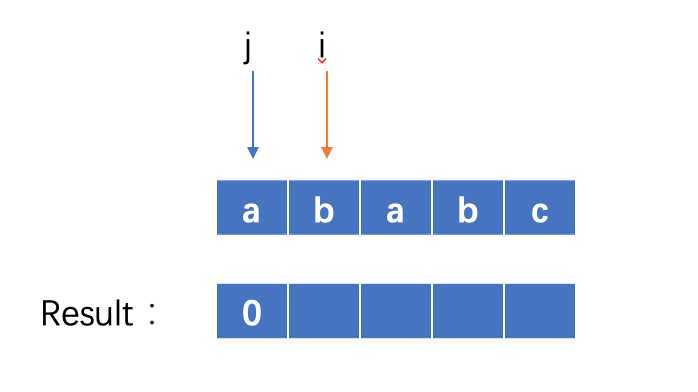
因为str[0] != str[1] 并且j=0,则result[i] = 0, i += 1
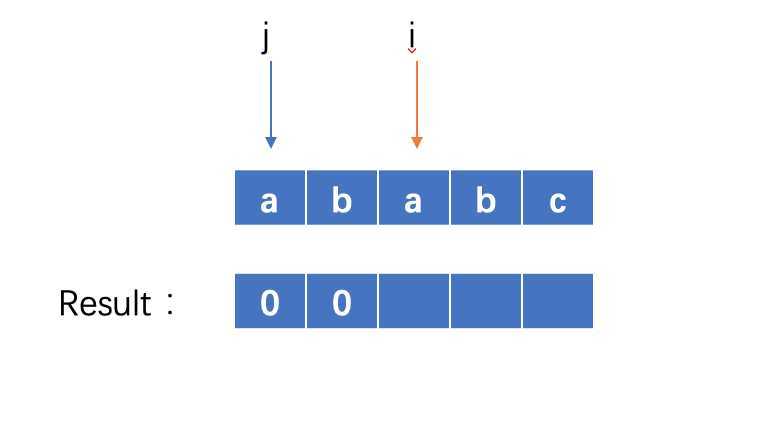
此时i = 2 ,j = 0,因为str[i]==str[j],则result[i] = j+1 , i +=1 ,j+= 1
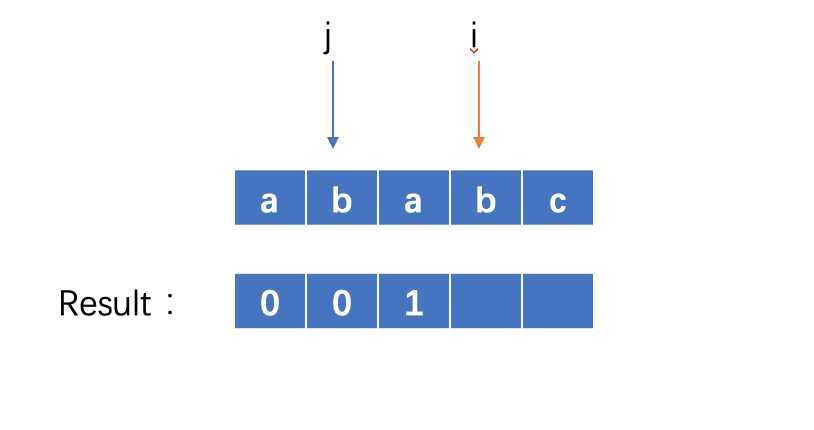
此时 i = 3,j = 1 ,因为str[i]==str[j],则result[i] = j+1 , i +=1 ,j+= 1
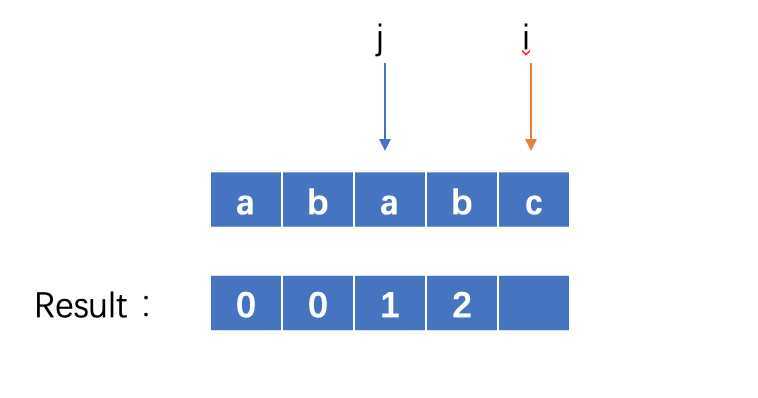
此时i = 4 ,j = 3,因为 str[i]!=str[j],又j!=0,则 j = result[j-1] 继续 比对 str[i] 和 str[j]
(ps: 因为当j!=0时,代表着以0开始j-1结尾的字符串str[0:j]是以0开始i-1结尾的字符串str[0:i]的一个最长前缀
此时由于 i 和 j 不匹配了,那么等价于两个子串aba 和 abc 在匹配过程中发生了不匹配的情况,此时由于前面子串中前缀最大长度都已经知道,所以可以知道 i 下一步要比对的位置即 j = result[j-1] )
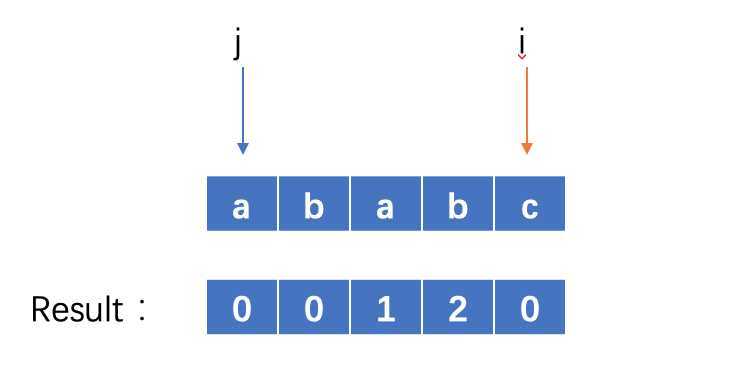
此时i = 4, j = result[1] = 0 , 因为str[4] != str[0] 并且j=0,则result[i] = 0
代码:
class Solution: def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int: def get_mnext(para): i, j =1,0 length = len(para) mnext= [0]*length while i < length: if (para[i] == para[j]): mnext[i] =j+ 1 j+= 1 i += 1 elif (j!=0): j = mnext[j-1] else: mnext[i] = 0 i += 1 return mnext n = len(haystack) m = len(needle) mnext = get_mnext(needle) i, j = 0, 0 while (i<n) and (j<m): if (haystack[i]==needle[j]): i += 1 j += 1 elif (j!=0): j = mnext[j-1] else: i += 1 if (j == m): return i-j else: return -1
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/nilhxzcode/p/12865580.html